Table of Contents
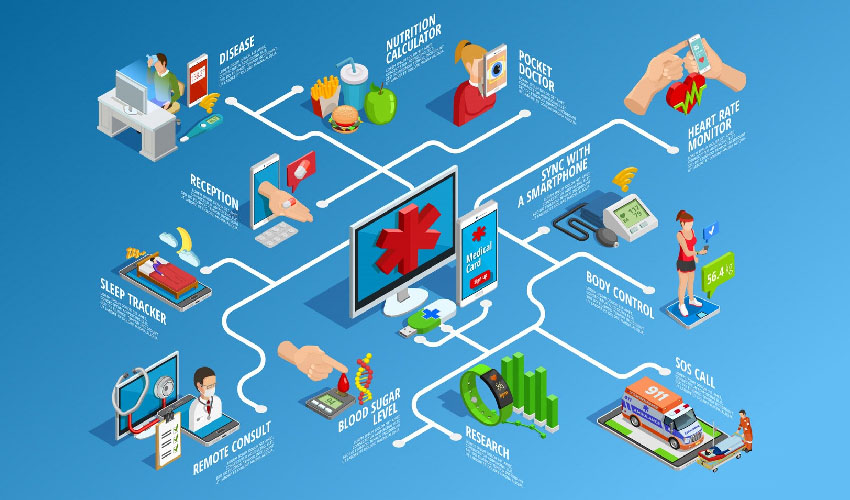
15 Types of Healthcare Software Services
In today’s digital age, healthcare software services play a pivotal role in transforming the way medical institutions operate and deliver care. These innovative solutions not only streamline administrative tasks but also enhance patient care delivery, ensuring accuracy, efficiency, and accessibility. Let’s delve into 15 types of healthcare software services that are revolutionizing the healthcare industry:
- Electronic Health Records (EHR) Systems: EHR systems digitize patient health records, enabling healthcare providers to access comprehensive patient information securely. These systems facilitate better coordination of care among different healthcare professionals and improve patient outcomes.
- Practice Management Software: Practice management software automates administrative tasks such as appointment scheduling, billing, and inventory management, allowing healthcare practices to run smoothly and efficiently.
- Telemedicine Platforms: Telemedicine platforms enable remote consultations between patients and healthcare providers through video conferencing, improving access to care, especially in remote or underserved areas.
- Medical Billing Software: Medical billing software streamlines the billing process by generating accurate invoices, submitting claims electronically, and tracking payments, reducing billing errors and improving revenue cycle management.
- Hospital Information Systems (HIS): HIS integrates various healthcare functions within a hospital, including patient registration, scheduling, billing, and inventory management, enhancing operational efficiency and patient care coordination.
- Picture Archiving and Communication Systems (PACS): PACS facilitates the storage, retrieval, distribution, and viewing of medical images such as X-rays, MRIs, and CT scans, enabling healthcare professionals to diagnose and treat patients more effectively.
- Pharmacy Management Software: Pharmacy management software automates pharmacy operations such as inventory management, prescription filling, and medication dispensing, ensuring accurate medication management and improving patient safety.
- Electronic Prescribing (e-prescribing) Systems: E-prescribing systems enable healthcare providers to electronically send prescriptions to pharmacies, reducing prescription errors, improving medication adherence, and enhancing patient convenience.
- Health Information Exchange (HIE) Platforms: HIE platforms allow healthcare providers to securely share patient information across different healthcare organizations, promoting care coordination and interoperability while maintaining patient privacy.
- Clinical Decision Support Systems (CDSS): CDSS analyzes patient data to provide healthcare professionals with evidence-based recommendations and alerts, assisting in clinical decision-making and improving patient outcomes.
- Remote Patient Monitoring (RPM) Solutions: RPM solutions use wearable devices and mobile apps to monitor patients’ vital signs and health metrics remotely, enabling early detection of health issues and proactive intervention, particularly for chronic disease management.
- Medical Practice Websites and Patient Portals: Medical practice websites and patient portals provide patients with access to medical information, appointment scheduling, lab results, and communication with healthcare providers, enhancing patient engagement and satisfaction.
- Healthcare Analytics Software: Healthcare analytics software leverages data analysis to identify trends, patterns, and insights from healthcare data, enabling healthcare organizations to make data-driven decisions, optimize operations, and improve patient outcomes.
- Population Health Management Systems: Population health management systems help healthcare organizations improve the health outcomes of entire populations by identifying at-risk patients, coordinating care interventions, and monitoring outcomes to enhance preventive care and reduce healthcare costs.
- Patient Engagement Platforms: Patient engagement platforms empower patients to actively participate in their healthcare journey through education, self-management tools, appointment reminders, and communication with healthcare providers, leading to improved health outcomes and satisfaction.
How to Create 15 Types of Healthcare Software
In today’s digitally driven world, healthcare software plays a pivotal role in revolutionizing patient care, streamlining operations, and enhancing overall efficiency within the healthcare industry. From electronic health records (EHR) systems to telemedicine platforms, the spectrum of healthcare software is vast and varied. If you’re looking to develop healthcare software, understanding the different types and their functionalities is crucial. In this guide, we’ll delve into how you can create 15 types of healthcare software to cater to diverse needs within the healthcare ecosystem.
- Electronic Health Records (EHR) Software:
- Focus on developing a user-friendly interface for healthcare professionals to access and manage patient records securely.
- Ensure compliance with healthcare regulations such as HIPAA to safeguard patient data.
- Practice Management Software:
- Develop features for appointment scheduling, billing, and administrative tasks to streamline the operations of healthcare practices.
