Table of Contents
Overview of Blockchain Technology
In the digital era, where data is increasingly becoming the currency of the future, blockchain technology has emerged as a groundbreaking innovation with the potential to transform industries and redefine the way we conduct transactions. From cryptocurrencies to supply chain management and beyond, blockchain is reshaping the way businesses and individuals interact, offering unparalleled security, transparency, and efficiency. Let’s delve into an overview of this revolutionary technology and understand its implications across various domains.
What is Blockchain Technology?
At its core, blockchain is a decentralized ledger system that records transactions across a network of computers. Unlike traditional centralized databases, where information is stored in a single location controlled by a central authority, blockchain distributes data across a network of nodes, making it immutable and tamper-proof. Each block in the chain contains a cryptographic hash of the previous block, creating a secure and transparent chronological record of transactions.
Key Features and Components:
- Decentralization: Blockchain operates on a peer-to-peer network, eliminating the need for intermediaries and central authorities. This decentralized structure ensures that no single entity has control over the entire network, making it resistant to censorship and fraud.
- Transparency: Every transaction on the blockchain is visible to all participants in real-time. This transparency fosters trust among users and ensures accountability within the network.
- Immutability: Once recorded, data on the blockchain cannot be altered or deleted. This immutability ensures the integrity of transactions and prevents fraudulent activities.
- Security: Blockchain employs advanced cryptographic techniques to secure data and verify transactions. Consensus mechanisms such as Proof of Work (PoW) or Proof of Stake (PoS) ensure that only valid transactions are added to the chain.
Applications of Blockchain Technology:
- Cryptocurrencies: Bitcoin, Ethereum, and other cryptocurrencies are built on blockchain technology, enabling secure peer-to-peer transactions without the need for intermediaries.
- Supply Chain Management: Blockchain enables end-to-end traceability and transparency in supply chains, reducing fraud, counterfeiting, and inefficiencies.
- Smart Contracts: Smart contracts are self-executing contracts with the terms of the agreement written into code. Blockchain facilitates the implementation of smart contracts, automating processes and reducing the need for intermediaries.
- Identity Management: Blockchain-based identity management systems offer secure and verifiable digital identities, enhancing privacy and reducing identity theft.
- Healthcare: Blockchain can revolutionize healthcare by securely storing and sharing patient data, ensuring interoperability among disparate systems, and enhancing data security and privacy.
Challenges and Future Outlook:
While blockchain technology holds immense promise, it also faces several challenges, including scalability, interoperability, and regulatory concerns. Addressing these challenges will be crucial for the widespread adoption of blockchain across industries.
Looking ahead, the future of blockchain technology is filled with possibilities. As the technology matures and evolves, we can expect to see further innovation and integration across various sectors, unlocking new opportunities for efficiency, transparency, and trust in the digital economy.
Fundamental Concepts of Blockchain
In the realm of technological innovations, few concepts have garnered as much attention and intrigue as blockchain. Originating as the underlying technology behind Bitcoin, blockchain has since transcended its cryptocurrency roots to become a revolutionary force across various industries. Its decentralized nature, immutability, and cryptographic security have propelled it into the spotlight, promising to reshape traditional systems and processes fundamentally. To grasp the essence of blockchain, let’s delve into its fundamental concepts.
What is Blockchain?
At its core, blockchain is a distributed ledger technology (DLT) that enables the secure recording of transactions across a network of computers. Unlike centralized systems where a single authority controls the ledger, blockchain operates on a decentralized network, ensuring transparency and trust among participants.
Decentralization: Decentralization lies at the heart of blockchain’s architecture. In a decentralized network, there is no central authority or intermediary controlling the system. Instead, transactions are validated and recorded by a network of nodes, each maintaining a copy of the ledger. This distributed nature eliminates the need for intermediaries, reducing the risk of fraud, censorship, and single points of failure.
Immutability: One of the key features of blockchain is immutability, which ensures that once a transaction is recorded on the ledger, it cannot be altered or deleted. Each block in the chain contains a cryptographic hash of the previous block, creating a tamper-evident record of transactions. This immutability fosters trust and integrity within the system, as participants can verify the history of transactions without relying on a trusted third party.
