Table of Contents
Understanding Augmented Reality (AR): Basics and Definition
In a world where technology is constantly evolving, augmented reality (AR) stands out as one of the most intriguing and transformative innovations of recent times. From enhancing gaming experiences to revolutionizing industries like healthcare and education, AR has transcended its initial novelty to become an integral part of our digital landscape. Let’s delve into the basics of augmented reality, unraveling its definition and exploring its vast potential.
Defining Augmented Reality
Augmented reality can be succinctly defined as the integration of digital information with the user’s real-world environment in real-time. Unlike virtual reality (VR), which immerses users in a completely simulated environment, AR overlays digital content onto the physical world, seamlessly blending the virtual and the real. This interaction between the digital and physical realms creates an immersive and interactive experience that has captivated users across various domains.
The Basics of AR Technology
At the heart of augmented reality technology lies a sophisticated combination of hardware and software components working in tandem to deliver seamless experiences. These components typically include:
- Sensors: AR-enabled devices are equipped with an array of sensors such as cameras, accelerometers, and gyroscopes that capture real-world data and provide crucial inputs for AR applications.
- Processing Units: Powerful processors handle the computational tasks involved in rendering and aligning virtual content with the user’s environment, ensuring smooth and accurate AR experiences.
- Displays: AR devices feature displays, ranging from smartphones and tablets to specialized headsets and glasses, through which users view the augmented content overlaid onto their surroundings.
- Software Platforms: AR software platforms and development kits provide the tools and frameworks necessary for creating, deploying, and managing AR applications across different devices and operating systems.
Applications of Augmented Reality
The versatility of augmented reality extends across various industries and use cases, revolutionizing how we interact with information and perceive the world around us. Some notable applications of AR include:
- Gaming: AR gaming experiences such as Pokémon GO have captivated millions of users worldwide, blending virtual creatures and objects seamlessly into real-world environments.
- Education and Training: AR enhances learning experiences by providing interactive and immersive educational content, allowing students to visualize complex concepts and simulations in real-time.
- Retail and Marketing: Retailers leverage AR to create virtual try-on experiences, allowing customers to preview products such as clothing and furniture in their own environment before making a purchase.
- Healthcare: AR technology finds applications in medical training, surgical navigation, and patient education, enabling healthcare professionals to visualize anatomical structures and medical data in 3D space.
- Architecture and Design: Architects and designers use AR to visualize building designs at scale, overlaying virtual models onto physical spaces to assess factors such as aesthetics and spatial relationships.
Evolution of Augmented Reality Technology: From Concept to Application

Augmented Reality (AR) has emerged as one of the most revolutionary technologies of the 21st century, blending the realms of the physical and digital worlds seamlessly. What began as a mere concept has rapidly evolved into a ubiquitous tool with diverse applications across various industries. This article delves into the fascinating journey of AR technology, tracing its evolution from inception to its current widespread adoption.
The Genesis of Augmented Reality: The roots of AR can be traced back to the 1960s, where computer scientist Ivan Sutherland conceptualized the “Sword of Damocles,” an early head-mounted display system that laid the foundation for immersive digital experiences. However, it wasn’t until the late 20th century that AR gained traction, with pioneers like Boeing researcher Tom Caudell coining the term “Augmented Reality” in 1990 to describe a digital display overlaying physical environments for aircraft assembly.
Early Development and Challenges: In the early 2000s, AR technology faced significant hurdles due to hardware limitations and computational constraints. However, breakthroughs in mobile computing, particularly with the advent of smartphones and tablets, paved the way for more accessible AR experiences. Applications like Layar, launched in 2009, allowed users to overlay digital content onto real-world scenes using their mobile devices, marking a significant milestone in AR development.
Mainstream Adoption and Innovation: The turning point for AR came with the release of Niantic’s Pokémon GO in 2016, which captivated millions worldwide and showcased the potential of AR for gaming and entertainment. Simultaneously, tech giants like Google and Apple began investing heavily in AR development, introducing ARKit and ARCore, respectively, to provide developers with robust frameworks for creating AR experiences on iOS and Android platforms.