- Telemedicine Software:
- Integrate video conferencing capabilities along with secure messaging to facilitate remote consultations between healthcare providers and patients.
- Health Information Exchange (HIE) Software:
- Design interoperable software that enables the seamless exchange of patient information between different healthcare organizations while maintaining data integrity and privacy.
- Medical Billing Software:
- Create a platform that automates the billing process, verifies insurance eligibility, and generates accurate invoices to optimize revenue cycle management.
- Medical Imaging Software:
- Develop software capable of viewing, storing, and analyzing medical images such as X-rays, MRIs, and CT scans with high precision and efficiency.
- Electronic Prescription Software:
- Build a secure platform for healthcare providers to electronically prescribe medications, check for drug interactions, and transmit prescriptions to pharmacies.
- Health and Wellness Apps:
- Develop mobile applications focused on promoting healthy lifestyles, tracking fitness goals, and providing personalized health recommendations to users.
- Remote Patient Monitoring Software:
- Create software solutions that enable healthcare providers to remotely monitor patients’ vital signs, symptoms, and medication adherence, thereby facilitating proactive healthcare management.
- Clinical Decision Support Systems (CDSS):
- Develop intelligent systems that provide healthcare professionals with evidence-based recommendations, alerts, and guidelines to aid clinical decision-making at the point of care.
- Healthcare Analytics Software:
- Design software capable of analyzing vast amounts of healthcare data to derive actionable insights, improve patient outcomes, and optimize resource utilization.
- Electronic Medical Records (EMR) Software:
- Focus on building software tailored to the needs of individual healthcare practices, allowing for the digital storage and retrieval of patient medical records within a single facility.
- Patient Portal Software:
- Develop intuitive portals that empower patients to access their medical records, schedule appointments, communicate with healthcare providers, and engage in their care journey.
- Health Monitoring Wearables:
- Create wearable devices and accompanying software that monitor vital signs, track activity levels, and provide real-time health notifications to users and their healthcare providers.
Why Should You Go for 15 Types of Healthcare Software?
In today’s rapidly evolving healthcare landscape, technological advancements play a pivotal role in improving patient care, streamlining operations, and enhancing overall efficiency. Healthcare software has emerged as a crucial component in modern medical facilities, offering a wide array of functionalities tailored to meet diverse needs. From electronic health records (EHR) to telemedicine platforms, the utilization of various types of healthcare software has revolutionized the way healthcare services are delivered and managed. Let’s delve into the reasons why integrating these 15 types of healthcare software into your practice can be advantageous:
- Electronic Health Records (EHR): EHR systems facilitate seamless storage and retrieval of patient information, ensuring comprehensive and accurate documentation while enhancing data accessibility across different healthcare settings.
- Practice Management Software: This software streamlines administrative tasks such as appointment scheduling, billing, and inventory management, allowing healthcare providers to focus more on patient care.
- Telemedicine Platforms: Telemedicine software enables remote consultations, improving access to healthcare services, especially in underserved areas, while minimizing the need for in-person visits.
- Medical Billing Software: Automating the billing process reduces errors, accelerates payment cycles, and enhances revenue management for healthcare providers.
- Health Information Exchange (HIE) Platforms: HIE software facilitates the secure exchange of patient information between different healthcare providers, promoting care coordination and continuity.
- Patient Engagement Solutions: These platforms empower patients to actively participate in their healthcare journey through features like online appointment scheduling, secure messaging, and health education resources.
- Clinical Decision Support Systems (CDSS): CDSS software offers evidence-based insights and alerts to healthcare professionals, aiding in clinical decision-making and enhancing patient safety.
- Radiology Information Systems (RIS): RIS software streamlines radiology workflows, from appointment scheduling to image interpretation, ensuring efficient management of diagnostic imaging processes.
- Picture Archiving and Communication Systems (PACS): PACS software enables the storage, retrieval, and distribution of medical images, fostering collaboration among healthcare professionals and facilitating timely diagnoses.
- Laboratory Information Management Systems (LIMS): LIMS software automates laboratory workflows, from sample tracking to result reporting, optimizing laboratory operations and ensuring data integrity.
- Pharmacy Management Software: Pharmacy software streamlines prescription filling, inventory management, and regulatory compliance, enhancing medication safety and efficiency.
- Electronic Prescribing (e-prescribing) Software: E-prescribing solutions enable healthcare providers to electronically send prescriptions to pharmacies, reducing medication errors and improving medication adherence.
- Population Health Management Platforms: These platforms analyze patient data to identify at-risk populations, enabling proactive interventions and tailored care plans to improve health outcomes on a broader scale.
- Remote Patient Monitoring Systems: Remote monitoring software allows healthcare providers to remotely track patient vital signs and health metrics, enabling early intervention and personalized care for chronic conditions.
- Medical Device Integration Software: Integrating medical devices with healthcare IT systems enhances data interoperability, streamlines clinical workflows, and improves patient monitoring and treatment.
Market Prospects of 15 Types of Healthcare Software and Platforms
In the ever-evolving landscape of healthcare, technology plays a pivotal role in enhancing efficiency, improving patient care, and streamlining operations. From electronic health records (EHR) to telemedicine platforms, the market is flooded with various types of healthcare software and platforms designed to cater to different needs. Let’s delve into the market prospects of 15 key types:
- Electronic Health Records (EHR): EHR systems continue to witness robust growth, driven by the need for digitization and interoperability in healthcare data management. The market is expected to expand further as healthcare providers seek integrated solutions for comprehensive patient records.
- Telemedicine Platforms: The telemedicine market has experienced exponential growth, especially in light of the COVID-19 pandemic. With increasing adoption by healthcare providers and patients alike, telemedicine platforms are poised for sustained growth, offering convenient access to care and reducing healthcare costs.
