Table of Contents
Introduction to the Indonesian Investment Landscape
In the realm of global investment opportunities, Indonesia stands as a beacon of potential, offering a diverse array of sectors ripe for exploration. With its robust economic growth, strategic geographical location, and a burgeoning middle class, Indonesia presents a compelling case for both domestic and foreign investors alike. This article serves as a compass, guiding you through the intricacies of the Indonesian investment landscape.
Understanding Indonesia’s Economic Context
Indonesia, the largest economy in Southeast Asia, boasts a Gross Domestic Product (GDP) exceeding $1 trillion. With a population exceeding 270 million, it’s the fourth most populous country globally, offering a vast consumer market. The country’s economic growth, driven by domestic consumption, infrastructure development, and a burgeoning digital economy, paints a promising picture for investors seeking long-term opportunities.
Key Investment Sectors
- Infrastructure: Indonesia’s ambitious infrastructure projects, including transportation, energy, and telecommunications, offer lucrative investment prospects. The government’s commitment to bridging infrastructure gaps creates openings for public-private partnerships (PPPs) and foreign direct investment (FDI).
- Manufacturing: With a burgeoning manufacturing sector, Indonesia presents opportunities across various industries, including automotive, electronics, and textiles. The country’s abundant labor force and strategic location for export-oriented manufacturing make it an attractive destination for investors seeking cost-effective production hubs.
- Natural Resources: Indonesia’s abundant natural resources, including coal, palm oil, and minerals, attract significant investment interest. However, sustainable practices and adherence to environmental regulations are becoming increasingly important considerations for investors in this sector.
- Tourism: As one of the world’s top tourist destinations, Indonesia’s tourism sector offers a myriad of investment opportunities, from hospitality and leisure to ecotourism and cultural experiences. The government’s focus on infrastructure development and tourism promotion initiatives further enhances the sector’s appeal.
- Digital Economy: Indonesia’s rapidly growing digital economy, fueled by a young and tech-savvy population, presents ample opportunities in e-commerce, fintech, and digital services. The country’s thriving startup ecosystem and increasing internet penetration rates underscore its potential as a regional tech hub.
Regulatory Environment and Investment Incentives:
Navigating Indonesia’s regulatory landscape can be complex, but the government has implemented measures to attract investment and streamline processes. The Indonesia Investment Coordinating Board (BKPM) serves as a one-stop service for investment facilitation, providing assistance to domestic and foreign investors alike.
Moreover, Indonesia offers various investment incentives, including tax holidays, tax allowances, and import duty exemptions, aimed at fostering economic growth and attracting investment across priority sectors.
Risks and Challenges:
While Indonesia presents vast investment opportunities, navigating the market entails certain risks and challenges. These include regulatory uncertainties, bureaucratic hurdles, infrastructure bottlenecks, and socio-political complexities. Additionally, investors must navigate cultural nuances and local business practices to establish successful ventures in the Indonesian market.
Rise of FinTech in Indonesia
In the archipelago of Indonesia, where tradition meets modernity, a new force is revolutionizing the financial landscape: FinTech. Over the past decade, the Southeast Asian giant has witnessed an unprecedented surge in financial technology, reshaping the way individuals and businesses manage their finances.
Indonesia, with its burgeoning population of over 270 million people, presents a ripe market for innovation in financial services. With a significant portion of the population still unbanked or underbanked, traditional banking systems have struggled to reach all corners of the vast nation. This gap has paved the way for FinTech startups to step in and offer accessible and efficient solutions.
One of the key drivers behind the rise of FinTech in Indonesia is the widespread adoption of smartphones and the internet. With a rapidly growing tech-savvy population, mobile apps have become the primary gateway to financial services for many Indonesians. From digital payments to peer-to-peer lending platforms, FinTech companies are leveraging technology to offer a wide range of services that cater to the diverse needs of consumers.
