Table of Contents
Introduction to Payment Gateways
In today’s digital age, where online transactions reign supreme, payment gateways have become an integral part of e-commerce. But what exactly are payment gateways, and how do they work? Let’s delve into the world of online payments and explore the fundamentals of payment gateways.
Understanding Payment Gateways
Imagine you’re at a virtual checkout counter, ready to make a purchase. Behind the scenes, a payment gateway is the bridge that securely connects the merchant’s website or app to the payment processor. It’s like a digital bouncer, ensuring that your transaction is safe and smooth.
How Payment Gateways Work
When you click that “Buy Now” button, the payment gateway springs into action. First, it encrypts your payment details, such as credit card information or digital wallet credentials, to protect them from prying eyes. Then, it sends this encrypted data to the payment processor for authorization.
The payment processor, often a financial institution or a third-party service, verifies the transaction details and checks if you have sufficient funds or credit limit. Once approved, the payment processor sends a confirmation back through the payment gateway to complete the transaction. This entire process typically takes just a few seconds.
Types of Payment Gateways
Payment gateways come in various flavors to cater to different business needs. Some are integrated directly into e-commerce platforms like Shopify or WooCommerce, while others are standalone solutions. Additionally, payment gateways can be classified into two main categories:
- Hosted Payment Gateways: With hosted gateways, customers are redirected to a secure payment page hosted by the gateway provider. This simplifies PCI compliance for merchants but may disrupt the user experience by taking customers away from the merchant’s site temporarily.
- Integrated Payment Gateways: Integrated gateways allow customers to complete transactions without leaving the merchant’s website. While this offers a seamless user experience, it requires merchants to handle more aspects of security and compliance themselves.
Key Features to Look For
When choosing a payment gateway for your business, several factors should be considered:
- Security: Look for gateways that comply with the Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard (PCI DSS) to safeguard sensitive information.
- Compatibility: Ensure the gateway integrates seamlessly with your e-commerce platform or website.
- Cost: Consider transaction fees, setup costs, and any monthly subscriptions associated with the gateway.
- Global Reach: If you operate internationally, prioritize gateways that support multiple currencies and payment methods.
Importance of Integrating Payment Gateways
In the digital era, where online transactions reign supreme, integrating payment gateways has become more than just a convenience—it’s a necessity. Whether you’re a small business owner, an e-commerce giant, or a service provider, having seamless and secure payment processing is paramount for success. Let’s delve into the importance of integrating payment gateways and how they revolutionize online transactions.
Streamlined Checkout Experience: Imagine this: a customer browses through your website, finds the perfect product or service, and proceeds to checkout. However, upon reaching the payment stage, they encounter a clunky, outdated payment system that requires multiple steps and redirects. Frustrated, they abandon their cart and seek alternatives. Integrating payment gateways eradicates this issue by providing a seamless checkout experience. With a few clicks, customers can securely complete their transactions without leaving your website, resulting in higher conversion rates and customer satisfaction.
Enhanced Security Measures: Security breaches and data theft are major concerns in the digital realm. Customers are wary of sharing sensitive information online, and rightfully so. Payment gateways offer advanced security features such as encryption, tokenization, and fraud detection algorithms to safeguard financial data during transactions. By integrating these gateways, businesses instill trust and confidence in their customers, reassuring them that their personal information is protected against cyber threats.
Global Expansion Opportunities: In today’s interconnected world, geographical boundaries are no longer barriers to business expansion. Integrating payment gateways enables businesses to accept payments from customers worldwide, regardless of their location or preferred currency. Whether you’re targeting local markets or venturing into international territories, a diverse range of payment options facilitates smoother transactions, attracts a broader customer base, and fosters global growth opportunities.
Real-Time Transaction Monitoring: Effective decision-making requires timely insights into transaction activities and financial performance. Payment gateways offer robust reporting tools that allow businesses to monitor transactions in real time, track sales trends, analyze customer behavior, and identify areas for improvement. By leveraging these analytical capabilities, businesses can make data-driven decisions, optimize their payment processes, and maximize revenue generation.