- Practice Management Software: Practice management software solutions are in demand among healthcare practices seeking to streamline administrative tasks, optimize scheduling, and improve billing processes. The market is expected to grow as practices embrace digital transformation initiatives.
- Medical Billing Software: With the complexities of healthcare billing, medical billing software is essential for accurate claim submissions and reimbursement. As healthcare billing regulations evolve, the demand for compliant and efficient billing solutions is projected to rise.
- Electronic Prescribing (ePrescribing) Software: ePrescribing software facilitates secure electronic transmission of prescriptions, enhancing medication management and patient safety. With the shift towards paperless prescribing processes, the market for ePrescribing solutions is expected to expand.
- Healthcare Analytics Platforms: Healthcare analytics platforms leverage data analytics to derive insights for better decision-making, quality improvement, and cost reduction. As healthcare organizations focus on value-based care and population health management, the demand for advanced analytics solutions is set to increase.
- Patient Engagement Software: Patient engagement platforms empower patients to actively participate in their healthcare journey, leading to improved outcomes and satisfaction. With a growing emphasis on patient-centered care, the market for patient engagement solutions is poised for steady growth.
- Remote Patient Monitoring (RPM) Solutions: RPM solutions enable continuous monitoring of patient health outside traditional clinical settings, promoting early intervention and proactive care management. As the healthcare industry shifts towards value-based care models, RPM solutions are gaining traction.
- Health Information Exchange (HIE) Platforms: HIE platforms facilitate the secure exchange of patient health information among healthcare providers, promoting care coordination and interoperability. With increasing emphasis on care continuity and interoperability standards, the HIE market is expected to expand.
- Population Health Management Software: Population health management software enables healthcare organizations to analyze and manage the health outcomes of defined populations, driving improvements in care delivery and cost containment. As healthcare systems focus on population health and risk-based contracting, the market for population health management solutions is poised for growth.
- Clinical Decision Support Systems (CDSS): CDSS provides clinicians with evidence-based guidance and recommendations at the point of care, improving clinical decision-making and patient safety. With the growing adoption of electronic health records and value-based care initiatives, the CDSS market is projected to grow.
- Health Information Management (HIM) Systems: HIM systems encompass various tools and technologies for managing, storing, and retrieving health information, ensuring data integrity and compliance with regulatory requirements. As healthcare organizations prioritize data governance and interoperability, the HIM market is expected to expand.
- Imaging and Radiology Informatics Software: Imaging and radiology informatics software facilitates the efficient management and interpretation of medical images, enhancing diagnostic accuracy and workflow efficiency. With advancements in imaging technology and increased demand for diagnostic services, the market for radiology informatics software is poised for growth.
- Healthcare Supply Chain Management Software: Healthcare supply chain management software enables efficient procurement, inventory management, and distribution of medical supplies and equipment, optimizing operational costs and ensuring patient safety. As healthcare systems focus on supply chain resilience and cost containment, the market for supply chain management solutions is expected to grow.
- Mobile Health (mHealth) Applications: Health applications leverage mobile devices to deliver healthcare services and information remotely, promoting patient engagement and self-management. With the widespread adoption of smartphones and wearable devices, the market for mHealth applications is projected to expand.
Essential Features of 15 Types of Healthcare Software
In today’s digital era, healthcare software has become indispensable for streamlining operations, enhancing patient care, and improving overall efficiency in medical facilities. From electronic health records (EHR) to telemedicine platforms, the healthcare industry relies on a diverse array of software solutions to meet the needs of patients and healthcare professionals alike. Understanding the essential features of these different types of healthcare software is crucial for selecting the right tools to support various aspects of medical practice. Let’s delve into the key features of 15 types of healthcare software:
- Electronic Health Records (EHR): EHR software should offer robust data security measures, customizable templates, interoperability with other systems, and easy accessibility to patient records.
- Practice Management Software: Features such as appointment scheduling, billing and invoicing, patient registration, and insurance claim processing are essential for efficient practice management.
- Telemedicine Platforms: Telemedicine software must support video conferencing, secure messaging, virtual visits, and integration with EHR systems for seamless patient care delivery.
- Medical Billing Software: Automation of billing processes, insurance verification, claims management, and compliance with regulatory requirements are vital features of medical billing software.
- Picture Archiving and Communication System (PACS): PACS software should offer high-quality image storage, retrieval, and sharing capabilities, along with advanced viewing and diagnostic tools for medical imaging professionals.
- Hospital Information System (HIS): Comprehensive HIS software should cover all aspects of hospital management, including patient admissions, bed management, pharmacy, laboratory, and inventory management.
- Pharmacy Management Software: Features like drug inventory tracking, prescription management, medication dispensing, and drug interaction alerts are essential for efficient pharmacy operations.
- Electronic Prescription Software: Electronic prescribing software should enable healthcare providers to electronically transmit prescriptions to pharmacies, ensuring accuracy, security, and convenience for patients.
- Medical Imaging Software: Advanced visualization tools, DICOM compatibility, 3D reconstruction capabilities, and support for various imaging modalities are key features of medical imaging software.
- Health Information Exchange (HIE) Platforms: HIE software should facilitate the secure sharing of patient health information among healthcare providers, ensuring continuity of care and interoperability.
- Remote Patient Monitoring Systems: Remote patient monitoring software should support real-time data collection from wearable devices, personalized alerts, trend analysis, and integration with EHR systems for remote patient management.