Digital payments have emerged as one of the most disruptive segments of the FinTech industry in Indonesia. With the advent of e-wallets and mobile payment apps, cashless transactions have become increasingly prevalent, even in remote areas. Players like GoPay, OVO, and Dana have captured significant market share by offering convenient, secure, and reliable payment solutions that appeal to both merchants and consumers.
Another area where FinTech is making waves is in the realm of peer-to-peer lending. With traditional banks often hesitant to extend credit to small businesses and individuals without a solid credit history, peer-to-peer lending platforms have filled the void by connecting borrowers with potential lenders through online marketplaces. This has not only provided much-needed access to capital for aspiring entrepreneurs but has also opened up new investment opportunities for individuals looking to grow their wealth.
Moreover, FinTech is not just limited to payments and lending. The rise of InsurTech, WealthTech, and RegTech startups further demonstrates the breadth of innovation happening in Indonesia’s financial sector. These companies are leveraging data analytics, artificial intelligence, and blockchain technology to offer personalized insurance products, automated investment solutions, and regulatory compliance services, respectively.
However, the rapid expansion of the FinTech industry in Indonesia is not without its challenges. Regulatory hurdles, cybersecurity threats, and the need for financial literacy among consumers are some of the key issues that must be addressed to ensure the sustainable growth of the sector. Regulatory bodies such as the Financial Services Authority (OJK) are actively working to create a conducive environment for FinTech innovation while safeguarding the interests of consumers and investors.
Understanding Millennial Investor Behavior
In the fast-paced realm of finance, the landscape is continually evolving, shaped by the unique perspectives and behaviors of each generation. Among these, millennials stand out as a cohort with distinctive inclinations and approaches towards investing. Born between the early 1980s and the mid-1990s, millennials, also known as Generation Y, are characterized by their digital nativity, social consciousness, and penchant for innovation. Understanding their investment behavior is pivotal for financial institutions and advisors seeking to engage with this burgeoning demographic.
The Digital Frontier: One of the defining features of millennial investor behavior is their seamless integration of technology into their financial endeavors. Having grown up in the digital age, millennials are well-versed in leveraging online platforms and mobile apps for investment purposes. They are more likely to utilize robo-advisors, investment apps, and online trading platforms compared to traditional methods. This preference for digital solutions stems from their comfort with technology, desire for convenience, and cost-effectiveness.
Ethical and Socially Responsible Investing: Beyond financial returns, millennials exhibit a keen interest in investing with purpose. Socially responsible investing (SRI), also known as environmental, social, and governance (ESG) investing, is gaining traction among this demographic. Millennials are inclined to allocate their capital towards companies that align with their values, such as those promoting sustainability, diversity, and ethical business practices. For them, investing is not just about maximizing profits but also making a positive impact on society and the environment.
Financial Education and Self-Directed Investing: Despite facing economic challenges such as student loan debt and stagnant wages, millennials display a proactive approach to financial literacy. Empowered by access to vast information resources online, they are more inclined to educate themselves about investing. Many millennials opt for self-directed investing, bypassing traditional financial advisors in favor of DIY investment strategies. This autonomy allows them to have greater control over their portfolios and align their investments with their personal goals and values.
Risk Aversion and Long-Term Perspective: Contrary to the stereotype of being risk-averse, millennials are more willing to embrace investment risk, provided they perceive potential rewards. However, their risk tolerance is tempered by a preference for long-term, diversified investment strategies. Having witnessed the volatility of financial markets, particularly during the 2008 global financial crisis, millennials prioritize stability and long-term growth over quick gains. They are more likely to opt for diversified portfolios, including investments in equities, real estate, and alternative assets, to mitigate risk and achieve their financial objectives.
The Influence of Social Media and Peer Networks: Social media plays a significant role in shaping millennial investor behavior. Platforms like Reddit, Twitter, and Instagram serve as forums for sharing investment tips, market insights, and success stories. Millennials are more likely to seek investment advice from online communities and peer networks rather than traditional financial institutions. This democratization of information empowers them to make informed investment decisions and stay updated on market trends in real-time.
