Table of Contents
Understanding Augmented Reality (AR)
Augmented Reality (AR) is revolutionizing the way we interact with the world around us. It merges the digital realm with the physical environment, enhancing our perception and providing immersive experiences. In this article, we will explore the fascinating world of AR, understand its fundamentals, applications, and potential impact on various industries.
What is Augmented Reality? Augmented Reality is a technology that overlays digital information, such as images, videos, or 3D models, onto the real-world environment, in real-time. Unlike Virtual Reality (VR), which creates a completely immersive virtual environment, AR enhances the existing environment by adding virtual elements to it. This can be achieved through specialized AR glasses, smartphone or tablet screens, or even through dedicated AR headsets.
Understanding How AR Works: AR technology relies on a combination of hardware and software components to deliver seamless experiences. The hardware typically includes sensors, cameras, displays, and processing units, which capture the real-world environment and render virtual elements. Meanwhile, sophisticated algorithms and software applications analyze the input data and superimpose digital content onto the user’s view.
Applications of Augmented Reality: The versatility of AR technology has led to its adoption across various industries, revolutionizing processes and enhancing user experiences. Some notable applications of AR include:
- Education: AR can transform traditional learning experiences by making educational content more interactive and engaging. Students can visualize complex concepts in 3D, interact with virtual models, and participate in immersive simulations.
- Gaming and Entertainment: AR has redefined gaming experiences, allowing users to engage in interactive games that blend seamlessly with their surroundings. Popular examples include Pokémon GO, which overlays virtual Pokémon characters onto real-world locations, creating a captivating gaming experience.
- Retail and Marketing: AR enables retailers to offer virtual try-on experiences, allowing customers to visualize products before making a purchase. From trying on clothes and accessories to previewing furniture placement in their homes, AR enhances the shopping experience and drives sales.
- Healthcare: In the healthcare sector, AR is used for training medical professionals, surgical planning, and patient education. Surgeons can visualize patient anatomy in 3D during procedures, improving precision and outcomes.
- Navigation and Wayfinding: AR-based navigation apps provide real-time guidance by overlaying directions onto the user’s view of the environment. This simplifies navigation in unfamiliar locations and enhances the overall travel experience.
Future Implications of AR: As technology continues to evolve, the potential applications of AR are boundless. From advanced industrial simulations and remote collaboration to immersive storytelling experiences and interactive art installations, AR will continue to shape the way we perceive and interact with the world.
Historical Evolution of AR Technology
In the realm of technological marvels, few innovations have captured the imagination quite like Augmented Reality (AR). From its humble beginnings to its transformative impact on various industries today, the journey of AR technology is a captivating narrative of innovation, ingenuity, and relentless pursuit of pushing the boundaries of human experience.
The Genesis: Seeds of Imagination The roots of AR can be traced back to the fertile grounds of science fiction and speculative imagination. Visionaries like Ivan Sutherland laid the conceptual groundwork with inventions such as the “Sword of Damocles” in the 1960s, which offered a glimpse into a world where digital information seamlessly blended with the physical environment.
Emergence of Prototypes: From Concept to Reality It wasn’t until the late 20th century that AR began to materialize in tangible forms. Early prototypes and research projects, such as the “Virtual Fixtures” developed by Louis Rosenberg at the U.S. Air Force’s Armstrong Laboratory in the early 1990s, showcased the potential of overlaying digital data onto the real world to enhance human capabilities in various fields, from military training to industrial maintenance.
The Advent of Consumer Applications: Bridging the Gap The dawn of the new millennium saw AR technology transitioning from the confines of research labs to the palms of consumers’ hands. With the proliferation of smartphones and the launch of pioneering applications like Layar and Wikitude, ordinary individuals were granted access to augmented experiences that merged the virtual and physical realms in unprecedented ways.
Breakthroughs and Milestones: Paving the Path Forward The evolution of AR technology has been punctuated by a series of breakthroughs and milestones that have propelled its growth and adoption across diverse domains. From the launch of Google Glass in 2013, heralding a new era of wearable AR devices, to the global phenomenon of Pokémon GO in 2016, which brought AR gaming into the mainstream consciousness, each achievement has pushed the boundaries of what was once deemed possible.