- Electronic Medical Record (EMR) Software: EMR software should offer structured documentation, clinical decision support, medication reconciliation, and patient portal access for enhanced patient engagement.
- Medical Practice Marketing Software: Features such as online reputation management, social media integration, appointment reminders, and patient feedback collection are essential for effective medical practice marketing.
- Medical Inventory Management Software: Inventory tracking, expiry date management, automatic reordering, and integration with accounting systems are crucial features of medical inventory management software.
- Patient Engagement Platforms: Patient engagement software should include features like patient education resources, appointment reminders, secure messaging, and feedback collection tools to empower patients in their healthcare journey.
15 Types of Healthcare Software Timelines
In today’s fast-paced world, technology plays a pivotal role in transforming various sectors, and healthcare is no exception. Healthcare software timelines have revolutionized the way medical professionals deliver care, manage patient data, and streamline administrative tasks. From electronic health records (EHR) to telemedicine platforms, there’s a plethora of software solutions tailored to meet the diverse needs of healthcare providers and patients alike. Let’s delve into 15 types of healthcare software timelines, unraveling their functionalities and significance in the healthcare landscape.
- Electronic Health Records (EHR): EHR software facilitates digital storage and retrieval of patient health information, including medical history, diagnoses, medications, and treatment plans. It ensures seamless access to vital patient data across healthcare settings, enhancing care coordination and decision-making.
- Practice Management Software: Practice management software automates administrative tasks such as appointment scheduling, billing, and insurance claims processing. It optimizes workflow efficiency, reduces paperwork, and improves revenue cycle management for healthcare practices.
- Telemedicine Platforms: Telemedicine software enables remote patient consultations via video conferencing, allowing healthcare providers to diagnose, treat, and monitor patients from a distance. It enhances access to care, especially in underserved areas, while minimizing the need for in-person visits.
- Health Information Exchange (HIE) Systems: HIE systems facilitate the secure exchange of patient health information between different healthcare organizations and systems. They promote interoperability, enabling seamless data sharing for improved care coordination and patient outcomes.
- Medical Imaging Software: Medical imaging software is used to capture, store, and analyze medical images such as X-rays, MRI scans, and CT scans. It aids in diagnostic interpretation, treatment planning, and medical research, enhancing the accuracy and efficiency of healthcare delivery.
- Electronic Prescribing (ePrescribing) Software: ePrescribing software enables healthcare providers to electronically send prescriptions to pharmacies, eliminating the need for paper-based prescriptions. It enhances medication safety, reduces errors, and improves medication adherence among patients.
- Patient Portal Systems: Patient portal systems provide patients with secure online access to their health records, lab results, appointment scheduling, and communication with healthcare providers. They empower patients to take an active role in managing their health and engaging in shared decision-making.
- Medical Billing Software: Medical billing software automates the billing and invoicing processes for healthcare services rendered to patients. It ensures accurate coding, timely reimbursement, and compliance with healthcare regulations, optimizing revenue management for healthcare organizations.
- Remote Patient Monitoring (RPM) Solutions: RPM solutions enable continuous monitoring of patient’s vital signs and health metrics outside traditional healthcare settings. They support early intervention, chronic disease management, and personalized care delivery, improving patient outcomes and reducing healthcare costs.
- Health Analytics Platforms: Health analytics platforms utilize data analytics and machine learning algorithms to derive actionable insights from vast amounts of healthcare data. They support population health management, predictive modeling, and clinical decision support, driving evidence-based practice and quality improvement initiatives.
- Medical Practice Marketing Software: Medical practice marketing software helps healthcare providers attract, engage, and retain patients through digital marketing channels. It encompasses tools for website optimization, social media management, online reputation management, and patient outreach, enhancing the visibility and growth of healthcare practices.
- Clinical Decision Support Systems (CDSS): CDSS leverages clinical knowledge and patient data to provide evidence-based guidance to healthcare providers at the point of care. They assist in diagnosis, treatment planning, and medication selection, promoting adherence to best practices and patient safety.
- Healthcare Asset Management Software: Healthcare asset management software tracks and manages medical equipment, supplies, and facilities within healthcare organizations. It optimizes resource utilization, prevents loss or theft, and ensures regulatory compliance, contributing to operational efficiency and cost savings.
- Population Health Management Platforms: Population health management platforms aggregate and analyze health data to identify and address the health needs of specific patient populations. They support risk stratification, care coordination, and preventive interventions, driving population health outcomes and value-based care initiatives.
- Mobile Health (mHealth) Applications: mHealth applications deliver healthcare services and information via mobile devices, empowering users to monitor their health, access educational resources, and engage in virtual care interactions. They promote wellness, disease management, and patient empowerment, transcending geographical barriers to healthcare access.
How to Create 15 Types of Healthcare Software – Team and Tech Stack
In the rapidly evolving landscape of healthcare technology, the development of various types of software has become paramount to enhance patient care, streamline processes, and improve overall efficiency within healthcare institutions. From electronic health records (EHR) to telemedicine platforms, each type of healthcare software serves a unique purpose and requires careful consideration in both team composition and technological infrastructure. In this guide, we’ll delve into how to create 15 different types of healthcare software, emphasizing the importance of assembling the right team and selecting the appropriate tech stack for each project.
- Electronic Health Records (EHR) Software: EHR software is fundamental in modern healthcare for storing, managing, and accessing patient medical records electronically. To develop robust EHR software, a team comprising software developers, UX/UI designers, healthcare domain experts, and compliance specialists is essential. Technologies like SQL databases, cloud computing, and encryption protocols are commonly utilized in building secure and scalable EHR systems.