Diverse Applications Across Industries: Today, AR technology transcends the realm of gaming, finding applications across a myriad of industries. In healthcare, AR is revolutionizing surgical procedures by providing real-time guidance and visualization for surgeons. In education, AR enhances learning experiences by bringing textbooks to life and creating interactive simulations. Moreover, AR is transforming retail and marketing, allowing consumers to visualize products in their own space before making purchase decisions.
Future Outlook and Potential: As AR technology continues to evolve, the future holds limitless possibilities. Advancements in hardware, such as lightweight AR glasses and wearable devices, promise to make AR more immersive and integrated into everyday life. Additionally, innovations in spatial computing and machine learning will enable more intelligent and context-aware AR applications, further blurring the line between the physical and digital worlds.
Industries and Sectors Embracing Augmented Reality
In today’s rapidly evolving technological landscape, augmented reality (AR) has emerged as a transformative force, reshaping the way industries and sectors operate. With its ability to overlay digital information onto the physical world, AR is not just a buzzword but a practical solution revolutionizing multiple fields. Let’s delve into how different industries are embracing augmented reality and unlocking its vast potential.
Retail and E-Commerce: Enhancing Customer Experience: The retail sector has been quick to adopt AR to enhance the customer shopping experience both online and offline. Through AR applications, customers can visualize products in their real-world environment before making a purchase. Whether it’s trying on clothes virtually, visualizing furniture in their living room, or test-driving cosmetics, AR bridges the gap between physical and digital shopping, reducing returns and increasing customer satisfaction.
Healthcare: Revolutionizing Patient Care and Training: In healthcare, augmented reality is transforming patient care, medical training, and surgical procedures. Surgeons can now overlay vital patient information, such as MRI scans, onto their field of view during operations, enhancing precision and reducing errors. AR is also being used for medical training, allowing students to practice procedures in a simulated environment before working with real patients, thus improving competency and safety.
Manufacturing and Maintenance: Streamlining Processes: In the manufacturing sector, AR is streamlining production processes and maintenance tasks. By overlaying digital instructions onto physical equipment, workers can receive real-time guidance, reducing errors and increasing efficiency. AR-enabled maintenance solutions provide technicians with hands-free access to manuals, schematics, and troubleshooting guides, minimizing downtime and maximizing productivity on the factory floor.
Education: Interactive Learning Experiences: AR is revolutionizing education by offering immersive and interactive learning experiences. Students can explore historical sites, dissect virtual organisms, or interact with 3D models of complex concepts, bringing subjects to life in ways that traditional methods cannot. AR enhances student engagement and comprehension, making learning more enjoyable and effective across various disciplines.
Tourism and Hospitality: Enriching Travel Experiences: In the tourism and hospitality industry, AR is enriching travel experiences by providing interactive guides, augmented reality city tours, and virtual previews of accommodations. Travelers can explore destinations in a more immersive way, discovering hidden gems and historical facts through AR-enhanced apps. Hotels are also utilizing AR to offer virtual room tours, allowing guests to preview their accommodations before booking.
Entertainment and Gaming: Blurring Realities: Entertainment and gaming have long been at the forefront of AR innovation, with popular games like Pokémon GO bringing augmented reality to the masses. AR gaming experiences allow players to interact with virtual elements overlaid onto the real world, blurring the lines between fantasy and reality. Beyond gaming, AR is also enhancing live events, museums, and theme parks, offering visitors immersive and interactive experiences.
Impact of Augmented Reality on Consumer Experience and Engagement
In an era where technology continuously shapes our daily lives, augmented reality (AR) emerges as a game-changer in revolutionizing consumer experience and engagement. From enhancing shopping experiences to transforming entertainment, AR has swiftly embedded itself into various industries, offering immersive and interactive encounters like never before.