Integration with Emerging Technologies: Synergy in Innovation In recent years, AR has become increasingly intertwined with other cutting-edge technologies, such as Artificial Intelligence (AI), Internet of Things (IoT), and 5G connectivity, amplifying its capabilities and expanding its potential applications. From immersive shopping experiences and interactive museum exhibits to revolutionary advancements in healthcare and education, the synergistic fusion of AR with these emerging technologies is reshaping the way we perceive and interact with the world around us.
The Future Horizon: Boundless Possibilities As we stand on the cusp of a new era defined by rapid technological advancement, the future of AR appears limitless. With ongoing research and development efforts focused on enhancing user experience, improving hardware capabilities, and unlocking novel use cases, AR is poised to become an integral part of our everyday lives, seamlessly integrated into the fabric of society.
Core Components of Augmented Reality Systems
In the realm of technology, few innovations have captivated the imagination quite like augmented reality (AR). From enhancing gaming experiences to revolutionizing industrial processes, AR has permeated various sectors, offering a tantalizing glimpse into a digitally augmented future. But what exactly constitutes the backbone of these immersive AR systems? Let’s delve into the core components that power this transformative technology.
- Hardware Infrastructure: At the heart of any AR system lies its hardware infrastructure. This encompasses devices such as headsets, glasses, or even smartphones equipped with AR capabilities. These devices typically integrate a range of components, including high-resolution displays, sensors (such as accelerometers, gyroscopes, and depth sensors), cameras, and processors. These elements work in tandem to perceive the physical environment and overlay digital content seamlessly.
- Sensors and Tracking Mechanisms: Central to the functioning of AR systems are sensors and tracking mechanisms that enable spatial awareness and precise positioning of virtual objects within the physical environment. These sensors collect real-time data, such as motion, orientation, and depth, allowing the system to accurately map and anchor digital content onto the user’s surroundings. Advanced techniques like simultaneous localization and mapping (SLAM) play a pivotal role in this process, facilitating dynamic tracking and interaction.
- Software Frameworks and Development Tools: AR experiences are brought to life through sophisticated software frameworks and development tools tailored for creating, deploying, and managing augmented reality content. These frameworks provide developers with access to APIs, libraries, and SDKs (Software Development Kits) that streamline the development process and empower them to build immersive AR applications across various platforms. Examples include ARKit for iOS and ARCore for Android, both of which offer robust toolsets for creating compelling AR experiences.
- Content Creation and Management Systems: Crafting engaging AR content requires specialized tools and platforms for content creation and management. These systems enable developers to design 3D models, animations, textures, and interactive elements that seamlessly integrate with the physical world. Additionally, content management systems facilitate the deployment and maintenance of AR experiences, allowing for real-time updates and analytics tracking to optimize user engagement.
- User Interfaces and Interaction Paradigms: The effectiveness of an AR system hinges on intuitive user interfaces and interaction paradigms that bridge the gap between the digital and physical realms. Gesture recognition, voice commands, spatial gestures, and haptic feedback mechanisms enrich user experiences, fostering natural and immersive interactions with virtual content. Designing user interfaces that prioritize simplicity, accessibility, and responsiveness is paramount to ensuring widespread adoption and usability.
- Integration with Backend Services: Seamless integration with backend services is essential for augmenting AR experiences with dynamic content, personalized recommendations, and real-time data synchronization. Cloud-based services handle tasks such as content delivery, data processing, user authentication, and collaboration features, enabling AR applications to deliver rich, context-aware experiences that evolve in real-time based on user inputs and environmental cues.
- Security and Privacy Protocols: As AR technologies become increasingly ubiquitous, safeguarding user data and privacy emerges as a critical consideration. Robust security protocols, encryption mechanisms, and privacy controls mitigate risks associated with data breaches, unauthorized access, and malicious exploits. Implementing stringent security measures ensures user trust and compliance with regulatory frameworks, fostering a safe and secure AR ecosystem for all stakeholders.