Consensus Mechanisms: Consensus mechanisms play a vital role in maintaining the integrity of the blockchain network. These mechanisms govern how nodes agree on the validity of transactions and the order in which they are added to the ledger. Popular consensus algorithms include Proof of Work (PoW), Proof of Stake (PoS), and Delegated Proof of Stake (DPoS), each with its own set of advantages and trade-offs.
Smart Contracts: Smart contracts are self-executing contracts with the terms of the agreement written into code. Deployed on blockchain networks, smart contracts automatically enforce and execute the terms of an agreement when predefined conditions are met. This automation streamlines processes, reduces the need for intermediaries, and enhances security by eliminating human error and potential disputes.
Cryptography: Cryptography forms the backbone of blockchain security, safeguarding sensitive data and ensuring the integrity of transactions. Techniques such as public-key cryptography, cryptographic hashing, and digital signatures are used to secure transactions, authenticate participants, and protect the privacy of data.
Applications of Blockchain: While initially synonymous with cryptocurrencies, blockchain has found applications across diverse sectors. From supply chain management and healthcare to finance and voting systems, the potential uses of blockchain are vast and far-reaching. Its ability to enhance transparency, security, and efficiency has sparked interest and experimentation across industries worldwide.
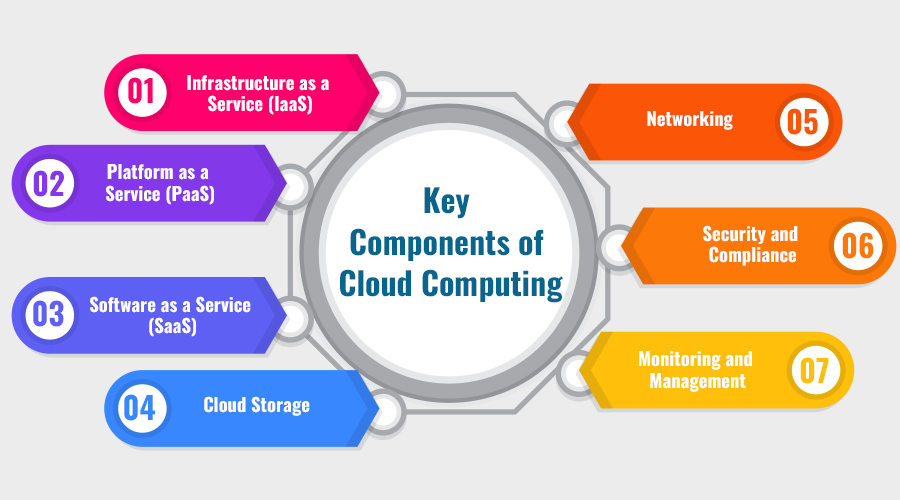
Key Components of Cloud Computing
In today’s digitally driven landscape, cloud computing has emerged as the cornerstone of modern IT infrastructure, revolutionizing the way businesses operate and innovate. With its unparalleled scalability, flexibility, and cost-effectiveness, cloud computing has become an indispensable asset for organizations of all sizes across various industries. However, to fully harness the power of the cloud, it’s essential to understand its key components and how they work together to deliver unparalleled performance and efficiency.
- Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS): At the foundation of cloud computing lies Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS), which provides virtualized computing resources over the internet. With IaaS, organizations can access and manage virtualized servers, storage, and networking infrastructure on-demand, eliminating the need for physical hardware investments. Leading providers such as Amazon Web Services (AWS), Microsoft Azure, and Google Cloud Platform (GCP) offer a comprehensive suite of IaaS solutions tailored to meet diverse business needs.
- Platform as a Service (PaaS): Platform as a Service (PaaS) builds upon the infrastructure layer by offering a complete development and deployment environment for applications. PaaS providers furnish developers with tools, frameworks, and middleware to streamline the development process and accelerate time-to-market for applications. By abstracting underlying infrastructure complexities, PaaS empowers developers to focus on building innovative solutions without worrying about hardware or software management.