Enhanced Shopping Experience: The retail landscape is undergoing a significant transformation, with AR leading the charge. Traditional shopping experiences are evolving into immersive adventures, thanks to AR applications. Imagine being able to visualize furniture in your living room before making a purchase or virtually trying on clothes without stepping into a fitting room. AR bridges the gap between physical and digital realms, providing consumers with a personalized and interactive shopping journey.
Interactive Marketing Campaigns: AR transcends conventional marketing strategies by enabling brands to create interactive campaigns that captivate audiences. Through AR-enabled advertisements and promotions, consumers can engage with products in innovative ways, fostering a deeper connection with brands. Whether it’s scanning a product to reveal additional information or participating in AR-powered games, consumers are drawn into a dynamic and memorable brand experience.
Immersive Entertainment: Entertainment experiences are undergoing a paradigm shift with the integration of AR technology. From interactive museum exhibits to location-based AR games like Pokémon GO, AR adds an extra layer of excitement and engagement to entertainment activities. By merging the digital and physical worlds seamlessly, AR redefines the way consumers interact with entertainment content, offering endless possibilities for immersive storytelling and engagement.
Educational Opportunities: AR isn’t just limited to entertainment and shopping; it also holds immense potential in education. By overlaying digital content onto the real world, AR transforms learning experiences into interactive and engaging journeys. Whether it’s exploring historical landmarks through AR-enhanced tours or conducting virtual science experiments, AR fosters active learning and enhances retention through experiential education.
Challenges and Future Prospects: While AR has revolutionized consumer experiences, challenges such as technological limitations and privacy concerns remain. However, as AR technology continues to evolve, these challenges are gradually being addressed, paving the way for even more immersive and seamless experiences. Looking ahead, the future of AR holds immense promise, with advancements in wearable AR devices, spatial computing, and augmented reality glasses poised to further elevate consumer engagement across various industries.
Software Development for Augmented Reality: Platforms and Tools
In the ever-evolving landscape of technology, augmented reality (AR) stands out as one of the most promising and exciting fields. As businesses and developers delve deeper into the realm of AR, the demand for robust software development platforms and tools continues to soar. In this comprehensive guide, we’ll navigate through the intricacies of software development for augmented reality, exploring the platforms and tools that empower developers to create immersive AR experiences.
Understanding Augmented Reality Development
Before diving into the platforms and tools, let’s briefly understand what augmented reality development entails. Augmented reality merges digital content with the real world, offering users an enriched perception of their surroundings. Whether it’s overlaying virtual objects onto physical environments or enhancing real-world experiences with digital information, AR opens up a myriad of possibilities across various industries, including gaming, education, healthcare, and marketing.
Platforms for AR Development
- Unity: Unity stands as one of the most popular and versatile platforms for AR development. With its robust suite of tools and extensive community support, Unity enables developers to create high-quality AR experiences for multiple platforms, including iOS, Android, and HoloLens. Its integration with AR Foundation simplifies cross-platform development, while features like real-time rendering and spatial mapping enhance the realism of AR applications.
- ARKit and ARCore: ARKit by Apple and ARCore by Google are frameworks specifically designed for building AR applications on iOS and Android devices, respectively. Leveraging the power of these frameworks, developers can access advanced AR features such as motion tracking, environmental understanding, and light estimation, ensuring seamless integration of virtual content into the real world.
- Vuforia: Vuforia offers a comprehensive set of tools for creating AR applications, with a focus on object recognition, tracking, and augmented reality experiences. Its computer vision technology enables developers to build applications capable of recognizing and tracking images, objects, and environments, making it ideal for applications ranging from industrial maintenance to interactive marketing campaigns.
Tools for AR Development
- ARToolKit: ARToolKit is an open-source toolkit for building AR applications, known for its robust tracking capabilities and support for a wide range of platforms, including Windows, macOS, Linux, iOS, and Android. With features like camera calibration, marker detection, and OpenGL-based rendering, ARToolKit empowers developers to create immersive AR experiences with ease.