Applications Across Industries
In the dynamic landscape of modern technology, the realm of applications transcends boundaries, permeating various industries with its transformative capabilities. From healthcare to finance, education to manufacturing, applications have become indispensable tools, revolutionizing operations and enhancing efficiency across the board.
Healthcare Sector: In the healthcare sector, applications are revolutionizing patient care and administrative processes alike. Patient management apps streamline appointments, prescriptions, and medical records, facilitating seamless communication between healthcare providers and patients. Moreover, telemedicine applications are bridging geographical gaps, enabling remote consultations and diagnosis, especially crucial in underserved areas. Wearable health monitoring apps track vital signs, providing real-time data for proactive healthcare management.
Finance Industry: The finance industry has embraced applications to deliver convenient and secure financial services. Mobile banking apps empower users with instant access to their accounts, facilitating transactions, bill payments, and investment management on-the-go. Moreover, fintech apps employ cutting-edge technologies like AI and blockchain to offer personalized financial advice, automate processes, and ensure robust security measures in transactions.
Education Sector: In the education sector, applications are reshaping the learning experience, making education more accessible and engaging. Learning management systems (LMS) facilitate online courses, providing interactive content, assessments, and progress tracking tools. Educational apps cater to diverse learning styles, offering everything from language learning to skill development courses. Virtual reality (VR) applications immerse students in immersive learning environments, enhancing understanding and retention of complex concepts.
Manufacturing and Logistics: In manufacturing and logistics, applications optimize processes and boost operational efficiency. Enterprise resource planning (ERP) systems integrate various facets of manufacturing operations, from supply chain management to production scheduling, ensuring seamless coordination and resource allocation. Warehouse management apps enhance inventory tracking and order fulfillment, minimizing errors and maximizing productivity. Additionally, IoT-powered applications monitor equipment performance in real-time, enabling predictive maintenance and minimizing downtime.
Retail Industry: In the retail industry, applications are reshaping the shopping experience, blurring the lines between online and offline retail channels. E-commerce apps offer personalized shopping experiences, recommending products based on past purchases and preferences. Mobile payment apps facilitate swift and secure transactions, eliminating the need for physical cash or cards. Augmented reality (AR) applications allow customers to visualize products in their real-world environment before making a purchase, enhancing decision-making and reducing return rates.
Advantages of Augmented Reality Adoption
In today’s fast-paced digital landscape, technology continues to redefine how we interact with the world around us. One such groundbreaking innovation that has captured the imagination of both businesses and consumers alike is augmented reality (AR). As businesses increasingly recognize the potential of AR, its adoption is on the rise, offering a plethora of advantages across various sectors.
Augmented reality seamlessly integrates digital information into the real world, providing an enhanced and interactive experience. From retail and healthcare to education and entertainment, the benefits of embracing AR are manifold.
Enhanced Customer Engagement: One of the most significant advantages of AR adoption is its ability to revolutionize customer engagement. In the retail sector, for instance, AR enables customers to visualize products in their real-world environment before making a purchase. By allowing consumers to virtually try on clothing, visualize furniture in their homes, or preview products before buying, businesses can significantly enhance the shopping experience, leading to increased customer satisfaction and loyalty.
Improved Learning and Training: In the realm of education and training, AR has emerged as a powerful tool for immersive learning experiences. By overlaying digital content onto physical objects, AR technology can transform traditional learning materials into interactive and engaging resources. Whether it’s simulating complex scientific concepts, providing hands-on training in medical procedures, or enhancing museum exhibits with interactive elements, AR has the potential to revolutionize the way we learn and teach.
Streamlined Operations: Businesses across industries are leveraging AR to streamline their operations and improve efficiency. In manufacturing, for example, AR-enabled smart glasses can provide workers with real-time instructions, diagrams, and data overlays, reducing errors and speeding up the production process. Similarly, in maintenance and repair tasks, AR applications can offer technicians instant access to manuals, schematics, and troubleshooting guides, facilitating quicker and more accurate repairs.
Innovative Marketing Opportunities: AR opens up new and innovative marketing avenues for businesses to engage with their target audience. Brands can create interactive AR experiences, such as gamified apps or immersive storytelling campaigns, to captivate consumers and drive brand awareness. By leveraging AR technology, marketers can create memorable and shareable experiences that resonate with their audience, ultimately leading to increased brand visibility and engagement.
