Accessing digital material is frequently problematic for those with vision impairments. Yet, people may now access and engage with digital information independently owing to assistive devices like screen readers. In this post, we’ll examine screen readers’ functions, features, and advantages for those with visual impairments.
Table of Contents
What is a Screen Reader?
A screen reader could be a program that reads uproariously the substance shown on a computer or versatile gadget screen. It empowers people with visual disabilities to get to and connect with computerized substances, counting websites, reports, and computer program applications. Screen perusers give a good yield, which clients can listen to through their computer’s speakers or an associated headset. They can yield substance in Braille, permitting clients to study it through a refreshable Braille show.
Screen readers are outlined to work with different working frameworks, counting Windows, macOS, iOS, and Android. They can, moreover, be utilized with diverse applications, such as web browsers, word processors, and email clients. Screen perusers come with customizable settings, permitting clients to alter the discourse rate, volume, and voice characteristics to suit their inclinations.
How do Screen Readers Work?
Screen readers employ a combination of procedures to extricate content and other content from the screen. The method of perusing the screen starts with the screen peruser analyzing the graphical client interface (GUI) and distinguishing its different components, such as windows, menus, buttons, and symbols.
Once the screen reader recognizes the GUI components, it analyzes the content related to each component, such as names, titles, and captions. This investigation includes the screen reader changing over the content into an organization that can be examined out loud or shown in Braille.
Screen perusers utilize Optical Character Recognition (OCR) to recognize picture content. OCR innovation can recognize content in pictures and change over it into machine-readable content that the screen peruser can, at that point, decipher. This is especially valuable when experiencing blocked-off PDFs and pictures with implanted content.
Another basic highlight of screen perusers is their capacity to explore the GUI. Screen perusers give a set of console alternate routes and commands that allow clients to explore the interface without employing a mouse. For occasion, clients can move the center from one GUI component to another, enact buttons and joins, and explore menus and dialogs.
Benefits of Screen Readers
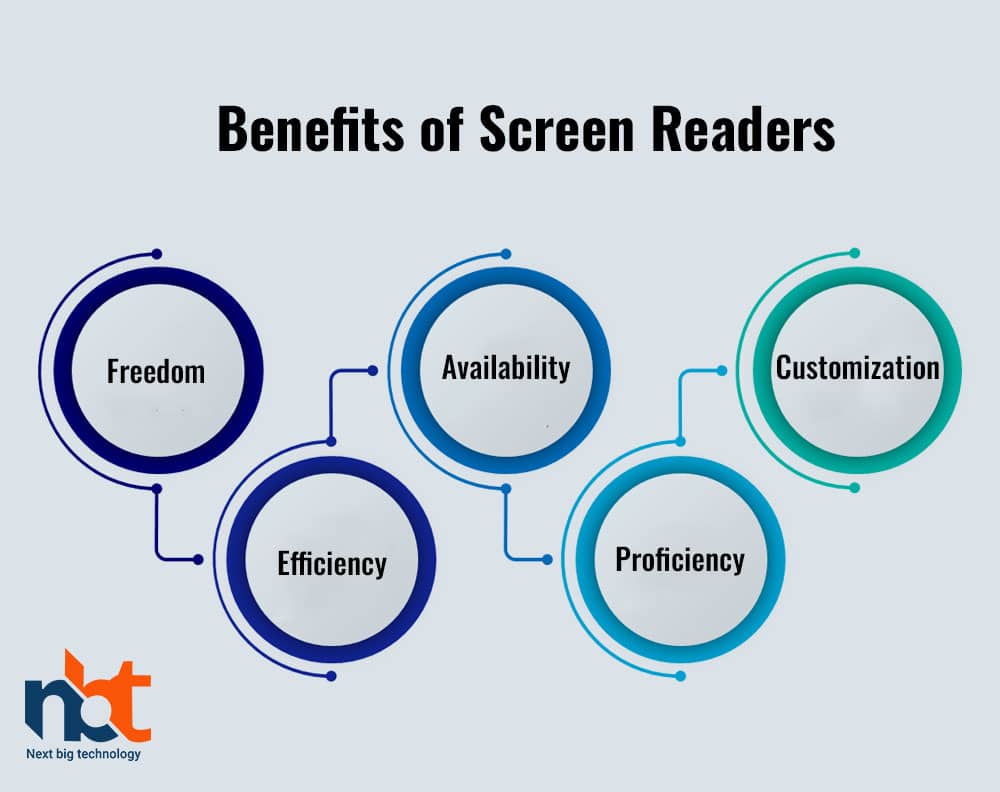
Screen readers offer a few benefits to people with visual impedances, counting:
- Freedom: Screen readers empower clients with visual disabilities to access computerized substances autonomously. They can peruse emails, browse the internet, and utilize computer program applications without help from others.