- Wikitude: Wikitude offers a powerful platform and SDK for developing location-based AR applications, allowing developers to overlay digital content onto real-world locations. Its support for geolocation, image recognition, and 3D tracking enables developers to build engaging AR experiences tailored to specific locations, making it ideal for tourism, navigation, and advertising applications.
- Adobe Aero: Adobe Aero provides a user-friendly interface for creating AR experiences without the need for extensive coding knowledge. Leveraging Adobe’s creative tools and cloud infrastructure, Aero allows designers to bring their ideas to life in augmented reality, whether it’s showcasing 3D artwork, designing immersive presentations, or prototyping interactive experiences.
Augmented Reality in Education and Training: Enhancing Learning Experiences
In today’s dynamic educational landscape, technology continues to redefine traditional learning methodologies. One such groundbreaking innovation is augmented reality (AR), which holds immense potential in enhancing educational and training experiences. Augmented reality seamlessly integrates digital information with the physical world, offering immersive and interactive learning opportunities. From classrooms to corporate training sessions, AR is reshaping the way we acquire knowledge and skills.
Transforming Learning Environments: Augmented reality transforms traditional classrooms into engaging and interactive learning environments. Imagine students exploring the solar system by simply pointing their devices at a poster or textbook, witnessing planets and constellations come to life in vivid detail. This hands-on approach not only captivates learners but also fosters deeper understanding and retention of complex concepts. By visualizing abstract ideas in a tangible manner, AR bridges the gap between theoretical knowledge and practical application.
Personalized Learning Experiences: One of the most significant advantages of AR in education and training is its ability to cater to individual learning styles and preferences. Through customizable AR applications, educators can tailor learning experiences to meet the diverse needs of students. Whether visual, auditory, or kinesthetic learners, AR can adapt content delivery to suit each student’s unique learning style, thereby maximizing comprehension and engagement.
Enhancing Skills Training: In addition to academic learning, augmented reality is revolutionizing skills training across various industries. From medical simulations to engineering prototyping, AR offers realistic and risk-free environments for hands-on practice. For instance, medical students can perform virtual surgeries, firefighters can undergo simulated rescue missions, and mechanics can troubleshoot complex machinery – all within the safety of a virtual setting. By providing immersive training experiences, AR accelerates skill acquisition and enhances competency levels.
Fostering Collaboration and Teamwork: Augmented reality fosters collaboration and teamwork by enabling shared experiences among learners. Whether in a classroom setting or a corporate training workshop, AR facilitates real-time collaboration, allowing participants to interact with virtual objects and environments simultaneously. This collaborative learning approach promotes active participation, communication, and problem-solving skills, essential for success in today’s interconnected world.
Overcoming Geographical Barriers: One of the significant advantages of AR-enabled education and training is its ability to overcome geographical barriers. With AR, learners can access educational content and training modules from anywhere in the world, breaking free from the constraints of physical distance. Remote learners can engage in virtual field trips, attend interactive lectures, and participate in group activities, regardless of their location. This accessibility ensures equitable access to quality education and training opportunities for all.
Augmented Reality in Retail: Transforming Shopping and Sales
In the dynamic landscape of retail, staying ahead requires innovation that not only attracts but engages consumers. Augmented Reality (AR) has emerged as a game-changer, revolutionizing the shopping experience by seamlessly integrating the virtual world with the physical. From enhancing product visualization to personalized interactions, AR is transforming the way we shop and boosting sales in the retail sector.
Enhanced Product Visualization: One of the most significant benefits of AR in retail is its ability to provide enhanced product visualization. Shoppers can now visualize products in their real-world environment before making a purchase, eliminating uncertainties and enhancing confidence. Whether it’s trying on virtual clothes or placing virtual furniture in their living room, AR empowers customers to make informed decisions, leading to higher satisfaction rates and reduced returns.
Personalized Interactions: AR technology enables retailers to deliver personalized interactions tailored to each customer’s preferences and needs. Through AR-powered applications, shoppers can receive customized product recommendations based on their past purchases, browsing history, and even their physical location within the store. This personalized approach not only enhances the shopping experience but also strengthens customer loyalty by making individuals feel valued and understood.