Enhanced Remote Collaboration: In an increasingly interconnected world, AR facilitates seamless remote collaboration and communication. Whether it’s conducting virtual meetings, collaborating on design projects, or providing remote assistance, AR technology bridges the gap between geographically dispersed teams. By enabling real-time sharing of information and visualizations, AR enhances collaboration, fosters creativity, and improves productivity.
Challenges and Limitations in AR Development
Augmented Reality (AR) technology has swiftly transitioned from the realm of science fiction to practical applications, transforming how we interact with the digital world. From enhancing gaming experiences to revolutionizing education and industrial training, AR holds immense potential. However, like any cutting-edge technology, AR development comes with its set of challenges and limitations that developers must navigate to unlock its full capabilities.
- Hardware Limitations: One of the primary challenges in AR development is the dependence on hardware. While smartphones and tablets have become the primary AR platforms, their capabilities are still limited compared to dedicated AR devices. Factors such as processing power, camera quality, and sensor precision can constrain the immersive experience and functionality of AR applications.
- User Interface and Experience: Creating intuitive user interfaces (UI) and seamless user experiences (UX) in AR applications presents a unique set of challenges. Designing interfaces that overlay digital content onto the physical world while maintaining usability and avoiding information overload requires careful consideration. Balancing visual clarity, interaction responsiveness, and real-world context is essential to ensure user engagement and satisfaction.
- Content Creation and Integration: Developing compelling AR content demands a fusion of creative vision and technical expertise. From 3D modeling and animation to spatial mapping and object recognition, content creation for AR environments involves diverse skill sets. Moreover, integrating digital assets seamlessly into the physical environment without disrupting immersion poses a significant technical hurdle for developers.
- Performance Optimization: Optimizing performance is crucial for delivering smooth and responsive AR experiences. Real-time rendering of 3D graphics, accurate tracking of physical objects, and efficient use of device resources are essential for maintaining immersion and preventing motion sickness. Balancing visual fidelity with performance across a wide range of hardware configurations requires meticulous optimization strategies.
- Privacy and Security Concerns: AR applications often rely on collecting and processing user data, raising concerns about privacy and security. Location tracking, camera access, and personal information are integral to many AR experiences but require robust privacy safeguards to protect user confidentiality. Developers must adhere to strict data protection regulations and implement secure authentication mechanisms to mitigate potential risks.
- Accessibility and Inclusivity: Ensuring accessibility and inclusivity in AR development is imperative to reach diverse audiences. Factors such as device compatibility, language localization, and accommodating users with disabilities pose significant challenges. Designing AR applications with features such as text-to-speech, gesture recognition, and customizable interfaces fosters inclusivity and enhances user engagement.
Augmented Reality in Education and Training
In recent years, the realm of education and training has witnessed a groundbreaking transformation with the integration of augmented reality (AR). This innovative technology has ushered in a new era of immersive learning experiences, offering a plethora of benefits that enhance comprehension, engagement, and retention among learners of all ages.
Augmented reality, often abbreviated as AR, blends the virtual world with the physical environment, overlaying digital content onto real-world settings through devices such as smartphones, tablets, or specialized AR glasses. Unlike virtual reality (VR), which creates entirely artificial environments, AR enriches the existing surroundings with interactive elements, thereby providing a seamless integration of digital information into the user’s real-world experience.
One of the most compelling applications of AR lies in its ability to transform traditional educational practices into dynamic and interactive sessions. By superimposing three-dimensional models, animations, and simulations onto textbooks, worksheets, or physical objects, AR technology enables students to explore complex concepts in a highly engaging manner. For instance, biology students can dissect virtual organisms in real-time, geography enthusiasts can embark on virtual field trips to distant locations, and history buffs can witness historical events unfold before their eyes.
Moreover, AR fosters personalized learning experiences tailored to individual preferences and learning styles. With adaptive AR applications, educators can customize content based on students’ proficiency levels, interests, and learning pace, ensuring that each learner receives targeted support and guidance. This personalized approach not only enhances comprehension but also cultivates a deeper appreciation for the subject matter, empowering students to take ownership of their learning journey.