Seamless Integration with Business Systems: Integration with existing business systems and software is crucial for operational efficiency and scalability. Payment gateways offer seamless integration capabilities with various platforms, including e-commerce platforms, accounting software, customer relationship management (CRM) systems, and more. This interoperability streamlines business operations, eliminates manual data entry errors, and enhances overall productivity.
Criteria for Selecting Payment Gateways
In the fast-paced world of e-commerce, selecting the right payment gateway can make all the difference in ensuring smooth transactions and customer satisfaction. With a myriad of options available, it’s crucial for businesses to carefully consider several key criteria before settling on a payment gateway that aligns with their needs and goals. Let’s delve into the essential factors to weigh when making this critical decision.
- Security: Security stands as the cornerstone of any payment gateway. Customers need to feel confident that their sensitive information, such as credit card details, is safe from potential threats. Look for payment gateways that comply with industry-standard security protocols such as PCI DSS (Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard) compliance. Additionally, consider features like tokenization and encryption to add an extra layer of protection to transactions.
- Payment Methods: Diverse payment methods cater to a wide range of customer preferences, enhancing convenience and expanding your customer base. Ensure that the payment gateway supports major credit and debit cards, as well as popular digital wallets like PayPal, Apple Pay, and Google Pay. Moreover, assess compatibility with alternative payment methods that may be prevalent in your target markets, such as bank transfers or local payment systems.
- Integration: Seamless integration with your e-commerce platform is essential for efficient operations. Choose a payment gateway that offers easy integration options with your website or mobile app. APIs (Application Programming Interfaces) and SDKs (Software Development Kits) should be well-documented and developer-friendly, enabling smooth integration without significant technical hurdles.
- Fees and Pricing: Payment processing fees can impact your bottom line, so it’s crucial to understand the fee structure of potential payment gateways. Compare transaction fees, setup fees, monthly subscriptions, and any additional charges such as currency conversion fees or chargeback fees. Balance the fees against the features and services offered by each payment gateway to determine the best value for your business.
- Reliability and Uptime: Downtime can result in lost sales and damage to your reputation. Choose a payment gateway with a proven track record of reliability and minimal downtime. Look for service level agreements (SLAs) that guarantee uptime and responsiveness, along with robust infrastructure and redundancy measures to ensure continuous operation, even during peak traffic periods.
- Customer Support: Prompt and reliable customer support is invaluable, especially in the event of technical issues or payment disputes. Evaluate the quality of customer support provided by each payment gateway, including available support channels, response times, and expertise in resolving payment-related issues. Opt for providers that offer 24/7 support and comprehensive documentation to assist with troubleshooting.
- Scalability: As your business grows, so should your payment infrastructure. Choose a payment gateway that can scale alongside your business without imposing limitations or requiring frequent migrations. Consider factors such as transaction volume limits, international expansion capabilities, and support for recurring payments or subscription models to accommodate future growth and evolving needs.
Security Considerations in Payment Gateway Integration
In today’s digitally driven world, the integration of payment gateways has become paramount for businesses aiming to offer seamless and secure transactions to their customers. Whether you’re an e-commerce giant or a small-scale vendor, ensuring the safety of sensitive financial information during payment processing is non-negotiable. Therefore, understanding and implementing robust security measures are vital to protect both your business and your customers from potential threats.
- Encryption Protocols: Encryption serves as the first line of defense against unauthorized access to payment data. Utilizing industry-standard encryption protocols, such as SSL/TLS (Secure Sockets Layer/Transport Layer Security), ensures that the data transmitted between the customer’s browser and your server remains encrypted and secure from interception by malicious actors.
- PCI DSS Compliance: Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard (PCI DSS) compliance is imperative for any entity involved in processing card payments. Adhering to PCI DSS guidelines helps in safeguarding cardholder data by implementing measures like network security, regular system monitoring, and maintaining secure payment applications.