- Availability: Screen readers make advanced substances available to people with visual impedances. This availability empowers people with inabilities to participate in the same exercises as their non-disabled peers.
- Customization: Screen readers offer customization highlights that permit clients to personalize how the substance is perused or shown. For occasion, clients can alter the discourse rate, volume, and voice characteristics to suit their inclinations.
- Efficiency: Screen readers upgrade efficiency by empowering clients to total assignments rapidly and proficiently. Clients can explore computerized stages more effortlessly, allowing them to complete assignments more proficiently.
- Proficiency: Screen readers can offer assistance to diminish blunders and make strides in precision. The sound yield can be edited to guarantee the exactness, and clients can tune in to sound substance whereas performing other errands.
Types of Screen Readers
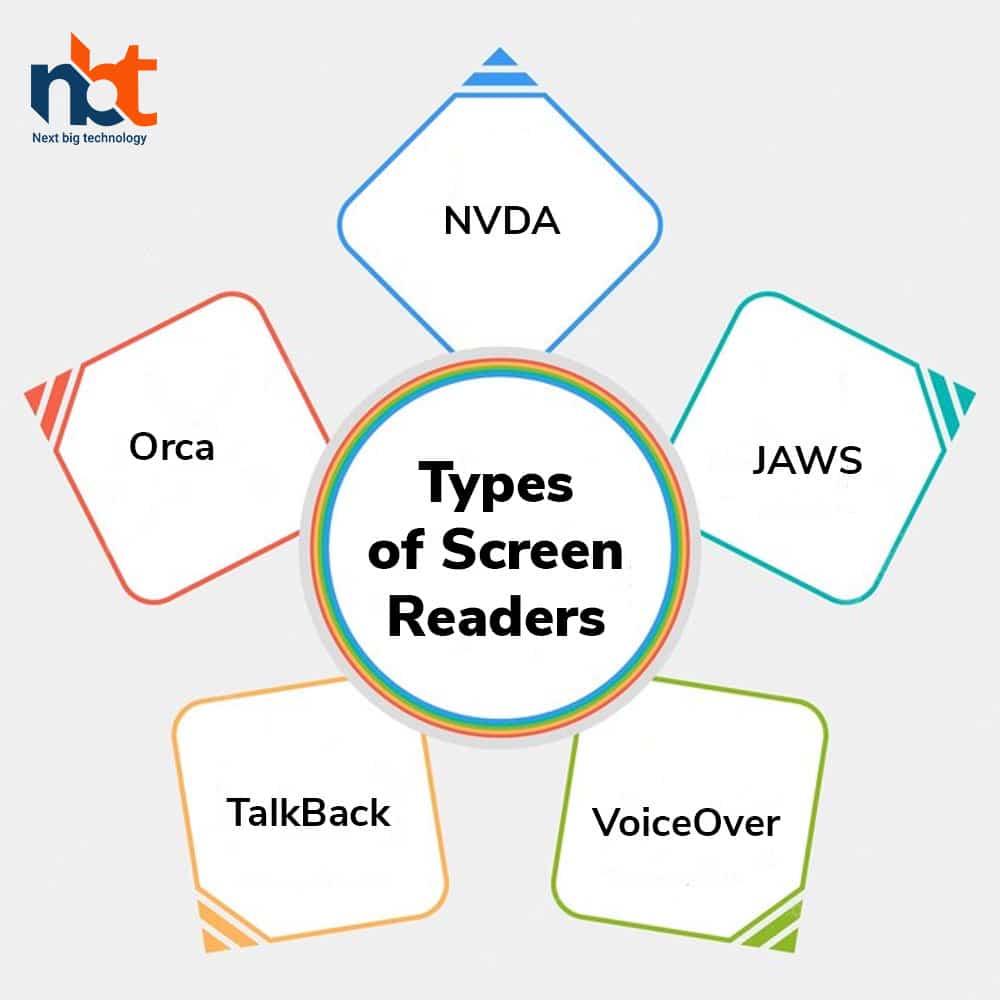
There are diverse sorts of screen readers accessible within the market. A few of the foremost well-known ones incorporate:
- NVDA: Non-Visual Desktop Get to (NVDA) could be a free, open-source screen reader for Windows. It underpins different applications and web browsers and comes with customizable settings.