Furthermore, AR serves as a powerful tool for skills development and training across various industries. From healthcare and engineering to manufacturing and aviation, AR simulations enable trainees to practice procedures, troubleshoot problems, and simulate real-world scenarios in a risk-free environment. This hands-on training not only accelerates skill acquisition but also minimizes the potential for errors, thereby enhancing safety and efficiency in high-stakes professions.
In addition to its educational benefits, AR cultivates collaboration and teamwork among learners. Through shared AR experiences, students can collaborate on projects, solve problems collaboratively, and engage in interactive group activities regardless of their physical location. This fosters a sense of community and connectivity, bridging geographical barriers and promoting cross-cultural exchange in the globalized world of education.
As AR technology continues to evolve and become more accessible, its potential to revolutionize education and training is boundless. However, it is essential to address challenges such as infrastructure limitations, cost barriers, and privacy concerns to ensure equitable access and ethical usage of AR in educational settings. By harnessing the transformative power of augmented reality responsibly, educators can unlock new possibilities for immersive, engaging, and effective learning experiences that empower students to thrive in the digital age and beyond.
Augmented Reality in Healthcare and Medicine
In recent years, the integration of augmented reality (AR) technology into the healthcare sector has marked a revolutionary advancement, promising to redefine patient care, medical training, and surgical procedures. Augmented reality, a cutting-edge technology that overlays digital information onto the real world, is rapidly gaining momentum in healthcare and medicine due to its potential to enhance clinical outcomes, streamline workflows, and improve patient satisfaction.
One of the most significant applications of augmented reality in healthcare is in medical training and education. Traditional methods of teaching anatomy and surgical techniques often rely on textbooks, cadavers, and two-dimensional images, which may not adequately prepare medical students and healthcare professionals for real-life scenarios. Augmented reality bridges this gap by providing immersive and interactive learning experiences. Medical students can use AR-enabled devices to visualize complex anatomical structures in 3D, dissect virtual organs, and practice surgical procedures in a simulated environment. This hands-on approach not only enhances learning retention but also fosters better decision-making skills and procedural competency among trainees.
Moreover, augmented reality has emerged as a valuable tool in preoperative planning and intraoperative guidance, particularly in complex surgical procedures. Surgeons can use AR headsets or smart glasses to overlay patient-specific medical imaging data, such as CT scans and MRI images, onto the surgical field in real-time. This enables surgeons to visualize internal structures, navigate critical anatomical landmarks, and precisely plan incisions and implant placements before making a single cut. By providing surgeons with enhanced spatial awareness and real-time feedback, AR technology can help minimize surgical errors, reduce operative times, and improve patient outcomes.
In addition to training and surgical applications, augmented reality is also transforming patient care and engagement. Healthcare providers can leverage AR to enhance patient education, allowing individuals to better understand their medical conditions, treatment options, and postoperative care instructions through interactive visualizations. For example, AR-enabled mobile applications can project animated models of the human body onto a smartphone or tablet screen, enabling patients to explore their anatomy, view disease processes, and comprehend the rationale behind medical interventions. This fosters greater patient empowerment, adherence to treatment plans, and shared decision-making between patients and providers.
Furthermore, augmented reality holds promise in telemedicine and remote patient monitoring, particularly in rural or underserved areas where access to specialized healthcare services may be limited. Patients can use AR-equipped devices to receive virtual consultations, wherein healthcare providers can remotely assess medical conditions, conduct examinations, and provide real-time guidance using augmented visuals. This not only improves access to care but also reduces the need for travel and enhances the overall patient experience.
Despite its vast potential, the widespread adoption of augmented reality in healthcare is not without challenges. Concerns regarding data privacy, regulatory compliance, interoperability, and cost-effectiveness must be addressed to ensure the seamless integration of AR technology into existing healthcare systems. Moreover, ongoing research and development efforts are needed to refine AR applications, optimize hardware capabilities, and validate clinical outcomes through rigorous studies.
