The real estate industry has undergone a digital revolution, with platforms like Zillow transforming property search and transactions. If you’re considering building a Zillow clone, understanding the costs, features, and development process is essential. This guide delves into the intricacies of creating your real estate platform.
Table of Contents
**1. Understanding the Zillow Model
- Zillow Overview: Zillow is a prominent real estate platform offering property listings, value estimates, and market insights.
- Key Features: Analyze Zillow’s features: property search, detailed listings, value estimates, neighborhood data, and user engagement tools.
**2. Defining Your Project Scope
- Feature Set: Specify the features for your Zillow clone: property listings, user profiles, saved searches, value estimation tool, and more.
- Platform Choice: Decide between web, iOS, Android, or cross-platform development.
**3. Cost Breakdown
**a. Development Costs
- Frontend Development: Design and implement the user interface, property search, and listing display.
- Backend Development: Set up databases, integrate APIs, user authentication, and listing management systems.
- Admin Dashboard: Develop a robust admin panel for easy property management and user moderation.
**b. Third-party Integrations
- Maps API: Integrating map services like Google Maps to display property locations.
- Property Data APIs: Accessing reliable property data sources to ensure accurate and up-to-date listings.
**c. Testing and Quality Assurance
- Functional Testing: Ensuring all features function seamlessly.
- Performance Testing: Evaluating app speed and responsiveness under various conditions.
- Security Testing: Identifying vulnerabilities and ensuring robust data protection.
**4. Key Features for Your Zillow Clone
**a. Property Listings
- Advanced Search Filters: Enable users to refine search results based on criteria such as location, price range, property type, and amenities.
- Interactive Maps: Display properties on an interactive map for better geographical understanding.
- Favorites and Alerts: Allow users to mark properties as favorites and set alerts for new listings or price changes.
**b. User Profiles and Engagement
- User Registration: Facilitate user sign-up and profile creation for personalized experiences.
- Saved Searches: Let users save their preferred searches for quick access.
- User Ratings and Reviews: Enable users to rate and review properties and agents.
**c. Advanced Property Valuation Tool
- Data-driven Estimates: Develop an algorithm that considers property data, market trends, and historical information for accurate value estimates.
- Comparative Market Analysis (CMA): Provide detailed reports comparing a property’s value with similar listings.
**d. Neighborhood Insights
- School Ratings and Reviews: Display educational institutions’ ratings and reviews for families.
- Commute Information: Integrate commute time data to nearby workplaces and amenities.
- Demographic Data: Show demographic statistics for each neighborhood.
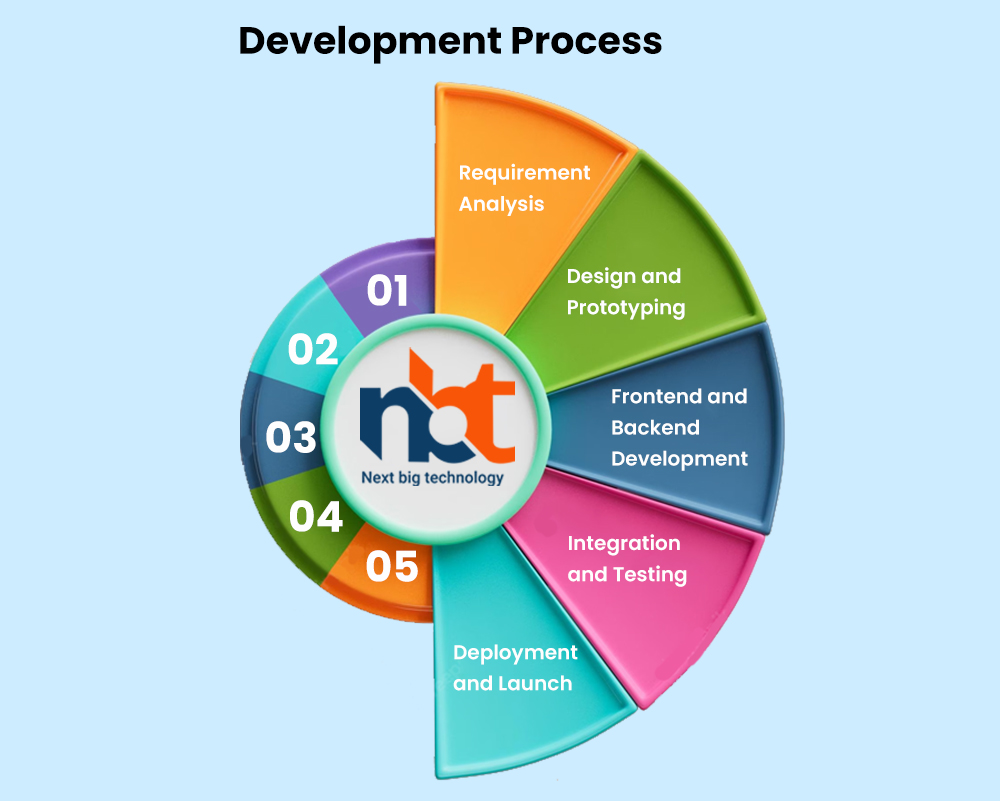
**5. Development Process
**a. Requirement Analysis
- Gather Requirements: Understand project goals, target audience, and desired features.
**b. Design and Prototyping
- UI/UX Design: Create visually appealing designs and user-friendly interfaces.
- Wireframing and Prototyping: Develop wireframes and interactive prototypes to visualize the app’s flow.
**c. Frontend and Backend Development
- Frontend: Implement the user interface using HTML, CSS, and JavaScript.
- Backend: Develop server-side logic using languages like Python, Ruby, or Node.js.
**d. Integration and Testing
- API Integrations: Integrate third-party APIs for maps, property data, and analytics.
- Testing Phases: Conduct thorough testing, including functional, performance, and security testing.
**e. Deployment and Launch
- Server Setup: Host the app on servers or cloud platforms like AWS or Azure.
- App Store Submission: Publish the app on app stores or deploy it on your website.
**6. Resource Allocation and Timeline
- Developers: Frontend, backend, and mobile app developers.
- Designers: UI/UX designers for visually appealing and user-centric designs.
- Quality Assurance: QA engineers for testing and bug fixing.
- Project Manager: Oversees development stages and resource coordination.
**7. Post-launch Considerations
- Ongoing Maintenance: Regular updates, bug fixes, and improvements based on user feedback.
- Scaling: Ensure the app’s architecture can accommodate increased user traffic.
**8. Monetization Strategies
- Listing Fees: Charge real estate agents for listing their properties prominently.
- Featured Listings: Offer premium placement for properties willing to pay extra.
- Advertising: Display ads from related industries like mortgage providers and contractors.
**9. Legal Considerations
- Data Privacy: Adhere to data protection regulations to safeguard user data.
- Copyright and Trademarks: Avoid infringing on Zillow’s intellectual property.
**10. The Road Ahead
Creating a Zillow clone demands meticulous planning, technical expertise, and a deep understanding of the real estate domain. By navigating the development process, estimating costs, and identifying essential features, you can build a platform that assists users in finding their ideal properties effortlessly.
Building a Zillow clone requires dedication, technical proficiency, and a commitment to user satisfaction. By following the steps outlined in this guide, you’ll be better equipped to create a real estate platform that delivers value to users and contributes positively to the industry. Remember, a successful Zillow clone not only empowers property seekers but also nurtures a thriving community of buyers, sellers,