The Need for Mobile Accessibility in Financial Services
In today’s digitally driven world, where smartphones are practically an extension of our hands, the significance of mobile accessibility in financial services cannot be overstated. Mobile technology has revolutionized the way we manage our finances, offering unparalleled convenience and accessibility. However, amidst this digital transformation, ensuring inclusivity for all users, including those with disabilities, remains a critical challenge.
Accessibility in financial services encompasses a wide range of considerations, from user interface design to functionality and compatibility across different devices and platforms. For individuals with disabilities, such as visual impairments or motor disabilities, navigating traditional banking channels can be daunting and, in many cases, impossible without assistance. Mobile accessibility bridges this gap, empowering users of all abilities to independently access and manage their finances.
One of the key advantages of mobile accessibility is its flexibility. Unlike traditional brick-and-mortar banks, which have limited operating hours and physical accessibility constraints, mobile banking apps are available 24/7, allowing users to perform transactions and access account information at their convenience. This flexibility is particularly beneficial for individuals with mobility impairments or those who may struggle to visit physical bank branches regularly.
Moreover, mobile accessibility fosters financial inclusion by expanding access to banking services for underserved populations. In many regions, especially in developing countries, traditional banking infrastructure is sparse, making it difficult for people in rural or remote areas to access basic financial services. Mobile banking apps provide a lifeline for these communities, enabling them to conduct transactions, pay bills, and even access credit and savings facilities from the comfort of their homes.
Another critical aspect of mobile accessibility is its role in promoting financial literacy and empowerment. By offering intuitive interfaces and educational resources within banking apps, financial institutions can help users make informed decisions about their finances. Features such as budgeting tools, financial calculators, and personalized insights empower users to manage their money effectively and plan for the future.
From a business perspective, investing in mobile accessibility makes sound financial sense. Not only does it open up new markets and customer segments, but it also enhances brand reputation and customer loyalty. In an increasingly competitive landscape, banks and financial institutions that prioritize accessibility demonstrate a commitment to social responsibility and inclusivity, which resonates with consumers.
However, achieving meaningful mobile accessibility requires a concerted effort from both financial institutions and technology providers. It involves incorporating accessibility standards and guidelines into the design and development process, conducting regular accessibility audits and user testing, and providing ongoing training and support for employees.
Overview of the Indonesian Investment Giant
In the vibrant landscape of Southeast Asia, Indonesia stands out not only for its breathtaking natural beauty but also for its robust economy fueled by a myriad of investment opportunities. At the heart of this economic dynamism lies an investment giant, whose influence resonates not only within the archipelago but also across the globe. In this article, we delve into the intricacies of the Indonesian investment powerhouse, exploring its origins, growth trajectory, and its significance in the global investment arena.
Origins and Evolution: The genesis of Indonesia’s investment prowess can be traced back to its rich endowment of natural resources and strategic geographical location. Blessed with abundant reserves of coal, gold, and natural gas, Indonesia emerged as a magnet for foreign investors seeking lucrative ventures in the extractive industries. However, it was the visionary policies of the Indonesian government that paved the way for the nation’s economic transformation.
The establishment of the Indonesia Investment Coordinating Board (BKPM) in 1973 marked a significant milestone, streamlining the investment process and fostering a conducive environment for both domestic and foreign investors. Subsequent economic reforms, such as deregulation and privatization initiatives, further bolstered Indonesia’s attractiveness as an investment destination, propelling its economy onto the global stage.
Key Players and Sectors: Central to Indonesia’s investment landscape are its prominent conglomerates, whose diversified portfolios span across various sectors, including banking, telecommunications, and infrastructure. Companies such as the Salim Group, Astra International, and the Lippo Group have played instrumental roles in driving economic growth and innovation, contributing to the nation’s burgeoning middle class and expanding consumer market.
Moreover, Indonesia’s strategic focus on infrastructure development has attracted substantial investments from both public and private entities. Ambitious projects such as the Jakarta-Bandung High-Speed Railway and the Trans-Java Toll Road reflect Indonesia’s commitment to enhancing connectivity and fostering regional integration, thereby unlocking new opportunities for investment and economic development.