- Telemedicine Platforms: Telemedicine platforms enable remote consultations, diagnosis, and treatment delivery, revolutionizing access to healthcare services. Building telemedicine software requires expertise in video conferencing technology, mobile app development, and integrations with electronic health records. A multidisciplinary team including developers, designers, and healthcare professionals is necessary to ensure seamless user experience and compliance with regulatory standards.
- Practice Management Software: Practice management software facilitates administrative tasks such as appointment scheduling, billing, and inventory management for healthcare practices. Developing such software demands a blend of software engineers, database administrators, and project managers who understand the intricacies of healthcare workflows. Technologies like APIs for payment gateways and appointment scheduling algorithms are integral to building efficient practice management solutions.
- Medical Billing Software: Medical billing software automates the complex process of generating and submitting medical bills to insurance companies. Building this type of software necessitates collaboration between software developers, billing experts, and regulatory compliance specialists. Utilizing technologies like blockchain for secure transactions and machine learning algorithms for claims processing can enhance the accuracy and efficiency of medical billing systems.
- Picture Archiving and Communication Systems (PACS): PACS software facilitates the storage, retrieval, and distribution of medical images such as X-rays, MRIs, and CT scans. Developing PACS solutions requires expertise in image processing, storage technologies, and interoperability standards like DICOM. A skilled team comprising software engineers, imaging specialists, and cybersecurity experts is crucial to ensuring the integrity and accessibility of medical imaging data.
- Health Information Exchange (HIE) Platforms: HIE platforms enable the electronic sharing of patient health information across different healthcare organizations, improving care coordination and interoperability. Building HIE software demands collaboration between software developers, data integration specialists, and legal experts well-versed in healthcare privacy regulations. Employing technologies like HL7 standards and OAuth for secure data exchange is essential in developing robust HIE solutions.
- Remote Patient Monitoring (RPM) Systems: RPM systems allow healthcare providers to remotely monitor patients’ vital signs and health metrics, enabling proactive interventions and personalized care plans. Developing RPM software requires expertise in sensor technology, data analytics, and mobile app development. A cross-functional team comprising software engineers, data scientists, and healthcare professionals is essential to create user-friendly RPM solutions that leverage technologies like IoT devices and machine learning algorithms.
- Electronic Prescription (e-prescribing) Software: E-prescribing software enables healthcare providers to electronically generate and transmit prescriptions to pharmacies, enhancing medication safety and adherence. Building e-prescribing solutions demands collaboration between software developers, pharmacists, and regulatory compliance specialists. Implementing technologies like secure messaging protocols and drug database APIs ensures accuracy and security in electronic prescription transmission.
- Clinical Decision Support Systems (CDSS): CDSS software provides clinicians with evidence-based information and recommendations to aid clinical decision-making at the point of care. Developing CDSS solutions requires expertise in medical informatics, artificial intelligence, and user interface design. A multidisciplinary team comprising software engineers, healthcare researchers, and clinicians is essential to create intuitive CDSS tools that leverage technologies like natural language processing and predictive analytics.
- Healthcare Analytics Platforms: Healthcare analytics platforms analyze vast amounts of clinical and operational data to derive actionable insights for improving patient outcomes and operational efficiency. Building analytics solutions demands collaboration between data scientists, healthcare analysts, and software engineers. Employing technologies like big data processing frameworks and data visualization libraries enables the development of powerful healthcare analytics platforms.
- Patient Engagement Applications: Patient engagement applications empower patients to actively participate in their healthcare journey through educational content, appointment reminders, and communication tools. Developing patient engagement apps requires expertise in mobile app development, user experience design, and healthcare communication strategies. A team comprising software developers, UX/UI designers, and healthcare educators is essential to create engaging and accessible patient engagement solutions.
- Population Health Management Software: Population health management software aggregates and analyzes patient data to identify at-risk populations and implement targeted interventions for improving health outcomes. Building population health management solutions demands collaboration between data scientists, public health experts, and software engineers. Leveraging technologies like predictive modeling and interoperable data platforms enables the development of comprehensive population health management tools.
- Chronic Disease Management Platforms: Chronic disease management platforms support the ongoing monitoring and self-management of chronic conditions such as diabetes and hypertension. Developing these platforms requires expertise in remote monitoring technology, behavior change interventions, and mobile health solutions. A multidisciplinary team comprising software developers, healthcare providers, and patient advocates is essential to create effective chronic disease management platforms that prioritize usability and patient empowerment.
- Medical Inventory Management Systems: Medical inventory management systems track and manage inventory levels of medical supplies, equipment, and medications within healthcare facilities. Building inventory management software demands collaboration between software developers, supply chain experts, and healthcare administrators. Utilizing technologies like RFID tagging and barcode scanning streamlines inventory tracking and ensures efficient supply chain management in healthcare settings.
- Telehealth Kiosks: Telehealth kiosks provide on-demand access to healthcare services in convenient locations such as retail stores and workplaces. Developing telehealth kiosks requires expertise in hardware integration, telemedicine software development, and user interface design. A multidisciplinary team comprising engineers, designers, and healthcare providers is essential to create user-friendly telehealth kiosks that deliver high-quality care experiences outside traditional healthcare settings.
15 Types of Healthcare Software Process
In today’s digital age, healthcare software has become indispensable in revolutionizing the industry, streamlining processes, and enhancing patient care. From managing electronic health records (EHR) to optimizing administrative tasks, healthcare software processes play a pivotal role in ensuring efficiency and accuracy across various healthcare settings. Let’s delve into 15 essential types of healthcare software processes that are shaping the future of healthcare delivery:
- Electronic Health Records (EHR) Systems: EHR systems digitally store patient health information, facilitating secure access by healthcare providers for comprehensive patient care management.