- Software as a Service (SaaS): Software as a Service (SaaS) represents the pinnacle of cloud computing, delivering fully functional applications over the internet on a subscription basis. From customer relationship management (CRM) to enterprise resource planning (ERP) and productivity suites, SaaS offerings cover a broad spectrum of business applications. By adopting SaaS solutions, organizations can leverage cutting-edge software without the burden of installation, maintenance, and upgrades, thereby enhancing operational efficiency and agility.
- Cloud Storage: Cloud storage services provide scalable and reliable storage solutions for data backup, archival, and disaster recovery purposes. By storing data in the cloud, organizations can mitigate the risks associated with on-premises storage, such as hardware failures and data breaches. Moreover, cloud storage offers seamless access to data from any location or device, enabling collaboration and data-driven decision-making across the enterprise.
- Networking: Networking plays a pivotal role in cloud computing, facilitating seamless connectivity between various cloud resources and users. Cloud providers offer a range of networking services, including virtual private clouds (VPCs), load balancing, and content delivery networks (CDNs), to ensure optimal performance, security, and reliability. By leveraging cloud networking capabilities, organizations can design robust and scalable architectures to support their evolving business needs.
- Security and Compliance: Security and compliance are paramount considerations in cloud computing, given the shared responsibility model between cloud providers and customers. Cloud providers implement robust security measures to safeguard infrastructure, data, and applications from cyber threats and unauthorized access. Additionally, they offer compliance certifications and adherence to regulatory standards to ensure data privacy and regulatory compliance across diverse industries.
- Monitoring and Management: Effective monitoring and management are essential for optimizing cloud performance, controlling costs, and ensuring service availability. Cloud management platforms (CMPs) offer centralized tools and dashboards to monitor resource utilization, track performance metrics, and automate routine tasks. By leveraging monitoring and management solutions, organizations can gain actionable insights into their cloud environment and make informed decisions to drive business growth.
Security Measures in Blockchain
In the realm of digital innovation, blockchain stands as a titan, revolutionizing various industries with its decentralized and immutable ledger system. However, as with any technological advancement, ensuring robust security measures within blockchain networks is paramount to safeguarding sensitive data and maintaining trust among users. Let’s delve into the fundamental security measures essential for fortifying the integrity of blockchain technology.
- Cryptography: The Pillar of Security Cryptography serves as the backbone of blockchain security, ensuring that data remains confidential, authenticated, and tamper-proof. Implementing strong cryptographic techniques such as hash functions, digital signatures, and encryption algorithms enhances the security posture of blockchain networks, making it exceedingly difficult for malicious actors to compromise data integrity.
- Consensus Mechanisms: Unwavering Trust through Agreement Consensus mechanisms play a pivotal role in maintaining the integrity and consensus within a blockchain network. Whether it’s the proof-of-work (PoW), proof-of-stake (PoS), or delegated proof-of-stake (DPoS), these mechanisms ensure that all network participants agree on the validity of transactions, thwarting potential threats such as double-spending and Sybil attacks.
- Network Security: Fortifying the Perimeter Securing the underlying network infrastructure is crucial in mitigating various security risks, including distributed denial-of-service (DDoS) attacks and node manipulation. Employing robust firewalls, intrusion detection systems (IDS), and regular security audits can bolster the resilience of blockchain networks against external threats, preserving the integrity of the decentralized ecosystem.
- Smart Contract Audits: Code is Law Smart contracts, self-executing agreements with predefined conditions, are integral to many blockchain applications. However, vulnerabilities within smart contract code can lead to catastrophic consequences, including fund theft and network disruption. Conducting comprehensive code audits and implementing formal verification techniques help identify and rectify potential security loopholes, ensuring the reliability and trustworthiness of smart contracts.
- Immutable Ledger: Trust through Transparency The immutable nature of blockchain ledgers instills trust and transparency by providing an indelible record of all transactions. By maintaining a decentralized ledger replicated across numerous nodes, blockchain networks eliminate the single point of failure inherent in centralized systems, reducing the risk of data manipulation and unauthorized access.