Global Impact and Future Prospects: The influence of the Indonesian investment giant extends far beyond its borders, as evidenced by its strategic partnerships and overseas ventures. With a growing emphasis on sustainable development and renewable energy, Indonesian companies are actively exploring opportunities in emerging markets, particularly in Southeast Asia and Africa. Additionally, Indonesia’s pivotal role in regional forums such as the Association of Southeast Asian Nations (ASEAN) further enhances its visibility and influence in shaping the future of global investment trends.
Looking ahead, Indonesia’s investment landscape holds immense potential, buoyed by demographic dividends, technological advancements, and a burgeoning digital economy. As the nation continues to embrace innovation and diversification, investors can expect a plethora of opportunities across various sectors, ranging from e-commerce and fintech to renewable energy and agritech.
Key Features of the FinTech Mobile App
In today’s fast-paced digital age, FinTech mobile apps have emerged as game-changers in the financial industry, offering unparalleled convenience, efficiency, and innovation to users worldwide. With just a few taps on their smartphones, users can access a myriad of financial services, manage their investments, and make transactions seamlessly. Let’s delve into the key features that make FinTech mobile apps indispensable in the modern era.
- Secure Authentication and Biometric Verification: Security is paramount in the FinTech sector, and mobile apps prioritize it through robust authentication measures. Biometric verification methods such as fingerprint and facial recognition add an extra layer of security, ensuring that only authorized users can access sensitive financial information.
- User-friendly Interface: FinTech mobile apps are designed with intuitive interfaces, making them user-friendly even for those with minimal technical expertise. Clear navigation, simplified menus, and interactive features enhance the user experience, enabling seamless navigation through various financial services.
- Personalized Financial Management: These apps offer personalized financial management tools tailored to individual user preferences and financial goals. From budget tracking and expense categorization to investment portfolio management, users can gain insights into their financial health and make informed decisions to achieve their objectives.
- Real-time Transaction Monitoring: Real-time transaction monitoring empowers users to keep track of their financial activities instantaneously. Whether it’s monitoring account balances, tracking incoming and outgoing transactions, or receiving instant alerts for suspicious activities, FinTech mobile apps provide users with full control over their finances.
- Integrated Payment Solutions: FinTech apps seamlessly integrate various payment solutions, including peer-to-peer transfers, bill payments, and mobile wallets, simplifying the way users transact in the digital realm. With features like QR code payments and NFC technology, completing transactions has never been easier or more convenient.
- AI-powered Financial Insights: Leveraging artificial intelligence (AI), FinTech apps analyze user data to offer personalized financial insights and recommendations. From suggesting optimized investment strategies to identifying potential savings opportunities, AI-driven algorithms empower users to make smarter financial decisions.
- Multi-platform Accessibility: Whether it’s iOS or Android, FinTech mobile apps are available across multiple platforms, ensuring accessibility to a wide range of users. Additionally, many apps offer web-based platforms, enabling seamless integration and synchronization across various devices.
- Regulatory Compliance and Data Protection: Compliance with regulatory standards and data protection measures is non-negotiable in the FinTech industry. Mobile apps adhere to stringent regulatory requirements such as GDPR and PCI DSS, safeguarding user data and ensuring privacy and confidentiality at all times.
- Customer Support and Assistance: Timely and responsive customer support services are integral to FinTech mobile apps, providing users with assistance and resolving queries promptly. Whether it’s through live chat support, email correspondence, or comprehensive FAQs, ensuring a seamless user experience is paramount.
- Continuous Innovation and Updates: FinTech companies prioritize innovation and regularly update their mobile apps with new features and enhancements to stay ahead of the curve. Whether it’s adopting emerging technologies like blockchain or implementing user feedback for iterative improvements, FinTech mobile apps strive for excellence.