- Tokenization: Tokenization replaces sensitive payment data with unique tokens, significantly reducing the risk associated with storing or transmitting confidential information. By substituting card details with tokens, even if a breach occurs, the stolen data holds no value to cybercriminals, enhancing overall security.
- Two-Factor Authentication (2FA): Implementing 2FA adds an extra layer of security by requiring users to provide two forms of authentication before granting access to payment processing systems. This could include a combination of passwords, biometric data, or one-time passcodes, significantly reducing the risk of unauthorized access.
- Fraud Detection and Prevention: Integrating robust fraud detection mechanisms can help identify and mitigate fraudulent activities in real-time. Utilizing AI-driven algorithms and machine learning techniques, payment gateways can analyze transaction patterns and detect anomalies that may indicate potential fraud, thereby minimizing financial losses and maintaining trust with customers.
- Regular Security Audits and Updates: Conducting regular security audits and staying updated with the latest security patches and software updates is essential to address vulnerabilities promptly. Proactive measures such as vulnerability scanning, penetration testing, and code reviews can help identify and rectify security loopholes before they are exploited by cyber threats.
- Secure Third-Party Integrations: If integrating third-party services or plugins into your payment gateway system, ensure that they adhere to stringent security standards. Vet third-party providers for their security protocols, compliance certifications, and track record in safeguarding sensitive data to prevent any potential security breaches.
- Data Access Controls: Limiting access to sensitive payment data only to authorized personnel is crucial in minimizing the risk of insider threats. Implementing robust access controls, role-based permissions, and encryption of stored data can prevent unauthorized access and mitigate the risk of data breaches from within the organization.
- Incident Response Plan: Despite the best preventive measures, security incidents may still occur. Having a well-defined incident response plan in place can help minimize the impact of security breaches by outlining the steps to be taken in the event of a breach, including containment, investigation, communication protocols, and recovery procedures.
Top 10 Payment Gateways Overview
In today’s digital era, where online transactions have become the norm, payment gateways play a pivotal role in facilitating secure and seamless transactions. With numerous options available, selecting the right payment gateway for your business can be a daunting task. To simplify this process, let’s delve into the top 10 payment gateways and gain insight into their features and functionalities.
- PayPal: PayPal is undoubtedly one of the most popular payment gateways globally, offering easy integration and a trusted brand name. It supports various payment methods, including credit cards, debit cards, and PayPal balance, making it convenient for both merchants and customers.
- Stripe: Stripe is renowned for its developer-friendly platform and robust security features. It supports a wide range of payment methods and currencies, making it an ideal choice for businesses operating internationally. Moreover, Stripe’s customizable checkout process enhances the user experience.
- Authorize.Net: With over 20 years of experience, Authorize.Net is a reliable payment gateway known for its robust fraud prevention tools and scalability. It offers seamless integration with numerous e-commerce platforms and supports recurring payments, making it suitable for subscription-based businesses.
- Square: Square is renowned for its simplicity and affordability, making it an excellent choice for small businesses and startups. Its intuitive interface and transparent pricing structure, with no monthly fees, make it appealing to merchants seeking a hassle-free payment solution.
- Braintree: Owned by PayPal, Braintree is a versatile payment gateway known for its global reach and comprehensive features. It supports multiple payment methods, including PayPal, credit cards, and digital wallets like Apple Pay and Google Pay, catering to a diverse customer base.
- 2Checkout: 2Checkout, now known as Verifone, offers a user-friendly platform with extensive customization options. It provides global payment capabilities, supporting over 87 currencies and 15 languages, making it suitable for businesses targeting international markets.
- Adyen: Adyen is a leading payment gateway trusted by global brands for its advanced fraud detection capabilities and seamless omnichannel integration. Its unified platform consolidates various payment methods, enabling merchants to streamline their payment processes effectively.
- Worldpay: Worldpay, now part of FIS, is a robust payment gateway offering scalable solutions for businesses of all sizes. With its extensive network and diverse payment options, including card payments, e-wallets, and alternative payment methods, Worldpay caters to the evolving needs of modern merchants.