- Privacy Enhancements: Balancing Transparency and Confidentiality While blockchain offers transparency, preserving user privacy remains paramount, especially in applications handling sensitive information. Integrating privacy-enhancing technologies such as zero-knowledge proofs and homomorphic encryption empowers users with greater control over their data while preserving the integrity and security of the blockchain network.
- Continuous Monitoring and Incident Response Vigilant monitoring of blockchain networks coupled with proactive incident response protocols is imperative to swiftly detect and mitigate security breaches. Real-time monitoring tools, anomaly detection algorithms, and rapid response mechanisms enable blockchain stakeholders to effectively thwart emerging threats and safeguard the integrity of the network.
Security Features in Cloud Computing
In today’s digital landscape, cloud computing has become the backbone of countless businesses worldwide, offering unparalleled flexibility, scalability, and accessibility. However, amidst the convenience lies a paramount concern: security. As organizations migrate their operations to the cloud, ensuring robust security measures is non-negotiable. Fortunately, cloud service providers have stepped up their game, implementing a myriad of security features to safeguard sensitive data and mitigate risks. Let’s delve into some of the top security features in cloud computing that are essential for maintaining a secure environment.
- Data Encryption: Encryption is the cornerstone of data security in the cloud. It involves converting data into a ciphertext format, making it unreadable to unauthorized users. Cloud providers employ robust encryption techniques to protect data both in transit and at rest. Advanced encryption standards, such as AES (Advanced Encryption Standard) with 256-bit keys, ensure that even if data is intercepted, it remains unintelligible without the decryption key.
- Identity and Access Management (IAM): IAM solutions play a pivotal role in controlling user access to cloud resources. By implementing granular access controls and multi-factor authentication (MFA), organizations can verify the identities of users and enforce least privilege principles. This ensures that only authorized personnel can access sensitive data or critical infrastructure, reducing the risk of unauthorized access or data breaches.
- Network Security: Cloud environments rely on robust network security measures to protect against external threats and unauthorized access. Firewalls, intrusion detection and prevention systems (IDPS), and virtual private networks (VPNs) are deployed to create secure perimeters and monitor network traffic for suspicious activity. Additionally, network segmentation helps isolate workloads and limit the impact of potential breaches.
- Regular Audits and Compliance: Cloud providers adhere to stringent security standards and undergo regular audits to ensure compliance with industry regulations such as GDPR, HIPAA, and PCI DSS. These audits assess the effectiveness of security controls, identify vulnerabilities, and provide recommendations for improvement. Compliance with these standards instills confidence in customers and demonstrates a commitment to data protection and privacy.
- Data Loss Prevention (DLP): Data loss prevention mechanisms help organizations prevent the unauthorized disclosure of sensitive information. DLP solutions monitor and analyze data as it moves within and outside the cloud environment, applying policies to detect and block unauthorized activities. By classifying data based on its sensitivity and implementing encryption, masking, or tokenization, organizations can mitigate the risk of data leakage or exposure.
- Incident Response and Disaster Recovery: Despite robust preventive measures, security incidents can still occur. Cloud providers offer comprehensive incident response and disaster recovery capabilities to minimize the impact of security breaches or service disruptions. Automated incident detection, real-time alerting, and predefined response protocols enable organizations to swiftly mitigate threats and restore operations with minimal downtime.
- Security Monitoring and Logging: Continuous monitoring and logging are essential for detecting and investigating security incidents in the cloud. Cloud providers offer robust logging capabilities, capturing detailed information about user activities, system events, and network traffic. Security information and event management (SIEM) solutions analyze these logs in real-time, correlating events and identifying suspicious behavior for prompt remediation.
Scalability in Blockchain vs Cloud Computing
In the realm of technology, scalability is the holy grail that ensures systems can handle growth without sacrificing performance. Two cutting-edge technologies, blockchain and cloud computing, stand at the forefront of innovation, each offering unique approaches to scalability. Let’s delve into the intricacies of scalability in both blockchain and cloud computing to understand their strengths and limitations.
Blockchain, renowned for its decentralized nature and immutable ledger, faces significant challenges when it comes to scalability. Traditional blockchains, like Bitcoin and Ethereum, operate on a consensus mechanism that requires every node to validate each transaction, leading to scalability bottlenecks. As the network grows, the processing power and time required for consensus increase exponentially, resulting in slower transaction speeds and higher fees.