- Practice Management Software: This software assists healthcare facilities in managing appointments, billing, claims processing, and other administrative tasks, enhancing operational efficiency.
- Telehealth Platforms: Telehealth software enables remote consultations, virtual visits, and remote patient monitoring, expanding access to healthcare services and improving patient convenience.
- Medical Billing and Coding Software: Streamlining the complex process of medical billing and coding, this software ensures accurate billing, reduces errors, and expedites reimbursement processes.
- Clinical Decision Support Systems (CDSS): CDSS provides healthcare professionals with evidence-based insights and recommendations to aid clinical decision-making, ultimately improving patient outcomes.
- Picture Archiving and Communication Systems (PACS): PACS software manages medical imaging data, such as X-rays and MRIs, allowing for efficient storage, retrieval, and sharing of images among healthcare providers.
- Health Information Exchange (HIE) Systems: HIE systems facilitate the secure exchange of patient health information between different healthcare organizations, promoting care coordination and interoperability.
- Electronic Prescription (e-prescribing) Software: E-prescribing software enables healthcare providers to electronically transmit prescriptions to pharmacies, enhancing medication management and reducing errors.
- Hospital Information Systems (HIS): HIS integrates various administrative, clinical, and financial functions within a hospital or healthcare system, improving overall workflow and resource utilization.
- Remote Patient Monitoring (RPM) Solutions: RPM software enables continuous monitoring of a patient’s health status outside of traditional healthcare settings, allowing for early intervention and personalized care.
- Population Health Management (PHM) Platforms: PHM software aggregates and analyzes health data to identify trends, manage chronic conditions, and improve population health outcomes.
- Healthcare Analytics and Business Intelligence: These tools analyze vast amounts of healthcare data to extract actionable insights, optimize operations, and support strategic decision-making.
- Electronic Medical Record (EMR) Systems: Similar to EHR systems, EMR software digitally stores patient health records within a single healthcare organization, enhancing data accessibility and care coordination.
- Mobile Health (mHealth) Applications: mHealth apps offer various healthcare services and resources, ranging from fitness tracking to chronic disease management, accessible via mobile devices.
- Quality Management Systems (QMS): QMS software helps healthcare organizations maintain compliance with regulatory standards, monitor quality metrics, and implement continuous improvement initiatives.
Next Big Technology – Your Trusted 15 Types of Healthcare Software Partner
In the rapidly evolving landscape of healthcare, technology stands as a cornerstone for efficiency, accuracy, and patient care. As the demand for innovative solutions continues to soar, finding the right healthcare software partner becomes crucial for healthcare providers and organizations. With a plethora of options available, it’s essential to identify the types of healthcare software that can truly elevate your practice or institution. Here, we delve into 15 types of healthcare software that can serve as your trusted partners in navigating the next big technological advancements.
- Electronic Health Records (EHR) Software: EHR software streamlines patient information, ensuring easy access, updating, and sharing among healthcare professionals securely.
- Practice Management Software: This software facilitates administrative tasks such as appointment scheduling, billing, and inventory management, optimizing the overall workflow of healthcare facilities.
- Telemedicine Software: Enabling remote consultations and virtual healthcare services, telemedicine software enhances accessibility and convenience for both patients and providers.
- Medical Billing Software: Simplifying the complex process of medical billing, this software ensures accurate invoicing, claims processing, and revenue management.
- Healthcare Analytics Software: Leveraging data analytics, this software provides valuable insights into patient outcomes, operational efficiency, and resource allocation for informed decision-making.
- Electronic Prescription Software: Enhancing medication management and safety, electronic prescription software enables healthcare professionals to electronically prescribe and track medications.
- Patient Engagement Software: Improving patient involvement in their healthcare journey, patient engagement software offers tools for appointment reminders, educational resources, and communication with providers.
- Radiology Information Systems (RIS): Specifically designed for radiology departments, RIS software facilitates image management, reporting, and workflow optimization for diagnostic imaging procedures.
- Picture Archiving and Communication Systems (PACS): PACS software stores and retrieves medical images such as X-rays, MRIs, and CT scans, enabling seamless access and sharing across healthcare networks.
- Clinical Decision Support Systems (CDSS): Integrating medical knowledge with patient data, CDSS software assists healthcare professionals in making evidence-based clinical decisions and treatment recommendations.
- Health Information Exchange (HIE) Software: Facilitating the exchange of patient information between different healthcare providers and systems, HIE software promotes interoperability and continuity of care.
- Remote Patient Monitoring (RPM) Software: RPM software enables real-time monitoring of patients’ vital signs and health metrics outside traditional healthcare settings, enhancing proactive care management for chronic conditions.
- Electronic Medical Record (EMR) Software: Similar to EHR software, EMR software focuses on digitizing and managing patient medical records within a single healthcare organization or practice.
- Medical Imaging Software: Beyond basic image viewing, medical imaging software offers advanced features such as 3D reconstruction, image analysis, and computer-aided diagnosis for enhanced diagnostics and treatment planning.
- Health Insurance Management Software: Streamlining insurance-related processes, this software assists in eligibility verification, claims processing, and coordination of benefits, ensuring smooth financial transactions between patients, providers, and insurers.
Top 15 Types of Healthcare Software Companies
In today’s fast-paced world, the healthcare industry is constantly evolving to meet the needs of patients and providers alike. One significant driver of this evolution is healthcare software companies, which play a pivotal role in transforming the delivery of care, improving patient outcomes, and enhancing operational efficiency within healthcare organizations. From electronic health records (EHR) to telemedicine platforms, these companies offer a diverse range of solutions tailored to address various aspects of healthcare delivery. In this article, we delve into the top 15 types of healthcare software companies that are making waves in the industry.