- Amazon Pay: Leveraging the trust and convenience of Amazon, Amazon Pay allows customers to make purchases using their Amazon accounts. It offers a seamless checkout experience and supports recurring payments, making it a preferred choice for merchants leveraging the Amazon ecosystem.
- Skrill: Skrill, formerly known as Moneybookers, is a popular payment gateway known for its low fees and fast transactions. It supports over 40 currencies and offers various payment options, including credit cards, bank transfers, and digital wallets, catering to a diverse global audience.
Detailed Analysis of Each Payment Gateway
In today’s digitally driven world, having a reliable payment gateway is crucial for businesses of all sizes. With an array of options available, selecting the right one can be overwhelming. Each payment gateway comes with its unique features, pricing structures, and integration processes. Let’s delve into a detailed analysis of some popular payment gateways to help you make an informed decision.
- PayPal:
- Overview: PayPal is one of the most widely used payment gateways globally, known for its user-friendly interface and secure transactions.
- Pros: Offers seamless integration, supports multiple currencies, and provides robust security features.
- Cons: Transaction fees can be relatively high, especially for international payments.
- Suitable For: Small to medium-sized businesses with a global customer base.
- Stripe:
- Overview: Stripe is favored by developers for its customizable API and extensive documentation.
- Pros: Transparent pricing, easy setup process, and excellent support for recurring payments.
- Cons: Limited currency support compared to other gateways.
- Suitable For: Online businesses requiring flexible payment options and recurring billing.
- Authorize.Net:
- Overview: Authorize.Net has been a trusted name in payment processing for over two decades, offering reliability and security.
- Pros: Robust fraud prevention tools, supports a wide range of payment methods, and offers advanced reporting features.
- Cons: Slightly higher setup fees and transaction charges compared to competitors.
- Suitable For: Established businesses needing scalable payment solutions and comprehensive reporting.
- Square:
- Overview: Square is renowned for its simplicity and versatility, catering to both online and offline businesses.
- Pros: No monthly fees, transparent pricing, and seamless integration with point-of-sale systems.
- Cons: Limited customization options for checkout pages.
- Suitable For: Small businesses, particularly those in the retail and service industries.
- Braintree:
- Overview: Owned by PayPal, Braintree offers a modern payment gateway solution with a focus on mobile transactions.
- Pros: Developer-friendly API, robust security features, and support for various payment methods including PayPal and Venmo.
- Cons: Pricing structure can be complex for high-volume transactions.
- Suitable For: Businesses requiring a flexible and scalable payment platform, especially in the mobile commerce sector.
- 2Checkout:
- Overview: 2Checkout provides a global payment solution, enabling businesses to accept payments from customers worldwide.
- Pros: Multi-language support, extensive fraud prevention tools, and customizable checkout options.
- Cons: Higher transaction fees for international payments.
- Suitable For: E-commerce businesses targeting a diverse international audience.
- Amazon Pay:
- Overview: Amazon Pay leverages the trust and familiarity of the Amazon brand, offering a streamlined checkout experience.
- Pros: Seamless integration with Amazon accounts, enhanced security through Amazon’s fraud detection technology.
- Cons: Limited customization options for checkout pages.
- Suitable For: Businesses seeking to enhance user experience and leverage the trust associated with the Amazon brand.
Comparison of Fees and Transaction Costs
In the realm of finance, where every penny counts, understanding the ins and outs of fees and transaction costs is paramount. Whether you’re an individual investor, a business entity, or a financial institution, being cognizant of these expenses can significantly impact your bottom line. In this article, we’ll delve into the world of fees and transaction costs, comparing their nuances and shedding light on how they can influence your financial decisions.
Fees: The Price of Participation
Fees are charges levied by financial service providers for the services they render. These charges can encompass a wide array of activities, ranging from account maintenance fees to advisory fees. Let’s explore some common types of fees:
- Account Maintenance Fees: Many financial institutions impose fees for the upkeep of accounts. These fees can vary depending on factors such as the type of account and the institution itself.