To tackle scalability issues, blockchain projects employ various solutions such as sharding, layer-two protocols, and consensus algorithm upgrades. Sharding divides the network into smaller partitions, allowing nodes to process transactions in parallel, thus increasing throughput. Layer-two solutions like the Lightning Network enable off-chain transactions, reducing the burden on the main blockchain. Moreover, consensus algorithm upgrades, like Ethereum’s transition from Proof of Work to Proof of Stake, aim to improve efficiency and scalability.
On the other hand, cloud computing offers a centralized approach to scalability, leveraging vast networks of servers to handle increasing workloads. Cloud providers offer scalable infrastructure as a service (IaaS), platform as a service (PaaS), and software as a service (SaaS) solutions tailored to the needs of businesses and developers. With cloud computing, scalability is achieved through elastic scaling, where resources are dynamically allocated based on demand. This flexibility allows businesses to rapidly scale up or down without the need for significant infrastructure investments.
However, despite its apparent advantages, cloud computing is not without limitations. Centralization poses security and privacy concerns, as data stored on centralized servers is vulnerable to hacking and unauthorized access. Moreover, reliance on third-party providers introduces the risk of service outages and downtime, impacting the availability of critical applications and services.
Smart Contracts vs Traditional Contracts
In the realm of legal agreements, traditional contracts have long been the cornerstone of business dealings, laying out terms, conditions, and obligations in written form. However, with the advent of blockchain technology, a new player has emerged – smart contracts. As businesses and industries continue to evolve, it’s crucial to understand the disparities between these two contract types and how they impact various aspects of transactions and agreements.
Definition and Functionality: Traditional contracts are physical or digital documents drafted by legal professionals, outlining the terms and conditions agreed upon by involved parties. These contracts typically require manual enforcement, interpretation, and execution by intermediaries such as lawyers or courts.
On the other hand, smart contracts are self-executing contracts with the terms of the agreement directly written into code. They run on blockchain technology and automatically execute and enforce when predefined conditions are met. Smart contracts eliminate the need for intermediaries, providing a decentralized and automated approach to agreements.
Security and Trust: One of the fundamental differences between smart contracts and traditional contracts lies in security and trust. Traditional contracts rely heavily on trust between parties and intermediaries for enforcement. However, smart contracts leverage cryptographic technology and decentralized networks to ensure tamper-proof execution, enhancing security and eliminating the need for trust in intermediaries.
Efficiency and Automation: Smart contracts offer significant advantages in terms of efficiency and automation. By automating the execution process based on predefined conditions, smart contracts reduce the need for manual intervention, thus minimizing the potential for errors and delays. This automation streamlines processes, leading to faster transactions and cost savings for parties involved.
Flexibility and Adaptability: Traditional contracts often require manual amendments or renegotiation to accommodate changes in circumstances or terms. Conversely, smart contracts offer greater flexibility and adaptability through programmable logic. Parties can easily update and modify smart contract terms without the need for extensive renegotiation, providing a more agile approach to agreements.
Cost and Accessibility: While traditional contracts involve costs associated with drafting, intermediaries, and enforcement, smart contracts can significantly reduce these expenses. With smart contracts, there’s no need for intermediaries, reducing overhead costs and making transactions more accessible to a wider range of participants, particularly in regions with limited access to legal services.
Regulatory Compliance: Traditional contracts are subject to existing legal frameworks and regulations, requiring compliance with jurisdiction-specific laws. Smart contracts, although autonomous, must still operate within legal boundaries and adhere to regulatory requirements. While blockchain technology offers transparency and auditability, ensuring compliance with legal standards remains a crucial consideration for smart contract implementation.
Cost Considerations: Blockchain vs Cloud Computing
In today’s digital landscape, businesses are constantly evaluating cost-effective solutions to meet their technological needs. Among the myriad of options available, two prominent contenders often stand out: blockchain and cloud computing. Both technologies offer unique advantages, but when it comes to cost considerations, understanding their differences is crucial for making informed decisions. In this article, we’ll delve into the intricacies of cost implications associated with blockchain and cloud computing, providing a comparative analysis to help businesses determine the most suitable option for their requirements.