User Experience Design Catering to Millennial Preferences
In today’s digital landscape, user experience (UX) design has emerged as a pivotal aspect of product success. And when it comes to catering to user preferences, understanding the nuances of different demographics is key. Among these, millennials stand out as a generation with distinct tastes and expectations. To resonate with this tech-savvy and socially conscious cohort, UX designers must tailor their strategies accordingly.
Understanding Millennial Preferences
Millennials, typically defined as those born between 1981 and 1996, have grown up in an era characterized by rapid technological advancements and shifting societal norms. As digital natives, they are accustomed to seamless digital experiences and expect nothing less from the products and services they engage with.
- Mobile-Centric Approach: Millennials are glued to their smartphones, using them for everything from socializing to shopping. Hence, prioritizing mobile responsiveness and intuitive app interfaces is paramount in UX design.
- Personalization: Millennials appreciate personalized experiences that cater to their individual preferences and interests. Leveraging data analytics and AI technologies can help in creating tailored user journeys, offering relevant content and recommendations.
- Social Integration: Social media plays a central role in the lives of millennials. Integrating social sharing features and enabling easy sign-in through platforms like Facebook or Google can enhance user convenience and foster social engagement.
- Minimalistic Design: Simplicity reigns supreme in millennial-centric UX design. Clean layouts, intuitive navigation, and concise content resonate well with this generation that values efficiency and instant gratification.
- Sustainability and Social Responsibility: Millennials are environmentally conscious and socially aware. Incorporating eco-friendly practices, such as reducing carbon footprint or supporting ethical sourcing, can bolster brand loyalty and resonate with their values.
Strategies for Millennial-Centric UX Design
- User-Centric Research: Conduct thorough user research, including surveys, interviews, and usability testing, to gain insights into millennial behaviors, pain points, and preferences.
- Mobile Optimization: Prioritize mobile optimization by adopting a responsive design approach and optimizing loading times for seamless mobile experiences.
- Personalization Engines: Implement AI-driven personalization engines to deliver customized content, product recommendations, and promotional offers based on user behavior and preferences.
- Social Media Integration: Integrate social media sharing buttons, user-generated content feeds, and social login options to enhance social connectivity and foster community engagement.
- Sustainable Design Practices: Embrace sustainable design principles, such as energy efficiency, recyclability, and ethical sourcing, to align with millennial values and contribute to a greener future.
- Accessibility: Ensure accessibility by adhering to WCAG (Web Content Accessibility Guidelines) standards, thereby catering to users of all abilities and enhancing inclusivity.
- Iterative Design Process: Adopt an iterative design process, incorporating user feedback and analytics insights to continuously refine and optimize the user experience.
Security Measures and Regulatory Compliance
In today’s digital age, ensuring the security of sensitive information and maintaining regulatory compliance is paramount for businesses across all sectors. With the ever-evolving landscape of cyber threats and stringent regulations, companies must adopt robust security measures and adhere to regulatory standards to safeguard their assets, protect customer data, and mitigate potential risks.
Understanding Security Measures
Implementing effective security measures involves a multifaceted approach aimed at fortifying the integrity of an organization’s systems, networks, and data. Here are some essential components of a comprehensive security strategy:
- Risk Assessment: Conducting regular risk assessments helps identify potential vulnerabilities and threats to the organization’s infrastructure and data. By understanding these risks, businesses can develop tailored security measures to mitigate them effectively.
- Access Control: Limiting access to sensitive information through user authentication, authorization protocols, and role-based access control (RBAC) ensures that only authorized personnel can access critical data and systems, reducing the risk of unauthorized breaches.
- Encryption: Encrypting data both in transit and at rest adds an extra layer of protection against unauthorized access. Strong encryption algorithms help secure confidential information, such as customer details and financial records, from interception or theft.
- Firewalls and Intrusion Detection Systems (IDS): Deploying firewalls and IDS helps monitor network traffic, detect suspicious activities, and prevent unauthorized access or malicious attacks. These tools act as virtual barriers, filtering out potential threats before they can breach the network perimeter.