- Transaction Fees: These fees are incurred each time a financial transaction takes place. Whether you’re buying stocks, bonds, or engaging in currency exchange, transaction fees apply.
- Management Fees: If you’ve entrusted your investments to a professional money manager or investment firm, you’re likely subject to management fees. These fees compensate the manager for their expertise and services.
- Performance Fees: In some cases, investment managers may charge performance fees based on the returns they generate for their clients. These fees are typically calculated as a percentage of profits earned.
- Withdrawal Fees: When you withdraw funds from certain types of accounts or investment vehicles, you may encounter withdrawal fees. These fees can vary depending on factors such as the frequency and method of withdrawal.
Transaction Costs: Beyond the Surface
While fees represent explicit charges imposed by financial service providers, transaction costs encompass a broader spectrum of expenses associated with executing financial transactions. Transaction costs include both explicit costs, such as brokerage commissions, and implicit costs, such as bid-ask spreads and market impact.
- Brokerage Commissions: When you buy or sell securities through a brokerage firm, you typically incur brokerage commissions. These commissions can vary depending on factors such as the type of security and the size of the transaction.
- Bid-Ask Spreads: The bid-ask spread represents the difference between the highest price a buyer is willing to pay and the lowest price a seller is willing to accept for a security. This spread effectively represents a transaction cost, as buyers generally purchase securities at the ask price and sell them at the bid price.
- Market Impact: Large trades can exert significant influence on market prices, resulting in market impact costs. These costs arise from the adverse price movements that occur as a result of executing sizable transactions.
- Clearing and Settlement Costs: Clearing and settlement processes involve the validation, matching, and finalization of trades. While these processes may seem mundane, they incur costs that are ultimately borne by investors.
Comparing Fees and Transaction Costs
While fees and transaction costs share the common goal of extracting value from investors, they differ in their structure and implications. Fees are explicit charges imposed by financial service providers for the services they render, whereas transaction costs encompass a broader range of expenses associated with executing financial transactions.
When comparing fees and transaction costs, investors should consider several factors, including transparency, magnitude, and impact on investment returns. While fees are typically transparent and explicitly disclosed by financial service providers, transaction costs may be more opaque and difficult to quantify. Moreover, while fees represent a direct deduction from investment returns, transaction costs can exert a subtler yet equally significant drag on performance.
Comparison of Fees and Transaction Costs
In the realm of finance, where every penny counts, understanding the ins and outs of fees and transaction costs is paramount. Whether you’re an individual investor, a business entity, or a financial institution, being cognizant of these expenses can significantly impact your bottom line. In this article, we’ll delve into the world of fees and transaction costs, comparing their nuances and shedding light on how they can influence your financial decisions.
Fees: The Price of Participation
Fees are charges levied by financial service providers for the services they render. These charges can encompass a wide array of activities, ranging from account maintenance fees to advisory fees. Let’s explore some common types of fees:
- Account Maintenance Fees: Many financial institutions impose fees for the upkeep of accounts. These fees can vary depending on factors such as the type of account and the institution itself.
- Transaction Fees: These fees are incurred each time a financial transaction takes place. Whether you’re buying stocks, bonds, or engaging in currency exchange, transaction fees apply.
- Management Fees: If you’ve entrusted your investments to a professional money manager or investment firm, you’re likely subject to management fees. These fees compensate the manager for their expertise and services.
- Performance Fees: In some cases, investment managers may charge performance fees based on the returns they generate for their clients. These fees are typically calculated as a percentage of profits earned.
- Withdrawal Fees: When you withdraw funds from certain types of accounts or investment vehicles, you may encounter withdrawal fees. These fees can vary depending on factors such as the frequency and method of withdrawal.