Augmented Reality Gaming and Entertainment
In an age where technology continually pushes the boundaries of our imagination, augmented reality (AR) has emerged as a groundbreaking force, revolutionizing the way we perceive and interact with the world around us. Augmented reality gaming, in particular, has captured the hearts and minds of enthusiasts worldwide, offering a tantalizing blend of virtual and real-world experiences. From immersive adventures to interactive storytelling, AR gaming has ushered in a new era of entertainment that promises to redefine the way we play.
Augmented reality gaming transcends the confines of traditional gaming platforms, transporting players into rich, dynamic environments where fantasy and reality seamlessly intertwine. By superimposing digital elements onto the physical world through the lens of a smartphone or AR headset, players are granted unprecedented agency, transforming ordinary spaces into vibrant playgrounds ripe for exploration. Whether battling fierce creatures in the urban jungle or uncovering hidden treasures in the comfort of one’s own home, AR gaming invites players to embark on exhilarating quests limited only by their imagination.
One of the most compelling aspects of augmented reality gaming is its ability to foster social interaction and collaboration on a scale never before seen. By leveraging the power of geolocation technology, AR games encourage players to venture outside and connect with others in their vicinity, blurring the lines between virtual and real-world communities. From impromptu meetups to large-scale events, AR gaming has become a catalyst for forging lasting friendships and shared experiences, transcending the solitary nature of traditional gaming and bringing people together in ways previously unimaginable.
Moreover, augmented reality gaming has also proven to be a powerful tool for education and learning, offering immersive experiences that engage and inspire learners of all ages. By incorporating educational content into gameplay mechanics, AR games have the potential to transform mundane subjects into captivating adventures, fostering curiosity and a thirst for knowledge in players young and old. Whether exploring the wonders of space or delving into the mysteries of history, AR gaming has the power to make learning not only informative but also incredibly fun and rewarding.
As the technology behind augmented reality continues to evolve and mature, the possibilities for gaming and entertainment are virtually limitless. From advanced AR glasses to wearable haptic feedback devices, developers are constantly pushing the boundaries of what’s possible, creating experiences that blur the line between fiction and reality in ways never before imagined. With each new innovation, AR gaming inches closer to realizing its full potential, promising a future where the boundaries between the virtual and physical worlds dissolve entirely, giving rise to a new era of entertainment unlike anything we’ve seen before.
Ethical Considerations in Augmented Reality
In the realm of technological innovation, few advancements have captured the imagination and intrigue of society quite like augmented reality (AR). Blurring the boundaries between the digital and physical worlds, AR has ushered in a new era of immersive experiences and transformative possibilities. However, with these advancements come a host of ethical considerations that demand careful examination and deliberation.
Understanding Ethical Considerations in Augmented Reality: Augmented reality holds immense promise across various domains, from entertainment and gaming to education and healthcare. Yet, as with any powerful tool, its implementation raises complex ethical dilemmas that necessitate a nuanced approach. One of the foremost concerns revolves around privacy and data security. AR applications often require access to sensitive personal information, raising questions about consent, surveillance, and the potential for misuse.
Moreover, the line between virtual and physical realities can become increasingly blurred in augmented environments, leading to potential psychological impacts and ethical quandaries. For instance, how do we ensure the well-being of users who may become disoriented or detached from reality while immersed in AR experiences? Addressing these concerns requires interdisciplinary collaboration and a commitment to prioritizing user safety and mental health.
Another ethical consideration is the potential for augmented reality to perpetuate bias and inequality. As with any technology, AR systems are susceptible to reflecting the biases of their creators, leading to issues of discrimination and exclusion. It is imperative for developers to actively mitigate these biases and strive for inclusivity in the design and implementation of AR applications.
Furthermore, the ethical implications of augmented reality extend to its impact on social interactions and cultural norms. AR has the power to reshape how we perceive and engage with the world around us, influencing everything from communication patterns to societal values. As such, it is essential to foster critical dialogue and ethical reflection to navigate these changes thoughtfully.