Blockchain Technology:
Blockchain, originally devised for Bitcoin, has evolved into a versatile technology with applications spanning various industries beyond cryptocurrency. Its decentralized and immutable nature ensures transparency, security, and trust in transactions, making it appealing for industries such as finance, supply chain, healthcare, and more. However, the cost considerations associated with blockchain implementation are noteworthy.
- Development Costs: Developing a blockchain network entails significant upfront costs. Building a blockchain from scratch or customizing existing blockchain platforms demands skilled developers proficient in cryptography and distributed systems, leading to higher development expenses.
- Infrastructure Costs: Running a blockchain network requires robust infrastructure to support nodes, maintain consensus mechanisms, and ensure data integrity. These infrastructure costs can escalate rapidly, especially for public blockchains, where nodes are distributed globally.
- Energy Consumption: Proof-of-Work (PoW) consensus algorithms, employed by popular blockchains like Bitcoin and Ethereum, consume substantial amounts of energy. The energy-intensive nature of PoW consensus not only drives up operational costs but also raises environmental concerns.
Cloud Computing:
Cloud computing has revolutionized the way businesses manage their IT infrastructure, offering scalability, flexibility, and cost-effectiveness. By outsourcing computing resources and services to third-party providers, organizations can reduce capital expenditures and operational overheads. However, assessing the true cost of cloud computing involves considering various factors.
- Pay-Per-Use Model: Cloud computing providers typically operate on a pay-per-use pricing model, allowing businesses to scale resources according to their needs. While this model offers flexibility and cost savings for fluctuating workloads, it requires diligent monitoring to avoid overspending on unused resources.
- Subscription Fees: Many cloud services are subscription-based, requiring businesses to pay recurring fees for accessing software, storage, and other resources. While subscription models provide predictable costs and eliminate upfront investments, long-term expenses can accumulate significantly.
- Data Transfer and Storage Costs: Cloud providers often charge for data transfer between different regions and data centers, as well as storage fees based on the volume of data stored. Organizations must optimize data usage and storage strategies to minimize costs without compromising performance.
Comparative Analysis:
When comparing the cost implications of blockchain and cloud computing, several key considerations emerge:
- Upfront Investment: Blockchain typically requires higher upfront investment due to development and infrastructure costs, whereas cloud computing offers lower barriers to entry with its pay-per-use model and minimal upfront investment.
- Operating Costs: While blockchain incurs ongoing operating costs for maintenance, energy consumption, and transaction fees, cloud computing expenses are primarily driven by resource usage, subscription fees, and data management.
- Scalability: Cloud computing offers unparalleled scalability, allowing businesses to dynamically adjust resources based on demand, while blockchain scalability remains a challenge, particularly for public blockchains with limited transaction throughput.
Regulatory Landscape and Compliance
In today’s rapidly evolving business environment, regulatory compliance has become more crucial than ever. With an increasingly complex web of laws, regulations, and industry standards, organizations face significant challenges in ensuring adherence to legal requirements while maintaining operational efficiency. Understanding the regulatory landscape and implementing effective compliance strategies are essential for businesses to mitigate risks, protect their reputation, and foster trust among stakeholders.
The Regulatory Maze: Understanding the Landscape
The regulatory landscape encompasses a myriad of rules, guidelines, and standards set forth by governmental bodies, industry associations, and international organizations. These regulations span across various domains such as finance, healthcare, cybersecurity, environmental protection, and data privacy, among others. Navigating through this maze of regulations requires a comprehensive understanding of applicable laws and their implications on business operations.
Importance of Compliance
Compliance with regulatory requirements is not merely a legal obligation but also a strategic imperative for businesses. Non-compliance can lead to severe consequences, including financial penalties, legal sanctions, reputational damage, and even operational disruptions. Moreover, in an era of increasing scrutiny and transparency, stakeholders such as investors, customers, and partners expect organizations to demonstrate ethical conduct and responsible governance.