Transaction Costs: Beyond the Surface
While fees represent explicit charges imposed by financial service providers, transaction costs encompass a broader spectrum of expenses associated with executing financial transactions. Transaction costs include both explicit costs, such as brokerage commissions, and implicit costs, such as bid-ask spreads and market impact.
- Brokerage Commissions: When you buy or sell securities through a brokerage firm, you typically incur brokerage commissions. These commissions can vary depending on factors such as the type of security and the size of the transaction.
- Bid-Ask Spreads: The bid-ask spread represents the difference between the highest price a buyer is willing to pay and the lowest price a seller is willing to accept for a security. This spread effectively represents a transaction cost, as buyers generally purchase securities at the ask price and sell them at the bid price.
- Market Impact: Large trades can exert significant influence on market prices, resulting in market impact costs. These costs arise from the adverse price movements that occur as a result of executing sizable transactions.
- Clearing and Settlement Costs: Clearing and settlement processes involve the validation, matching, and finalization of trades. While these processes may seem mundane, they incur costs that are ultimately borne by investors.
Comparing Fees and Transaction Costs
While fees and transaction costs share the common goal of extracting value from investors, they differ in their structure and implications. Fees are explicit charges imposed by financial service providers for the services they render, whereas transaction costs encompass a broader range of expenses associated with executing financial transactions.
When comparing fees and transaction costs, investors should consider several factors, including transparency, magnitude, and impact on investment returns. While fees are typically transparent and explicitly disclosed by financial service providers, transaction costs may be more opaque and difficult to quantify. Moreover, while fees represent a direct deduction from investment returns, transaction costs can exert a subtler yet equally significant drag on performance.
Integration Process and Technical Requirements
In the digital landscape, where interconnectedness reigns supreme, integration has become the cornerstone of efficiency and seamless operations for businesses worldwide. Whether it’s merging disparate systems within an organization or linking external applications for enhanced functionality, mastering the integration process is vital. Let’s delve into the intricacies of integration, unraveling its process and the technical prerequisites necessary for success.
Understanding Integration:
Integration, in its essence, is the art of harmonizing diverse components to function as a unified whole. It involves bridging gaps between systems, applications, or data sources to enable smooth communication and collaboration. Whether it’s integrating customer relationship management (CRM) software with an e-commerce platform or synchronizing data between different departments within an enterprise, the goal remains consistent – to streamline operations and enhance productivity.
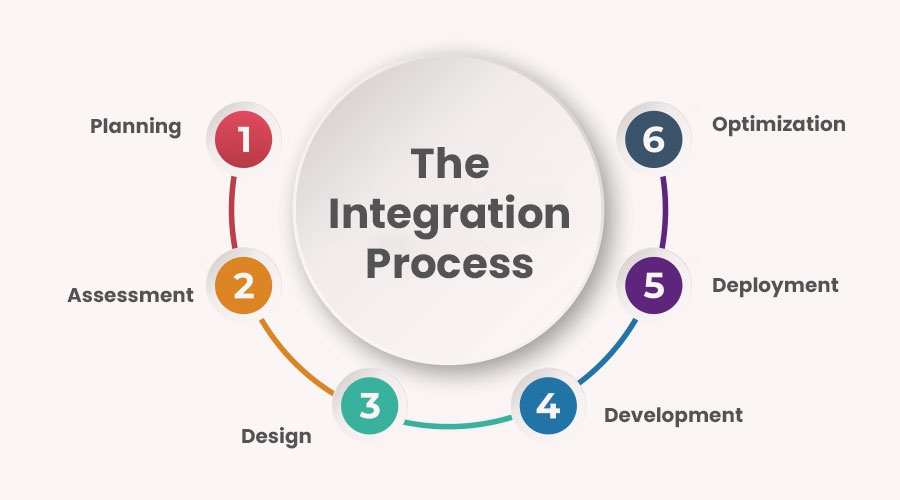
The Integration Process
1. Planning: Successful integration begins with meticulous planning. Identify the systems or applications that need to be integrated, define objectives, and establish key performance indicators (KPIs) to measure success. Understanding the workflow and data flow between various components is crucial at this stage.