Interactive In-Store Experiences: AR transforms brick-and-mortar stores into immersive environments where customers can engage with products in entirely new ways. Interactive AR displays and kiosks allow shoppers to explore additional product information, view customer reviews, and even participate in virtual try-on experiences. By blending the physical and digital realms, retailers create memorable experiences that drive foot traffic, increase dwell time, and ultimately boost sales.
Bridge Between Online and Offline Channels: AR serves as a bridge between online and offline retail channels, providing a seamless shopping journey for consumers. For instance, customers can use AR-enabled mobile apps to virtually try on products at home and then seamlessly transition to making a purchase in-store or online. This omnichannel approach not only enhances convenience but also allows retailers to leverage the strengths of both online and offline channels to maximize sales and customer engagement.
Innovative Marketing Campaigns: Retailers are harnessing the power of AR to create innovative and interactive marketing campaigns that captivate audiences and drive sales. From AR-powered advertisements to gamified shopping experiences, brands are leveraging AR technology to create memorable moments that resonate with consumers. By incorporating AR into their marketing strategies, retailers can differentiate themselves from competitors and capture the attention of tech-savvy consumers in today’s crowded marketplace.
Augmented Reality in Architecture and Design: Visualization and Planning
Augmented Reality (AR) has emerged as a transformative tool in the field of architecture and design, revolutionizing the way professionals visualize and plan their projects. By seamlessly blending digital elements with the physical environment, AR offers unparalleled opportunities for architects and designers to enhance their creative process, streamline workflow, and improve communication with clients. In this article, we delve into the profound impact of augmented reality in architecture and design, exploring its applications, benefits, and future potential.
Augmented Reality in Visualization: Traditionally, architects and designers have relied on 2D drawings, blueprints, and scale models to visualize their concepts. However, these methods often fall short in conveying the true essence of a design and may lead to misunderstandings or misinterpretations. Augmented Reality addresses these limitations by overlaying digital renderings onto physical spaces in real-time, allowing stakeholders to experience designs in a highly immersive manner. Whether it’s visualizing interior layouts, exploring façade options, or assessing spatial relationships, AR provides a comprehensive and interactive platform for design exploration.
Enhanced Planning and Collaboration: Beyond visualization, augmented reality facilitates more efficient planning and collaboration throughout the design process. Architects can use AR-powered tools to simulate real-world conditions, such as lighting effects, material textures, and structural integrity, enabling them to make informed decisions early on. Moreover, AR enhances communication between architects, clients, and other project stakeholders by offering a shared understanding of the design vision. Clients can actively participate in the design review process, providing feedback and suggestions in real-time, leading to more personalized and satisfactory outcomes.
Streamlined Construction Processes: AR is also reshaping the construction phase by improving coordination and reducing errors on-site. Construction workers can use AR-enabled devices to overlay digital blueprints onto physical spaces, ensuring accurate placement of structural elements and installations. This not only minimizes the risk of errors but also expedites the construction timeline, resulting in cost savings and increased efficiency. Furthermore, AR-based training modules empower construction teams with interactive tutorials and safety protocols, enhancing productivity and reducing workplace accidents.
Future Potential and Innovations: As technology continues to evolve, the potential of augmented reality in architecture and design is limitless. Innovations such as holographic displays, wearable AR devices, and real-time collaboration platforms are poised to further revolutionize the industry. Imagine architects designing buildings in virtual reality, clients experiencing immersive walkthroughs from anywhere in the world, or urban planners visualizing entire cityscapes in augmented reality. These advancements not only push the boundaries of creativity but also democratize access to architectural design, making it more inclusive and accessible to all.
Challenges and Limitations of Augmented Reality Implementation
Augmented Reality (AR) has emerged as a transformative technology, blurring the lines between the digital and physical worlds. From enhancing gaming experiences to revolutionizing industries like healthcare and education, AR holds immense promise. However, like any burgeoning technology, its implementation comes with a set of challenges and limitations that need to be addressed for widespread adoption and seamless integration into everyday life.