Challenges Faced by Organizations
Achieving and maintaining compliance poses several challenges for organizations of all sizes and industries. These challenges may include:
- Complexity: Regulatory requirements are often complex and subject to frequent changes, making it challenging for organizations to keep pace with evolving standards.
- Resource Constraints: Limited resources, including financial, human, and technological, can impede the implementation of robust compliance programs.
- Cross-border Compliance: Globalization has resulted in businesses operating across multiple jurisdictions, each with its own set of regulatory requirements, creating additional compliance burdens.
- Data Privacy Concerns: The proliferation of data and the enactment of stringent data protection laws such as the GDPR and CCPA have raised concerns regarding data privacy compliance.
Strategies for Compliance Success
Despite these challenges, organizations can adopt several strategies to enhance their compliance efforts:
- Proactive Compliance Monitoring: Implementing robust monitoring mechanisms to track regulatory changes and assess their impact on business operations in real-time.
- Risk Assessment and Mitigation: Conducting regular risk assessments to identify potential compliance risks and implementing appropriate measures to mitigate them.
- Investing in Technology: Leveraging technology solutions such as compliance management software, artificial intelligence, and data analytics to streamline compliance processes and enhance efficiency.
- Training and Awareness Programs: Providing comprehensive training and awareness programs to employees to ensure understanding of regulatory requirements and promote a culture of compliance throughout the organization.
- Engaging with Regulatory Authorities: Establishing open lines of communication with regulatory authorities to seek guidance, clarify regulatory ambiguities, and demonstrate a commitment to compliance.
Top Overview of Blockchain Technology Companies
In the ever-evolving landscape of technology, one innovation stands out prominently: blockchain technology. With its decentralized and transparent nature, blockchain has revolutionized various industries, from finance to supply chain management. At the forefront of this digital revolution are several pioneering companies driving innovation and reshaping the future. Let’s delve into an insightful overview of the top blockchain technology companies leading the charge:
-
-
Next Big Technology:

Focus Area
- Mobile App Development
- App Designing (UI/UX)
- Software Development
- Web Development
- AR & VR Development
- Big Data & BI
- Cloud Computing Services
- DevOps
- E-commerce Development
Industries Focus
- Art, Entertainment & Music
- Business Services
- Consumer Products
- Designing
- Education
- Financial & Payments
- Gaming
- Government
- Healthcare & Medical
- Hospitality
- Information Technology
- Legal & Compliance
- Manufacturing
- Media
-
- Ripple: As a leading provider of enterprise blockchain solutions for global payments, Ripple has redefined cross-border transactions. Its RippleNet network enables instant, low-cost international payments, disrupting traditional banking systems. With partnerships with major financial institutions worldwide, Ripple continues to spearhead innovation in the fintech sector.
- Consensys: A powerhouse in the Ethereum ecosystem, Consensys is dedicated to building decentralized applications and infrastructure. From developer tools to enterprise solutions, Consensys plays a pivotal role in advancing Ethereum-based projects, fostering innovation in decentralized finance (DeFi), supply chain management, and more.
- Coinbase: Recognized as one of the largest cryptocurrency exchanges globally, Coinbase has become synonymous with accessibility and reliability in the digital asset space. Catering to both retail and institutional investors, Coinbase offers a user-friendly platform for buying, selling, and storing various cryptocurrencies, including Bitcoin, Ethereum, and Litecoin.
- Chainlink: Specializing in decentralized oracle networks, Chainlink connects smart contracts with real-world data, enabling automation and interoperability across blockchain platforms. Its secure and reliable oracles have applications in decentralized finance, gaming, insurance, and beyond, fueling the growth of the broader blockchain ecosystem.
- Binance: With its comprehensive suite of services, including cryptocurrency exchange, trading platform, and blockchain ecosystem, Binance has emerged as a global leader in the digital asset space. Continuously expanding its offerings, Binance fosters innovation through initiatives like Binance Smart Chain and Binance Launchpad, supporting blockchain projects and startups worldwide.
- Tezos: Built upon a self-amending blockchain, Tezos enables on-chain governance and formal verification, ensuring security and upgradability. Its focus on scalability, security, and sustainability has garnered attention from developers and enterprises seeking a robust platform for building decentralized applications and digital assets.