2. Assessment: Conduct a thorough assessment of existing systems and infrastructure. Evaluate compatibility, scalability, and security considerations. Determine whether custom development or off-the-shelf solutions are more suitable based on specific requirements and budget constraints.
3. Design: Designing the integration architecture entails mapping out data flows, defining communication protocols, and selecting appropriate integration patterns (e.g., point-to-point, hub-and-spoke, or event-driven architecture). Pay close attention to data mapping and transformation requirements to ensure seamless interoperability between systems.
4. Development: Implementation involves developing connectors, APIs (Application Programming Interfaces), or middleware to facilitate communication between disparate systems. Leverage industry-standard integration frameworks and protocols to minimize complexity and maximize interoperability. Rigorous testing at this stage is imperative to identify and rectify any discrepancies or performance bottlenecks.
5. Deployment: Deploy the integrated solution in a controlled environment, closely monitoring performance metrics and user feedback. Conduct comprehensive training sessions to familiarize stakeholders with the new system and address any usability concerns. Implement robust monitoring and error handling mechanisms to ensure uninterrupted operation post-deployment.
6. Optimization: Continuous optimization is key to maintaining the effectiveness of the integrated solution. Regularly assess performance metrics, solicit user feedback, and iterate on the integration architecture to address evolving business needs and technological advancements.
Technical Requirements for Integration:
1. Compatibility: Ensure compatibility between systems in terms of data formats, protocols, and interfaces. Invest in middleware or integration platforms that support a wide range of connectors and protocols to facilitate seamless interoperability.
2. Scalability: Scalability is essential to accommodate growing data volumes and user loads. Choose integration solutions that can scale horizontally or vertically to meet evolving demands without compromising performance or reliability.
3. Security: Security is paramount when integrating disparate systems, especially when sensitive data is involved. Implement robust authentication, authorization, and encryption mechanisms to safeguard data integrity and confidentiality throughout the integration process.
4. Performance: Optimize performance by minimizing latency, reducing overhead, and optimizing data transfer mechanisms. Employ caching, compression, and parallel processing techniques to enhance throughput and responsiveness.
5. Flexibility: Flexibility is crucial to adapt to changing business requirements and technological landscapes. Choose integration solutions that offer extensibility, configurability, and support for emerging standards and protocols.
Top 10 Payment Gateways Companies
In today’s digitally-driven era, the efficacy of online payment gateways is paramount for businesses worldwide. As e-commerce continues to flourish, the reliance on secure and efficient payment processing solutions has never been greater. Whether you’re a small-scale entrepreneur or a multinational corporation, choosing the right payment gateway can significantly impact your bottom line and customer satisfaction. Here’s a curated list of the top 10 payment gateway companies leading the charge in transforming the online payment landscape:
-
-
Next Big Technology:

Focus Area
- Mobile App Development
- App Designing (UI/UX)
- Software Development
- Web Development
- AR & VR Development
- Big Data & BI
- Cloud Computing Services
- DevOps
- E-commerce Development
Industries Focus
- Art, Entertainment & Music
- Business Services
- Consumer Products
- Designing
- Education
- Financial & Payments
- Gaming
- Government
- Healthcare & Medical
- Hospitality
- Information Technology
- Legal & Compliance
- Manufacturing
- Media
-
- Stripe: Renowned for its developer-friendly platform and extensive customization options, Stripe empowers businesses to accept online payments with ease. From startups to enterprise-level enterprises, Stripe’s scalable solutions and innovative features make it a preferred choice among merchants worldwide.
- Square: As a pioneer in mobile payment technology, Square has revolutionized the way businesses accept payments. With its sleek hardware and intuitive software, Square enables merchants to process transactions swiftly, whether in-store or online.
- Authorize.Net: Trusted by millions of merchants, Authorize.Net offers a comprehensive suite of payment solutions tailored to meet the evolving needs of businesses. From simple payment processing to advanced fraud detection, Authorize.Net ensures a secure and seamless payment experience for both merchants and customers.