-
Next Big Technology:
Next Big Technology is one of the top development companies for the high-quality development of mobile apps and web development services. They have having experienced in-house team of developers who provide top-notch development services according to the business requirements. NBT provides highly business-oriented services and implements all the latest and trending tools and technologies. They always work hard to deliver a top-notch solution at an affordable cost. They are having experience of more than 13 years and delivered lots of projects around the globe to businesses and clients.
NBT is highly focused on providing top-notch development solutions at a very affordable cost. By using their market experience and development experience, they are delivering proper solutions to clients and various industries for their custom requirements.
Location: India, USA, UK, Australia
Hourly Rate :< $25 per Hour
Employees: 50 – 249
Focus Area
- Mobile App Development
- App Designing (UI/UX)
- Software Development
- Web Development
- AR & VR Development
- Big Data & BI
- Cloud Computing Services
- DevOps
- E-commerce Development
Industries Focus
- Art, Entertainment & Music
- Business Services
- Consumer Products
- Designing
- Education
- Financial & Payments
- Gaming
- Government
- Healthcare & Medical
- Hospitality
- Information Technology
- Legal & Compliance
- Manufacturing
- Media
- Practice Management Software: These companies specialize in developing software that helps healthcare practices efficiently manage administrative tasks such as scheduling appointments, billing, and inventory management.
- Telemedicine Platforms: Telemedicine software companies enable remote consultations between patients and healthcare providers through video conferencing and secure messaging, improving access to care, particularly in remote or underserved areas.
- Medical Billing and Revenue Cycle Management (RCM) Solutions: RCM software companies provide tools for managing billing processes, claims submission, and revenue optimization, helping healthcare organizations maximize their financial performance.
- Health Information Exchange (HIE) Providers: HIE software companies develop platforms that facilitate the secure exchange of patient health information among healthcare providers, enhancing care coordination and interoperability.
- Clinical Decision Support Systems (CDSS) Developers: CDSS companies create software solutions that assist healthcare providers in making informed clinical decisions by integrating patient data, evidence-based guidelines, and best practices.
- Healthcare Analytics and Business Intelligence (BI) Firms: These companies offer advanced analytics tools and BI platforms tailored to the healthcare industry, enabling organizations to derive actionable insights from large volumes of clinical and operational data.
- Patient Engagement and Education Platforms: Patient engagement software companies focus on developing tools that empower patients to take an active role in their healthcare journey through personalized education, remote monitoring, and interactive communication.
- Healthcare IoT (Internet of Things) Solutions Providers: IoT companies in healthcare develop connected devices and sensors that collect real-time data for monitoring patients, managing chronic conditions, and improving clinical outcomes.
- Population Health Management (PHM) Software Developers: PHM software companies offer comprehensive solutions for analyzing population health data, identifying at-risk patients, and implementing targeted interventions to improve health outcomes at the community level.
- Healthcare Compliance and Regulatory Solutions: These companies develop software solutions to help healthcare organizations navigate complex regulatory requirements, ensure compliance with standards such as HIPAA, and mitigate risk.
- Medical Imaging and Diagnostic Software Vendors: Medical imaging software companies specialize in developing advanced imaging tools for interpreting medical images, enhancing diagnostic accuracy, and supporting clinical decision-making.
- Healthcare Supply Chain Management (SCM) Providers: SCM software companies offer solutions for optimizing the procurement, inventory management, and distribution of medical supplies and pharmaceuticals, ensuring seamless operations within healthcare facilities.
- Telehealth and Remote Monitoring Platforms: These companies focus on developing telehealth and remote monitoring solutions that enable virtual consultations, remote patient monitoring, and chronic disease management, fostering continuity of care beyond traditional healthcare settings.
- Healthcare AI and Machine Learning (ML) Startups: AI and ML companies in healthcare leverage advanced algorithms and data analytics to automate tasks, predict clinical outcomes, and drive innovations in personalized medicine, drug discovery, and treatment optimization.
Add Comparison Table 15 Types of Healthcare Software
In today’s rapidly advancing healthcare landscape, the integration of technology has become indispensable. Healthcare software plays a pivotal role in enhancing patient care, streamlining administrative tasks, and improving overall efficiency within medical facilities. With a myriad of options available, it can be challenging for healthcare providers to choose the most suitable software for their specific needs. In this article, we’ll delve into 15 types of healthcare software, providing insights and comparisons to aid in decision-making.
1. Electronic Health Records (EHR) Software
EHR software digitizes patient health records, facilitating easy access, updating, and sharing among healthcare professionals. It centralizes patient data, streamlining workflows and enhancing care coordination.
2. Practice Management Software
Practice management software automates administrative tasks such as appointment scheduling, billing, and inventory management. It optimizes practice operations, leading to increased efficiency and revenue.
3. Telemedicine Software
Telemedicine software enables remote consultations between patients and healthcare providers through video conferencing and secure messaging. It expands access to healthcare services, especially in rural or underserved areas.
4. Medical Billing Software
Medical billing software automates the billing process, including claims submission, payment processing, and revenue cycle management. It minimizes errors and accelerates reimbursement.
5. Picture Archiving and Communication System (PACS)
PACS software stores and retrieves medical images such as X-rays, MRIs, and CT scans. It enhances image management, allowing for easier interpretation and collaboration among radiologists and clinicians.
6. Electronic Prescribing (e-prescribing) Software
E-prescribing software enables healthcare providers to electronically send prescriptions to pharmacies, reducing errors and enhancing medication adherence. It improves patient safety and medication management.