- Hyperledger: Hosted by the Linux Foundation, Hyperledger is an open-source collaborative effort aimed at advancing cross-industry blockchain technologies. With a diverse community of developers and enterprises, Hyperledger offers a suite of modular frameworks and tools, including Hyperledger Fabric and Hyperledger Sawtooth, empowering organizations to create tailored blockchain solutions.
- VeChain: Targeting supply chain management and product authentication, VeChain utilizes blockchain technology to enhance transparency and traceability. Through its enterprise blockchain platform, VeChainThor, the company enables businesses to digitize assets, track goods from origin to consumption, and verify product authenticity, fostering trust and efficiency in global trade.
- Ethereum: As the pioneer of smart contract platforms, Ethereum remains a dominant force in the blockchain space. Empowering developers to build decentralized applications (dApps) and deploy smart contracts, Ethereum serves as the foundation for a multitude of innovative projects, including decentralized finance, non-fungible tokens (NFTs), and decentralized autonomous organizations (DAOs).
FAQs On Blockchain vs Cloud Computing Development
In the realm of technology, two groundbreaking innovations have been making waves in recent years: blockchain and cloud computing. Both have revolutionized how data is stored, managed, and processed, albeit in different ways. As businesses increasingly explore these technologies for their development projects, it’s natural for questions to arise regarding their differences, advantages, and best use cases. In this article, we’ll delve into some frequently asked questions about blockchain versus cloud computing development to provide clarity on these transformative technologies.
- What is the fundamental difference between blockchain and cloud computing? Blockchain is a decentralized, distributed ledger technology that records transactions across a network of computers. It ensures transparency, immutability, and security through cryptographic techniques. On the other hand, cloud computing refers to the delivery of computing services—including storage, servers, databases, networking, software, and more—over the internet on a pay-as-you-go basis. The key distinction lies in the architecture: blockchain operates on a peer-to-peer network without the need for a central authority, while cloud computing relies on centralized servers managed by service providers.
- When should I choose blockchain over cloud computing for my development project? Blockchain is best suited for scenarios where data integrity, security, and decentralization are paramount. Use cases include supply chain management, financial transactions, identity verification, and smart contracts. If your project involves multiple parties with a need for trustless interactions and immutable record-keeping, blockchain could be the preferred choice. However, it’s important to note that blockchain development often requires specialized skills and may entail higher costs compared to traditional cloud solutions.
- Conversely, when is cloud computing a better option than blockchain? Cloud computing shines in situations where scalability, flexibility, and cost-efficiency are top priorities. If your project involves large-scale data processing, real-time analytics, collaborative applications, or rapid prototyping, cloud computing offers a more practical solution. With cloud services, you can easily scale resources up or down according to demand, pay only for what you use, and leverage a wide range of pre-built tools and integrations. Additionally, cloud platforms typically offer robust security measures and compliance certifications, making them suitable for various industries and regulatory requirements.
- Can blockchain and cloud computing be used together? Absolutely. In fact, many organizations are exploring hybrid solutions that combine the strengths of both technologies. For instance, you could use blockchain for data authentication and audit trails while leveraging cloud computing for storage, computation, and user interface. This hybrid approach allows you to achieve the benefits of decentralization and security offered by blockchain, along with the scalability and convenience of cloud infrastructure. It’s a powerful combination that can address diverse business needs effectively.
- What are the main challenges associated with blockchain and cloud computing development? While both technologies offer immense potential, they also present unique challenges that developers must navigate. Blockchain development requires a deep understanding of cryptographic principles, consensus algorithms, smart contract programming, and regulatory compliance. Moreover, scalability, interoperability, and energy consumption are ongoing concerns within the blockchain space. On the other hand, cloud computing development entails managing complex infrastructure, optimizing resource usage, ensuring data privacy, and mitigating cybersecurity risks. Keeping abreast of evolving standards, best practices, and industry trends is essential for success in both domains.
Thanks for reading our post “Overview of Blockchain Technology”. Please connect with us to learn more about Best Overview of Blockchain.