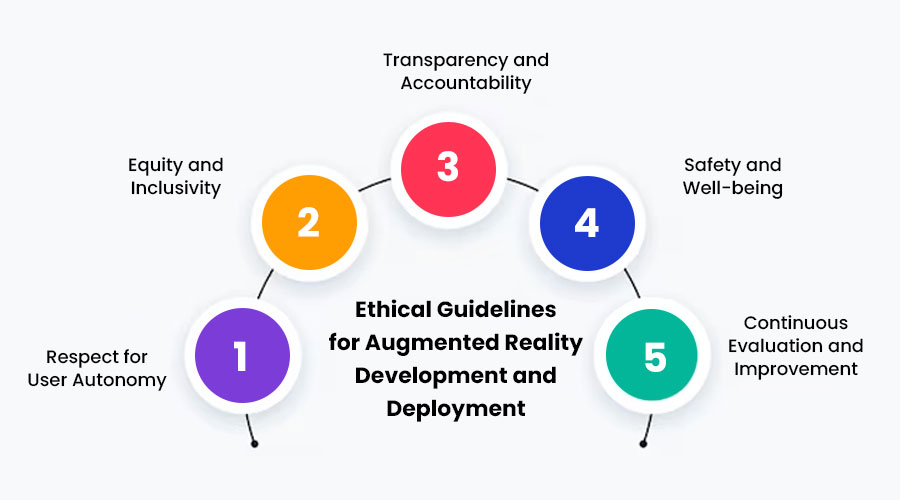
Ethical Guidelines for Augmented Reality Development and Deployment: To address these ethical considerations effectively, stakeholders in the AR ecosystem must adhere to a set of guiding principles:
- Respect for User Autonomy: Ensure that users have informed consent and control over their personal data and AR experiences.
- Equity and Inclusivity: Strive to create AR applications that are accessible to diverse populations and do not perpetuate biases or stereotypes.
- Transparency and Accountability: Provide clear information about how AR technologies function and how data is collected, used, and protected.
- : Prioritize the physical and mental health of users by designing AR experiences that minimize risks and promote responsible usage.
- Continuous Evaluation and Improvement: Regularly assess the ethical implications of AR technologies and iterate on designs to address emerging concerns and challenges.
Top Augmented Reality Scope Companies
In the ever-evolving landscape of technology, augmented reality (AR) has emerged as a transformative force, blurring the lines between the physical and digital worlds. From enhancing gaming experiences to revolutionizing industrial training, AR has found its way into various sectors, promising endless possibilities. Among the pioneers driving this innovation forward, several companies stand out for their significant contributions and promising scope in the AR realm.
-
-
-
Next Big Technology:

Focus Area
- Mobile App Development
- App Designing (UI/UX)
- Software Development
- Web Development
- AR & VR Development
- Big Data & BI
- Cloud Computing Services
- DevOps
- E-commerce Development
Industries Focus
- Art, Entertainment & Music
- Business Services
- Consumer Products
- Designing
- Education
- Financial & Payments
- Gaming
- Government
- Healthcare & Medical
- Hospitality
- Information Technology
- Legal & Compliance
- Manufacturing
- Media
-
-
- Google: Google’s ARCore platform has become a cornerstone for developers looking to create AR experiences across Android devices. Through initiatives like Google Lens and Google Maps’ AR navigation feature, the tech giant has demonstrated its dedication to leveraging AR for practical applications in everyday life.
- Microsoft Corporation: Microsoft’s HoloLens has been a game-changer in the realm of mixed reality, blending holographic content with the real world. The company’s focus on enterprise solutions has seen applications in fields such as manufacturing, healthcare, and education. With the recent launch of HoloLens 2, Microsoft continues to lead the way in AR innovation.
- Niantic, Inc.: Known for creating the groundbreaking AR game Pokémon GO, Niantic has been at the forefront of location-based AR experiences. The company’s unique approach to combining augmented reality with real-world exploration has captivated millions of users worldwide. Niantic’s ongoing efforts to expand its AR platform showcase its potential for future growth.
- Snap Inc.: Snapchat, owned by Snap Inc., has been instrumental in popularizing AR among younger audiences through its innovative AR lenses and filters. The company’s focus on augmented reality as a social platform has led to creative collaborations with brands and artists, driving engagement and user interaction.