7. Healthcare Analytics Software
Healthcare analytics software analyzes large volumes of healthcare data to derive insights for decision-making, performance monitoring, and predictive modeling. It aids in population health management and quality improvement initiatives.
8. Clinical Decision Support (CDS) Software
CDS software provides evidence-based guidance and alerts to healthcare providers at the point of care. It assists in clinical decision-making, reducing errors and improving patient outcomes.
9. Hospital Information System (HIS)
HIS software integrates various administrative and clinical functions within a hospital, including patient registration, laboratory management, and inventory control. It enhances operational efficiency and patient care delivery.
10. Patient Engagement Software
Patient engagement software empowers patients to actively participate in their healthcare journey through educational resources, appointment reminders, and secure communication with providers. It fosters patient satisfaction and loyalty.
11. Population Health Management Software
Population health management software aggregates and analyzes data to identify at-risk populations, manage chronic conditions, and implement preventive interventions. It supports value-based care initiatives and improves health outcomes.
12. Home Health Software
Home health software facilitates the delivery and coordination of care for patients receiving treatment at home. It includes features such as remote monitoring, care planning, and caregiver communication, ensuring continuity of care outside traditional healthcare settings.
13. Electronic Medical Records (EMR) Software
EMR software digitalizes patient medical records within a single healthcare organization, offering functionalities similar to EHR software but tailored for internal use. It improves documentation accuracy and care coordination among providers.
14. Radiology Information System (RIS)
RIS software manages radiology workflow, including appointment scheduling, image tracking, and report generation. It enhances the radiology department’s efficiency and communication with referring physicians.
15. Dental Practice Management Software
Dental practice management software streamlines administrative tasks specific to dental practices, such as appointment scheduling, treatment planning, and patient communication. It optimizes practice workflows and enhances patient satisfaction.
Comparison Table:
| Software Type | Key Features | Benefits |
|---|---|---|
| EHR | Centralized patient records | Enhanced care coordination |
| Practice Management | Administrative automation | Increased efficiency and revenue |
| Telemedicine | Remote consultations | Expanded access to healthcare |
| Medical Billing | Claims processing | Minimized errors, accelerated billing |
| PACS | Image storage and retrieval | Improved image management |
| E-prescribing | Electronic prescription transmission | Enhanced medication management |
| Healthcare Analytics | Data analysis for decision-making | Informed strategies for improvement |
| Clinical Decision Support | Evidence-based guidance | Error reduction, improved outcomes |
| HIS | Integration of hospital functions | Enhanced operational efficiency |
| Patient Engagement | Interactive patient tools | Improved patient satisfaction |
| Population Health Management | At-risk population identification | Support for value-based care initiatives |
| Home Health | Remote care coordination | Continuity of care outside hospitals |
| EMR | Digitalized medical records | Internal use, improved documentation |
| RIS | Radiology workflow management | Enhanced radiology department efficiency |
| Dental Practice Management | Dental-specific administrative tools | Optimized practice workflows |
FAQs on 15 Types of Healthcare Software
In today’s rapidly evolving healthcare landscape, technology plays a crucial role in enhancing patient care, streamlining operations, and improving overall efficiency. Healthcare software, in particular, has emerged as a cornerstone in modern medical practices, offering a wide array of solutions tailored to diverse needs. If you’re navigating the realm of healthcare software, here are some frequently asked questions (FAQs) to help you gain a better understanding of the various types available:
- Electronic Health Record (EHR) Software:
- What functionalities does EHR software typically offer?
- How does EHR software ensure patient data security and privacy?
- Practice Management Software:
- What features can I expect from practice management software?
- How does it streamline administrative tasks for healthcare providers?
- Medical Billing Software:
- How does medical billing software facilitate the billing process?
- Can it handle complex billing scenarios and insurance claims?
- Telemedicine Software:
- What are the key benefits of telemedicine software for patients and providers?
- How does it ensure HIPAA compliance during virtual consultations?
- Electronic Prescribing (ePrescribing) Software:
- How does ePrescribing software improve medication management?
- Is it integrated with pharmacies to enable seamless prescription refills?
- Radiology Information System (RIS) Software:
- What functionalities does RIS software offer radiology departments?
- How does it streamline imaging workflow and reporting?
- Picture Archiving and Communication System (PACS) Software:
- How does PACS software facilitate the storage and retrieval of medical images?
- Can it integrate with other healthcare systems for comprehensive patient care?
- Medical Practice Website and Patient Portal Software:
- What features are essential for a medical practice website and patient portal?
- How does it enhance patient engagement and communication?
- Clinical Decision Support (CDS) Software:
- How does CDS software assist healthcare providers in making informed decisions?
- Can it integrate with EHR systems to provide real-time guidance?
- Health Information Exchange (HIE) Software:
- What role does HIE software play in interoperability and data exchange?
- How does it ensure secure sharing of patient information between healthcare organizations?
- Population Health Management Software:
- What strategies does population health management software employ to improve outcomes?
- How does it analyze data to identify at-risk populations and implement preventive measures?
- Healthcare Analytics Software:
- What types of insights can healthcare analytics software provide?
- How does it leverage data to optimize clinical and operational performance?
- Patient Scheduling Software:
- How does patient scheduling software streamline appointment booking?
- Can it send reminders and notifications to reduce no-shows?
- Home Health Care Software:
- What functionalities are essential in home health care software?
- How does it support remote monitoring and care coordination?
- Dental Practice Management Software:
- What specific features are tailored to dental practices in management software?
- How does it streamline patient records, appointments, and billing in dental settings?