- JAWS: Job Access With Discourse (JAWS) could be a well-known screen peruser for Windows. It may be a paid computer program that gives progressed highlights, such as back for OCR innovation and Braille displays.
- VoiceOver: VoiceOver may be a built-in screen peruser on macOS and iOS devices. It provides fundamental screen perusing usefulness and route commands.
- TalkBack: TalkBack may be a screen peruser built into Android gadgets. It gives the entire screen perusing usefulness and route commands.
- Orca: Orca may be a free, open-source screen peruser for Linux. It gives bolster for different applications and customizable settings.
Choosing the proper screen peruser depends on a few variables, counting the user’s needs and inclinations, the working framework utilized, and the applications they require to get to.
Screen Route/Navigation:
Screen reader clients explore a page using console and screen reader-specific commands. Here are a few common route methods utilized by screen reader clients:
- Heading Route: Screen readers allow clients to explore headings on a page. This enables clients to get the page’s structure and effectively move from one segment to another. The client can explore another heading by pressing the H key or the next heading by squeezing the Move + H key.
- Connect Route: Screen readers allow clients to explore joins on a page. This empowers clients to hop to particular parts of the page or other web pages. Clients can explore the following connection by squeezing the K key or pressing the Move + K key to the next connection.
- List Route: Screen perusers allow clients to explore records on a page. This empowers clients to get to things in a list or menu effectively. Clients can explore the other list by pressing the I key or the past list by pressing the Move + I key.
- Table Route: Screen readers allow users to explore tables on a page. This empowers users to get the table’s structure and its substance. Clients can explore the following table cell by pressing the Ctrl + Alt + Bolt keys or the next table cell by pressing the Move + Ctrl + Alt + Bolt keys.
- Frame Route: Screen readers allow clients to explore shapes on a page. This empowers clients to get to shape areas and yield shapes effortlessly. Clients can explore the following frame field by pressing the Tab key or the past frame field by squeezing the Move + Tab key.
- Look Route: Screen readers allow clients to explore what comes about on a page. This empowers clients to discover the data they require rapidly. Clients can explore the following look result by pressing the G key or the next look result by squeezing the Move + G key.
In these route strategies, screen peruser clients can utilize different screen reader-specific commands to get to particular parts of the page. For example, clients can utilize the screen reader’s virtual cursor to study the content on the page or the screen reader’s reading modes to center on particular sorts of substance, such as headings or joins.
Using Voice Over feature:
- Turning on Turning on VoiceOver on macOS:
- Press Command + F5 or Command + Option + F5 to turn on VoiceOver.
- On the other hand, go to the Apple menu, select “Framework Inclinations,” and then select “Availability.” From there, press “VoiceOver” and flip it on.
- Turning on VoiceOver on iOS:
- Go to “Settings,” then select “Accessibility,” and after that, select “VoiceOver.” Flip it on to empower VoiceOver.
