Visual Format is used to apply constraints programmatically with fewer lines of code.
It follows a syntax:-
(< orientation >:)?
(< superview >< connection >)?
< view >(< connection >< view >)*
(< connection >< superview >)?
Terms
1. < orientation > –
1. Horizontal Orientation – denote by “H”
2. Vertical Orientation – denote by “V”
2. < superview >< connection > –
Spacing between superview and view (top and leading spacing) – denotes by “ | ”
3. < view >(< connection >< view >) –
Views can be button, textview, etc
4. (< connection >< superview >)
Spacing between view and superview (bottom and trailing spacing) – denotes by “ | ”
Available Symbols:-
1. “ – ” —> Standard spacing (Default is 8)
2. “ == ” —> Equal width and height
for example, view1 == view2 i.e view2 will have the same width as view1
3. “-20- ” —> 20 points spacing will be giving on both ends
4. “ <= ” —> less than or equal to
5. “ >= “ —> greater than or equal to
6. “@250” —> priority of constraint (250 Lower, 750 Higher, 1000 required)
7. “ ( ) ” —> Defines Size of view
8. “ [ ] ” —> Brackets use to define the name of the view (label, button, etc)
Example :-
View1 —>H:|-10-[view1]-10-|
View2 —> H:|-10-[view2]-10-|
View3 —> H:|-10-[view3]-10-|
View4 —>. H:|-10-[view4]-10-|
NSLayoutConstraint.constraintsWithVisualFormat(“V: |-20-[view1(30)]-10-[view2(==view1]-10-[view3(==view1)]-10-[view4(<=20,>=50)]]
In this
There are 4 views which are giving 10 leading and trailing spacing from safeArea
Then they all are vertically align to each other
. On top there is view1 having 20 top spacing from safe area and 10 Bottom spacing from view2 and having size(height) of 30
. View2 has assign equal width that of view1 and having 10 top spacing to view1 and 10 bottom spacing to view 3
. View3 has assign equal width that of view1 and having 10 top spacing to view1 and 10 bottom spacing to view 4
. View4 having 10 top spacing to view3 and have a height of at least 20 points but no more than 50 points (>=20,<=50)
import UIKit
class FirstViewController: UIViewController {
overridefunc viewDidLoad() {
super.viewDidLoad()
let topBar = UIView()
let middleFrameTop = UIView()
let middleFrameBottom = UIView()
let bottomBar = UIView()
topBar.backgroundColor = UIColor.green
middleFrameTop.backgroundColor = UIColor.black
middleFrameBottom.backgroundColor = UIColor.blue
bottomBar.backgroundColor = UIColor.purple
self.view.addSubview(topBar)
self.view.addSubview(middleFrameTop)
self.view.addSubview(middleFrameBottom)
self.view.addSubview(bottomBar)
topBar.translatesAutoresizingMaskIntoConstraints = false
middleFrameTop .translatesAutoresizingMaskIntoConstraints = false
middleFrameBottom.translatesAutoresizingMaskIntoConstraints = false
bottomBar.translatesAutoresizingMaskIntoConstraints = false
let viewsDict = [“topBar”:topBar,”middleFrameTop”:middleFrameTop,”middleFrameBottom”: middleFrameBottom,”bottomBar”:bottomBar]
var viewConstraints = [NSLayoutConstraint]()
let topBarCondtraintsHorizontal = NSLayoutConstraint.constraints(withVisualFormat: “H:|-10-[topBar]-10-|”, options: [], metrics: nil, views: viewsDict)
viewConstraints += topBarCondtraintsHorizontal
let middleFrameTopHorizontal = NSLayoutConstraint.constraints(withVisualFormat: “H:|-10-[middleFrameTop]-10-|”, options: [], metrics: nil, views: viewsDict)
viewConstraints += middleFrameTopHorizontal
let middleFrameBottomHorizontal = NSLayoutConstraint.constraints(withVisualFormat: “H:|-10-[middleFrameBottom]-10-|”, options: [], metrics: nil, views: viewsDict)
viewConstraints += middleFrameBottomHorizontal
let bottomBarHorizontal = NSLayoutConstraint.constraints(withVisualFormat: “H:|-10-[bottomBar]-10-|”, options: [], metrics: nil, views: viewsDict)
viewConstraints += bottomBarHorizontal
let verticalConstraints = NSLayoutConstraint.constraints(
withVisualFormat: “V:|-20-[topBar(50)]-10-[middleFrameTop(==topBar)]-10-[middleFrameBottom(==topBar)]-10-[bottomBar(<=20,>=50)]-20-|”,
options: [], metrics: nil, views: viewsDict)
viewConstraints += verticalConstraints
NSLayoutConstraint.activate(viewConstraints)
}
}
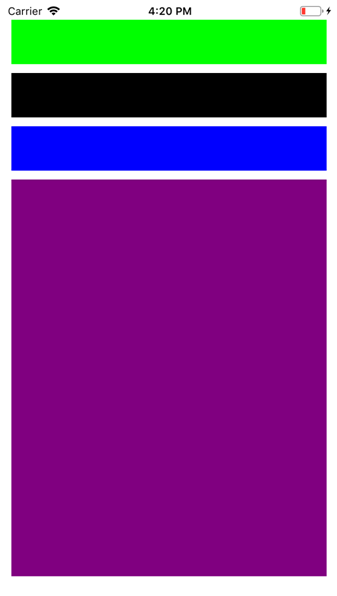
Output: –