- Hardware Limitations: One of the primary challenges of AR implementation lies in hardware constraints. While smartphones and wearable devices serve as the primary platforms for AR applications, their processing power, battery life, and display capabilities often fall short of delivering a truly immersive experience. Moreover, the cost associated with high-end AR devices poses a barrier to entry for many users and businesses.
- Content Creation and Integration: Creating compelling and contextually relevant AR content is another hurdle. Designing interactive overlays that seamlessly integrate with the physical environment requires specialized skills and resources. Additionally, ensuring compatibility across different devices and operating systems adds complexity to content creation and distribution.
- User Experience and Interface Design: The success of AR hinges on delivering intuitive and user-friendly experiences. Designing interfaces that enhance rather than detract from the user’s interaction with the real world is a formidable task. Issues such as occlusion, where digital objects obscure real-world elements, and user fatigue due to prolonged use of AR devices must be addressed through thoughtful interface design and user testing.
- Privacy and Security Concerns: As AR blurs the boundaries between public and private spaces, concerns regarding privacy and security come to the forefront. Collecting and processing user data, especially in the context of location-based AR experiences, raises ethical and legal implications. Safeguarding sensitive information and ensuring user consent are paramount to building trust and fostering widespread adoption of AR technology.
- Regulatory and Ethical Considerations: The regulatory landscape surrounding AR is still evolving, presenting challenges for developers and businesses navigating compliance requirements. Issues such as intellectual property rights, liability for augmented content in real-world settings, and ensuring accessibility for users with disabilities necessitate clear guidelines and standards.
- Infrastructure and Connectivity: For AR to reach its full potential, robust infrastructure and high-speed connectivity are essential. Real-time rendering of AR content and seamless communication between devices rely on reliable networks and low latency. Bridging the digital divide and ensuring equitable access to AR experiences across different geographic regions remains a significant challenge.
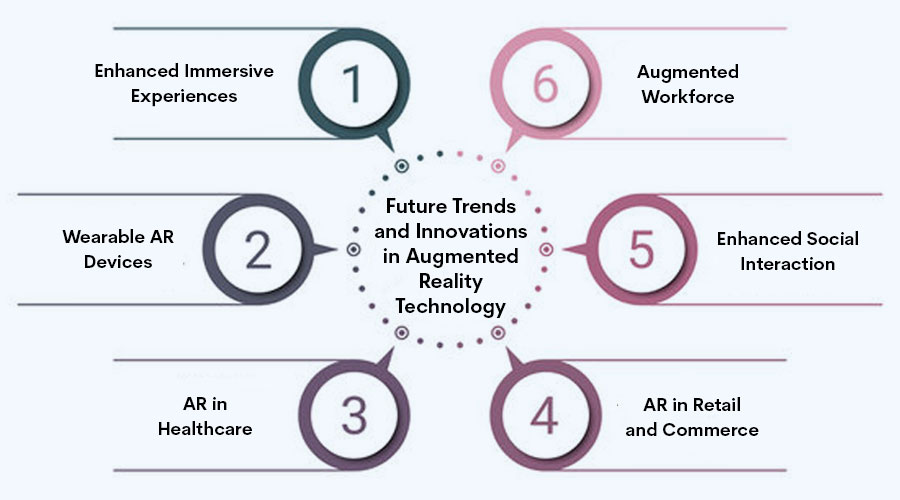
Future Trends and Innovations in Augmented Reality Technology
Augmented Reality (AR) has leaped from the pages of science fiction into our everyday lives, transforming the way we perceive and interact with the world around us. As technology advances at a rapid pace, the future of AR holds boundless possibilities, promising to revolutionize various industries and redefine human experiences. In this article, we delve into the upcoming trends and innovations that will shape the landscape of augmented reality in the years to come.