- Adyen: Recognized for its global reach and extensive payment methods, Adyen powers payment solutions for some of the world’s leading brands. With its unified platform and real-time analytics, Adyen enables businesses to optimize their payment processes and enhance customer engagement.
- Braintree: Acquired by PayPal, Braintree continues to innovate in the payment gateway space with its flexible APIs and robust features. Whether it’s online, in-app, or mobile payments, Braintree simplifies the payment process while prioritizing security and compliance.
- 2Checkout: Formerly known as Avangate, 2Checkout offers a comprehensive e-commerce platform that encompasses payment processing, subscription billing, and digital commerce solutions. With its global reach and localized payment options, 2Checkout facilitates seamless transactions across borders.
- Worldpay: As one of the largest payment processing companies globally, Worldpay provides end-to-end payment solutions tailored to the needs of businesses across various industries. With its advanced fraud prevention tools and extensive payment network, Worldpay ensures secure transactions and optimal uptime.
- PayU: Catering primarily to emerging markets, PayU offers a suite of payment solutions designed to drive financial inclusion and e-commerce growth. With its seamless checkout experience and localized payment options, PayU empowers merchants to tap into new markets and expand their customer base.
- Skrill: Renowned for its low-cost international money transfers and digital wallet services, Skrill is a preferred choice for businesses and consumers alike. With its user-friendly platform and competitive fees, Skrill facilitates frictionless transactions across borders, making it ideal for global commerce.
FAQs On 10 Payment Gateways
In today’s fast-paced digital world, payment gateways serve as the backbone of online transactions, ensuring seamless and secure money transfers. With a plethora of options available, it’s natural for businesses and individuals alike to have questions regarding these essential tools. Here, we delve into the frequently asked questions (FAQs) surrounding 10 popular payment gateways, shedding light on their functionalities and benefits.
- PayPal:
- Q: Is PayPal suitable for international transactions?
- A: Yes, PayPal supports transactions across borders, making it a preferred choice for businesses with global clientele.
- Stripe:
- Q: How does Stripe ensure security?
- A: Stripe employs advanced encryption and security protocols, complying with industry standards to safeguard sensitive payment information.
- Square:
- Q: Can Square be integrated with e-commerce platforms?
- A: Absolutely, Square offers seamless integration with various e-commerce platforms, facilitating online transactions effortlessly.
- Authorize.Net:
- Q: What types of payment methods does Authorize.Net support?
- A: Authorize.Net accepts a wide array of payment methods, including credit cards, e-checks, and digital payment wallets.
- 2Checkout:
- Q: Is 2Checkout compatible with subscription-based services?
- A: Yes, 2Checkout provides robust support for subscription-based models, enabling businesses to manage recurring payments efficiently.
- Braintree:
- Q: How does Braintree handle disputes and chargebacks?
- A: Braintree offers dispute resolution services and assists merchants in handling chargebacks through its comprehensive platform.
- Worldpay:
- Q: Can Worldpay accommodate high transaction volumes?
- A: Indeed, Worldpay is designed to handle high volumes of transactions securely, making it suitable for businesses of all sizes.
- Authorize.Net:
- Q: Does Authorize.Net offer fraud detection features?
- A: Yes, Authorize.Net provides robust fraud detection tools to help merchants identify and prevent fraudulent transactions effectively.
- Payoneer:
- Q: How does Payoneer facilitate cross-border payments?
- A: Payoneer streamlines cross-border payments through its global network, offering competitive exchange rates and low transfer fees.
- Skrill:
- Q: Can Skrill be used for online gambling transactions?
- A: Yes, Skrill is a popular choice for online gambling transactions, providing a secure and reliable payment solution for gaming enthusiasts.
Thanks for reading our post “Top 10 Payment Gateways you Should Integrate to Your Web Application”. Please connect with us to learn more about Best Top 10 Payment Gateways .