- Regular Updates and Patch Management: Keeping software, applications, and operating systems up to date with the latest security patches and updates is crucial for addressing known vulnerabilities and strengthening overall resilience against cyber threats.
Ensuring Regulatory Compliance
In addition to implementing robust security measures, businesses must also comply with various regulatory frameworks and standards relevant to their industry. Non-compliance not only exposes organizations to legal and financial repercussions but also tarnishes their reputation and erodes customer trust. Here are some key regulations and standards that businesses need to adhere to:
- General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR): GDPR mandates strict guidelines for the processing and protection of personal data of individuals within the European Union (EU). Businesses must obtain explicit consent for data collection, ensure data accuracy, and implement measures to safeguard data privacy and security.
- Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard (PCI DSS): PCI DSS applies to organizations that handle credit card payments, requiring them to maintain a secure network, protect cardholder data, and regularly monitor and test their systems for vulnerabilities.
- Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA): HIPAA regulates the handling of protected health information (PHI) in the healthcare industry, ensuring the confidentiality, integrity, and availability of patient data.
- ISO/IEC 27001: This international standard provides a framework for establishing, implementing, maintaining, and continually improving an information security management system (ISMS). Compliance with ISO/IEC 27001 demonstrates a commitment to robust information security practices.
- Sarbanes-Oxley Act (SOX): SOX imposes strict regulations on financial reporting and corporate governance to prevent fraudulent activities and ensure transparency and accountability in financial operations.
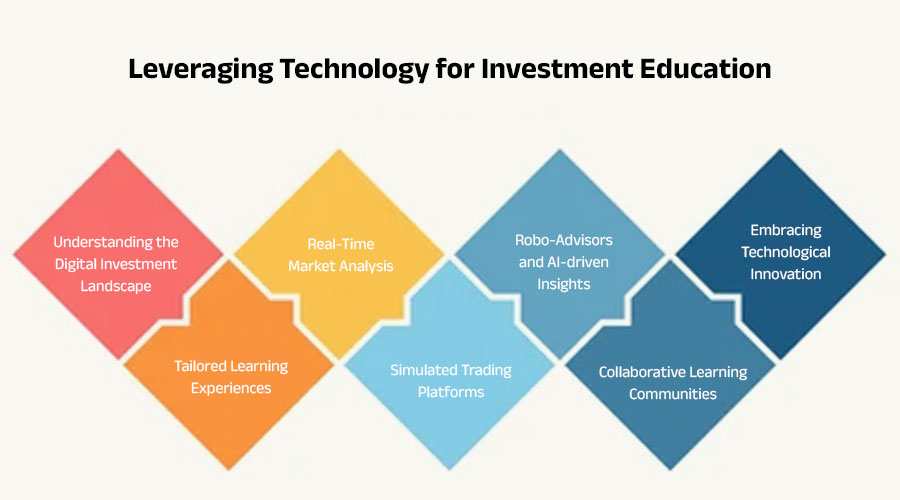
Leveraging Technology for Investment Education
In today’s dynamic financial landscape, the realm of investment holds unprecedented opportunities and complexities. With markets evolving at lightning speed and investment instruments diversifying, staying ahead demands continuous learning. Fortunately, the digital age offers a myriad of tools and resources to empower investors. Leveraging technology for investment education isn’t just a trend; it’s a necessity in maximizing returns and minimizing risks.
Understanding the Digital Investment Landscape: Gone are the days when investment education relied solely on textbooks and seminars. Today, the internet serves as a vast reservoir of knowledge, offering insights from seasoned experts and cutting-edge research. Online platforms provide a gateway to understanding diverse investment vehicles, from stocks and bonds to cryptocurrencies and alternative assets.
Tailored Learning Experiences: Technology enables personalized learning experiences tailored to individual preferences and expertise levels. Interactive tutorials, webinars, and online courses cater to beginners eager to grasp investment fundamentals. Advanced investors can delve into specialized topics like algorithmic trading or sustainable investing through targeted content.