- Enhanced Immersive Experiences: The future of AR is poised to deliver even more immersive experiences by seamlessly integrating digital content with the physical environment. Advanced AR glasses and headsets will offer users lifelike overlays, blurring the lines between the virtual and real worlds. From interactive gaming and immersive storytelling to educational simulations and remote collaboration, AR will enrich our lives in unprecedented ways.
- Wearable AR Devices: Gone are the days of clunky headsets and bulky equipment. The future of AR lies in sleek, lightweight wearable devices that seamlessly blend into our daily routines. From smart glasses and contact lenses to AR-enabled clothing and accessories, wearable AR technology will become more discreet and accessible, empowering users to harness its potential wherever they go.
- AR in Healthcare: Augmented Reality is poised to revolutionize the healthcare industry, offering innovative solutions for medical training, patient care, and surgical procedures. Surgeons will utilize AR-enabled tools to overlay patient data and imaging directly onto their field of view, enhancing precision and reducing the risk of errors. Medical students will benefit from lifelike simulations, gaining hands-on experience in a risk-free environment.
- AR in Retail and Commerce: The future of shopping will be transformed by AR technology, offering consumers immersive and personalized shopping experiences. AR-powered apps will enable shoppers to visualize products in their own space before making a purchase, revolutionizing the way we shop for furniture, clothing, and home decor. Retailers will leverage AR to create interactive marketing campaigns and virtual try-on experiences, driving engagement and sales.
- Enhanced Social Interaction: AR will reshape the way we connect and communicate with one another, blurring geographical boundaries and fostering deeper social interactions. From AR-enhanced social media platforms to virtual meeting spaces and multiplayer gaming experiences, AR will bridge the gap between physical and digital worlds, enabling people to share experiences and memories in real-time.
- Augmented Workforce: In the workplace of the future, AR technology will empower employees to work more efficiently and collaboratively. From remote assistance and virtual training to hands-free workflows and real-time data visualization, AR will enhance productivity across various industries, from manufacturing and logistics to engineering and design.
Top Augmented Reality Scope – All You Need to Know Companies
In the ever-evolving landscape of technology, Augmented Reality (AR) stands out as a revolutionary force, transforming the way we perceive and interact with the world around us. From enhancing gaming experiences to revolutionizing industries like healthcare, education, and retail, AR has transcended its novelty status to become a powerful tool driving innovation across various sectors. In this article, we delve into the expansive scope of augmented reality and highlight some of the top companies at the forefront of this transformative technology.
Understanding Augmented Reality
Augmented Reality integrates digital information seamlessly into the real-world environment, thereby augmenting the user’s perception and enhancing their sensory experience. Unlike Virtual Reality (VR), which immerses users in a completely virtual environment, AR overlays digital elements onto the physical world, creating a blended reality. This unique capability has unlocked a multitude of applications across diverse fields, promising unprecedented levels of engagement, efficiency, and creativity.
Scope of Augmented Reality
The scope of Augmented Reality extends far beyond entertainment and gaming. In healthcare, AR is revolutionizing medical training, surgical procedures, and patient care by providing real-time data visualization, anatomical overlays, and interactive learning experiences. Educational institutions are leveraging AR to create immersive learning environments, allowing students to explore complex concepts in a tangible and engaging manner.
In retail, AR is reshaping the customer shopping experience, enabling virtual try-ons, product visualizations, and interactive advertisements. Industries such as architecture, engineering, and construction benefit from AR’s ability to facilitate 3D modeling, spatial planning, and virtual prototyping, streamlining the design and development process while minimizing errors and costs.
Leading Augmented Reality Companies
Several companies have emerged as pioneers in the field of Augmented Reality, driving innovation and pushing the boundaries of what’s possible. Here are some of the top players shaping the future of AR:
-
Next Big Technology:

Focus Area
- Mobile App Development
- App Designing (UI/UX)
- Software Development
- Web Development
- AR & VR Development
- Big Data & BI
- Cloud Computing Services
- DevOps
- E-commerce Development
Industries Focus
- Art, Entertainment & Music
- Business Services
- Consumer Products
- Designing
- Education
- Financial & Payments
- Gaming
- Government
- Healthcare & Medical
- Hospitality
- Information Technology
- Legal & Compliance
- Manufacturing
- Media
- Microsoft Corporation: Through its HoloLens platform, Microsoft has established itself as a leader in enterprise AR solutions. HoloLens offers spatial computing capabilities, enabling businesses to leverage holographic technology for training, remote assistance, and industrial applications.