- Turning on TalkBack on Android:
- Go to “Settings,” at that point, select “Accessibility,” and after that, select “TalkBack.” Flip it on to empower TalkBack.
- Turning on Narrator on Windows:
- Press the Windows key + Ctrl + Enter to turn on the Narrator.
- Or go to “Settings,” select “Ease of Access,” and after that, select “Narrator.” Flip it on to empower the Narrator.
- Turning on Orca on Linux:
- Orca is regularly pre-installed on Linux frameworks. To empower it, go to the “Widespread Access” menu and select “Screen Reader.” On the other hand, utilize the command line and sort “orca -s” to dispatch Orca.
Making Screen Reader more Friendly to Users:

Making the screen reader-friendly and interfacing is basic for guaranteeing that outwardly disabled people can get to and utilize your site or application. Here are a few tips for making screen reader-friendly interfacing:
- Utilize clear and brief dialect: Use straightforward and direct dialect to guarantee that screen perusers can study the substance on your site or application effortlessly.
- Give elective content for pictures: Give elective content for all pictures so that screen perusers can depict them to outwardly impeded clients. The elective content should be brief, clear, and significant to the picture.
- Utilize semantic markup: Utilize semantic markups such as HTML headings, records, and tables to structure your substance. This makes a difference to screen readers to get the progression of the substance and explore it more effortlessly.
- Utilize clear names: Utilize clear names for shape areas, buttons, and other intelligently designed components, so screen perusers can precisely depict them to outwardly impeded clients.
- Give good portrayals for recordings: Give good portrayals to portray the visual substance not passed on through exchange or sound impacts.
- Give console easy routes: Give the console easy routes for commonly utilized capacities to permit clients to explore your site or application without a mouse.
- Test with screen perusers: Testing with screen perusers is pivotal to guarantee that your site or application is available to outwardly disabled clients. Test with distinctive screen perusers to guarantee compatibility.
- Utilize ARIA qualities: Utilize ARIA (Accessible Rich Internet Applications) traits to supply extra data almost your site or application to screen perusers. This incorporates parts, states, and properties.
- Utilize suitable color differentiation: Utilize suitable color differentiation between the text and foundation to form it simpler for outwardly impeded clients to peruse the substance.
- Maintain a strategic distance from utilizing tables for format: Maintain a strategic distance from utilizing tables for format purposes, as screen perusers can have trouble deciphering them. Instep, use CSS for the format.
After these tips, you’ll be able to make a more screen reader-friendly interface available to outwardly impeded clients. It’s vital to remember that accessibility is a continuous handle and should be frequently tried and upgraded to guarantee that it remains comprehensive and available to all clients.
Challenges with Screen Readers
Despite the numerous benefits of screen readers, they, too, come with a few challenges. One of the important challenges is the availability of certain advanced substances. A few web pages, archives, and program applications need to be outlined with availability in intellect, making them troublesome or inconceivable to explore with a screen reader.
Another challenge is the learning bend related to utilizing screen readers. Clients learned console commands and navigation strategies to utilize screen readers successfully. This will be challenging for a few clients, especially those with constrained computer abilities or involvement.
At long last, screen readers may not work with all sorts of substance. Occasionally, a few mixed media substances, such as recordings and sound records, may not be available with screen perusers, or the accessibility highlights may be restricted.
Conclusion
Screen readers are fundamental apparatuses that empower people with visual disabilities to get to and connect with advanced substances freely. They utilize different procedures to extricate content and other substances from the screen and give a good yield that clients can listen to or show in Braille. Screen perusers offer numerous benefits, counting freedom, openness, customization, efficiency, and effectiveness. Moreover, they come with a few challenges, such as the availability of certain computerized substances and the learning bend related to utilizing screen readers. Generally, screen perusers are profitable assistive advances that make strides in the lives of people with visual impedances by giving rise to computerized substances.
Thanks for reading our post “What is Screen Reader? How it works?”. Please connect with us to know more about screen reader.