Real-Time Market Analysis: One of the most significant advantages of technology in investment education is access to real-time market data and analysis. From financial news websites to dedicated investment apps, investors can stay informed about market trends, economic indicators, and geopolitical events shaping global markets. This real-time insight empowers investors to make informed decisions and adapt their strategies swiftly.
Simulated Trading Platforms: For those new to investing, the prospect of risking capital can be daunting. Simulated trading platforms offer a risk-free environment to practice trading strategies and experiment with different asset classes. These virtual platforms simulate real market conditions, allowing users to gain hands-on experience without financial exposure. Such platforms bridge the gap between theory and practice, fostering confidence and competence among novice investors.
Robo-Advisors and AI-driven Insights: Robo-advisors, powered by artificial intelligence algorithms, have democratized investment advisory services. These automated platforms analyze investors’ risk profiles, financial goals, and market trends to offer personalized investment recommendations. By leveraging AI-driven insights, investors can optimize portfolio allocation, rebalance assets, and mitigate risks more efficiently than ever before.
Collaborative Learning Communities: Beyond individual learning, technology fosters collaborative learning communities where investors can exchange ideas, share strategies, and learn from each other’s experiences. Social media platforms, online forums, and investment clubs provide avenues for networking and mentorship, enriching the learning journey and cultivating a sense of camaraderie among investors.
Embracing Technological Innovation: As technology continues to evolve, so too does the landscape of investment education. Emerging technologies such as blockchain, machine learning, and augmented reality are poised to revolutionize how investors learn and interact with financial markets. Embracing these innovations equips investors with the agility and foresight to navigate the ever-changing investment landscape effectively.
Top FinTech Mobile App Companies
In the dynamic landscape of finance, technology has emerged as a game-changer, reshaping traditional financial services and paving the way for innovative solutions. At the heart of this transformation are FinTech mobile app companies, leveraging cutting-edge technology to provide seamless, user-friendly financial experiences. Let’s delve into the world of finance and technology to uncover the top players in this realm.
-
-
Next Big Technology:

Focus Area
- Mobile App Development
- App Designing (UI/UX)
- Software Development
- Web Development
- AR & VR Development
- Big Data & BI
- Cloud Computing Services
- DevOps
- E-commerce Development
Industries Focus
- Art, Entertainment & Music
- Business Services
- Consumer Products
- Designing
- Education
- Financial & Payments
- Gaming
- Government
- Healthcare & Medical
- Hospitality
- Information Technology
- Legal & Compliance
- Manufacturing
- Media
-
- PayPal Holdings, Inc.: PayPal, a household name in digital payments, continues to innovate with its mobile app offerings. With features like peer-to-peer payments, PayPal.me, and the ability to link multiple bank accounts and cards, the PayPal app remains a convenient choice for individuals and businesses alike. Moreover, the integration of Venmo has further expanded PayPal’s reach, especially among younger demographics.
- Robinhood Markets, Inc.: Robinhood disrupted the traditional brokerage model by introducing commission-free trading through its mobile app. Catering to both novice and experienced investors, Robinhood offers a user-friendly interface, real-time market data, and the ability to trade stocks, options, cryptocurrencies, and more. The app’s intuitive design has attracted millions of users, making investing accessible to everyone.
- Revolut Ltd: Revolut has made waves in the banking industry with its innovative approach to personal finance. The Revolut app offers features like fee-free currency exchange, budgeting tools, and cryptocurrency trading, catering to a global user base. With its sleek interface and focus on affordability and convenience, Revolut has become a preferred choice for international travelers and digital nomads.
- Stripe, Inc.: Stripe has become synonymous with online payments, powering transactions for millions of businesses worldwide. While not a consumer-facing app per se, Stripe’s developer-friendly platform and robust APIs enable businesses to accept payments seamlessly across web and mobile channels. From startups to enterprise-level organizations, Stripe has revolutionized online commerce with its suite of payment solutions.