- Google: Google’s ARCore platform provides developers with the tools to build AR applications for Android devices, extending the reach of augmented reality to a vast user base. From AR-enhanced Google Search results to immersive educational experiences with Google Expeditions, Google is driving AR innovation across multiple domains.
- Snap Inc.: Snapchat, owned by Snap Inc., has popularized AR through its innovative camera filters and lenses, allowing users to overlay digital effects onto their photos and videos in real-time. Snap’s AR technology is not only entertaining but also serves as a platform for brands to engage with their audience in creative ways.
- Magic Leap: Magic Leap’s mixed reality headset offers users a truly immersive AR experience, blending virtual content with the real world in a seamless manner. With applications ranging from gaming and entertainment to enterprise solutions, Magic Leap is pushing the boundaries of what’s possible in spatial computing.
FAQs On Augmented Reality Scope – All You Need to Know
Augmented Reality (AR) has emerged as a groundbreaking technology that blurs the line between the physical and digital worlds. As its applications continue to expand across various industries, it’s natural to have questions about its scope and potential. In this article, we’ll delve into some frequently asked questions about the scope of augmented reality, providing you with comprehensive answers to broaden your understanding of this transformative technology.
- What exactly is augmented reality (AR)? Augmented reality is a technology that overlays digital information such as images, videos, or 3D models onto the real-world environment, enhancing the user’s perception of reality. Unlike virtual reality, which immerses users in a completely virtual environment, AR integrates digital elements into the physical world in real-time.
- What are the key components of augmented reality? The primary components of augmented reality include hardware devices (such as smartphones, tablets, smart glasses, and headsets), software applications, sensors (such as cameras and GPS), and algorithms that enable the recognition and rendering of digital content in the real world.
- What are the practical applications of augmented reality? Augmented reality finds applications across various industries, including:
- Retail: AR enables virtual try-on experiences for clothing and accessories, interactive product demonstrations, and in-store navigation.
- Education: AR enhances learning experiences by providing immersive simulations, interactive textbooks, and virtual field trips.
- Healthcare: AR aids in medical training, surgical planning, patient education, and visualization of complex medical data.
- Gaming: AR games blend virtual elements with the real world, allowing players to engage in interactive experiences in their surroundings.
- Manufacturing: AR assists in assembly line maintenance, remote assistance, quality control, and product design.
- What is the future scope of augmented reality? The future of augmented reality is promising, with ongoing advancements in technology and increasing adoption across industries. Some potential future developments include:
- Enhanced AR glasses: The development of lightweight, stylish AR glasses with improved display quality and battery life.
- Integration with artificial intelligence: AI-powered AR systems capable of recognizing and interpreting the surrounding environment more accurately.
- Augmented reality in transportation: AR navigation systems for cars, trains, and airplanes to provide real-time guidance and safety alerts.
- Spatial computing: Advancements in spatial computing technology, enabling more seamless integration of digital content into physical spaces.
- How can businesses leverage augmented reality? Businesses can leverage augmented reality to enhance customer engagement, improve operational efficiency, and drive innovation. Some strategies include:
- Developing AR-based marketing campaigns to create interactive brand experiences.
- Implementing AR-powered training programs to enhance employee skills and knowledge.
- Incorporating AR into product design and development processes to streamline prototyping and visualization.
- Offering AR-enabled customer support and service solutions for remote troubleshooting and guidance.
Thanks for reading our post “Augmented Reality Scope – All You Need to Know”. Please connect with us to learn more about Best Augmented Reality Scope.