- Magic Leap, Inc.: Magic Leap’s spatial computing technology aims to seamlessly integrate digital content into the physical world. With its Magic Leap One headset, the company offers developers a platform to create immersive AR experiences across various industries, from entertainment to enterprise solutions.
- Facebook Technologies, LLC (Oculus): Facebook’s Oculus division has been exploring the potential of AR through projects like the Oculus Quest, which combines virtual reality with passthrough AR capabilities. With Facebook’s vast user base and resources, the company is poised to make significant advancements in AR technology in the coming years.
- Unity Technologies: Unity’s game engine has become a go-to platform for developers looking to create AR experiences across multiple devices and platforms. With its robust development tools and supportive community, Unity plays a crucial role in democratizing AR development and fueling innovation in the industry.
- Vuforia (PTC): As a leading provider of AR development tools, Vuforia enables developers to create marker-based and markerless AR experiences with ease. Acquired by PTC, Vuforia continues to evolve its platform to meet the growing demands of businesses seeking to integrate AR into their products and services.
- DAQRI: Specializing in AR solutions for the industrial sector, DAQRI offers smart glasses and augmented reality software designed to enhance productivity and safety in various industries, including manufacturing, construction, and automotive.
FAQs On Augmented Reality Scope
In a world where technology is constantly evolving, augmented reality (AR) has emerged as a groundbreaking innovation with vast potential. As businesses and consumers alike explore the possibilities of AR, it’s natural for questions to arise. To shed light on this exciting field, let’s delve into some frequently asked questions about the scope of augmented reality.
What is Augmented Reality (AR) and How Does it Work? Augmented reality (AR) is a technology that superimposes computer-generated images, sounds, or other sensory enhancements onto the real-world environment. Unlike virtual reality (VR), which creates a completely immersive experience, AR enhances the existing environment by overlaying digital elements onto it. This is typically achieved through specialized AR devices like smartphones, tablets, or AR glasses, which use cameras, sensors, and algorithms to blend virtual content with the physical world in real-time.
What Are the Current Applications of Augmented Reality? Augmented reality finds applications across various industries, revolutionizing processes and enhancing user experiences. In retail, AR enables customers to visualize products in their own space before making a purchase, leading to increased engagement and sales. In healthcare, AR facilitates medical training, surgical planning, and patient education by providing interactive 3D visualizations. Additionally, AR is transforming education, gaming, marketing, tourism, and manufacturing, among other sectors, offering innovative solutions to diverse challenges.
What Is the Scope of Augmented Reality in the Future? The future of augmented reality is exceptionally promising, with projections indicating exponential growth and widespread adoption. As technology continues to advance, AR devices will become more compact, affordable, and seamlessly integrated into everyday life. This will open up new opportunities for businesses to create immersive brand experiences, deliver personalized services, and streamline operations. Moreover, as AR evolves, we can expect to see breakthroughs in areas such as remote collaboration, navigation, healthcare diagnostics, and beyond, ultimately reshaping how we interact with the world around us.
How Can Businesses Leverage Augmented Reality? Businesses can leverage augmented reality in myriad ways to gain a competitive edge and drive innovation. By incorporating AR into their marketing strategies, companies can engage customers with interactive product demonstrations, immersive storytelling, and virtual try-on experiences. AR also enables businesses to enhance employee training, improve productivity, and optimize workflows through hands-on simulations and real-time guidance. Furthermore, by embracing AR as a tool for design visualization and prototyping, organizations can accelerate the product development cycle and bring concepts to market faster.
What Challenges Does Augmented Reality Face? Despite its immense potential, augmented reality faces several challenges that must be addressed for widespread adoption. These include technical limitations such as hardware constraints, latency issues, and the need for robust tracking and rendering capabilities. Moreover, concerns related to privacy, security, and ethical considerations surrounding AR content and data usage must be carefully navigated. Additionally, there is a need for greater standardization, interoperability, and collaboration within the AR ecosystem to ensure seamless integration across platforms and devices.
Thanks for reading our post “Augmented Reality Scope – All You Need to Know”. Please connect with us to learn more about Best Augmented Reality Scope.