- Chime Financial, Inc.: Chime has disrupted traditional banking with its mobile-first approach and commitment to fee-free banking. The Chime app offers features like early direct deposit, automatic savings, and no-fee overdraft protection, resonating with a younger, tech-savvy demographic. With its emphasis on financial wellness and transparency, Chime has gained traction as a viable alternative to traditional banks.
- N26 GmbH: N26 is reimagining banking for the digital age with its sleek mobile app and minimalist design. As a fully licensed bank, N26 offers essential banking services like checking accounts, savings accounts, and debit cards, all accessible through its intuitive app. With features like real-time notifications and budgeting tools, N26 aims to empower users to take control of their finances effortlessly.
- SoFi Technologies, Inc.: SoFi combines finance and technology to offer a comprehensive suite of financial products through its mobile app. From student loan refinancing to investment management to mortgage loans, SoFi provides a one-stop solution for all things finance. The app’s emphasis on community and financial education sets it apart, fostering a sense of empowerment among users.
FAQs On FinTech Mobile App
In today’s fast-paced digital world, FinTech (Financial Technology) mobile apps have become an indispensable tool for managing finances conveniently and securely. As the popularity of these apps continues to soar, it’s natural for users to have questions regarding their functionality, security, and benefits. To shed light on this innovative technology, let’s delve into some frequently asked questions (FAQs) surrounding FinTech mobile apps.
1. What exactly is a FinTech mobile app? A FinTech mobile app is a software application designed to provide financial services, ranging from banking and investing to budgeting and payments, through smartphones and tablets. These apps leverage cutting-edge technology to streamline financial processes, enhance user experience, and promote financial inclusion.
2. Are FinTech mobile apps safe to use? Yes, reputable FinTech mobile apps prioritize security by implementing robust encryption protocols, multi-factor authentication, and advanced fraud detection mechanisms. Additionally, regulatory bodies often oversee these apps to ensure compliance with industry standards and protect users’ sensitive information.
3. How do FinTech mobile apps differ from traditional banking services? Unlike traditional banking services, FinTech mobile apps offer greater convenience, accessibility, and customization. Users can perform various financial transactions anytime, anywhere, without visiting a physical bank branch. Moreover, FinTech apps often provide personalized recommendations, insights, and tools to help users make informed financial decisions.
4. What features can I expect from a FinTech mobile app? FinTech mobile apps typically offer a wide array of features tailored to meet users’ diverse financial needs. These may include account management, budget tracking, bill payments, money transfers, investment management, loan applications, and real-time financial insights. Some apps even incorporate innovative features like round-up savings and peer-to-peer payments.
5. How can FinTech mobile apps benefit me? FinTech mobile apps offer numerous benefits, such as convenience, efficiency, cost-effectiveness, and financial empowerment. By centralizing financial activities in one app, users can save time, streamline processes, and gain better control over their finances. Moreover, these apps often provide access to exclusive deals, discounts, and rewards, further enhancing their value proposition.
6. Are FinTech mobile apps suitable for everyone? While FinTech mobile apps cater to a wide audience, their suitability may vary depending on individual preferences, financial goals, and comfort levels with technology. While some users embrace the convenience and innovation offered by these apps, others may prefer the familiarity and human interaction provided by traditional banking services.
7. How can I choose the right FinTech mobile app for my needs? When selecting a FinTech mobile app, consider factors such as security features, ease of use, range of services offered, customer support, and compatibility with your devices. Additionally, read reviews, compare different apps, and assess their reputation, user ratings, and feedback from existing users to make an informed decision.
8. What should I do if I encounter issues or have concerns about a FinTech mobile app? If you encounter issues or have concerns about a FinTech mobile app, contact the app’s customer support team for assistance. Most apps provide multiple channels for support, such as in-app chat, email, or phone support. Additionally, you can reach out to relevant regulatory authorities or consumer protection agencies if you believe your rights or privacy have been violated.
Thanks for reading our post “FinTech Mobile App for Indonesian Investment Giant to Cater to Millennial Retail Investors”. Please connect with us to learn more about Best FinTech Mobile App.