Let us start actual programming with Android Framework. Before you start writing your first example using Android SDK, you have to make sure that you have set up your Android development environment properly as explained in the Android – Environment Setup tutorial. We also assume that you have a little bit of working knowledge with Eclipse IDE.
So let us proceed to write a simple Android Application that will print “Hello World!”.
Table of Contents
Create Android Application
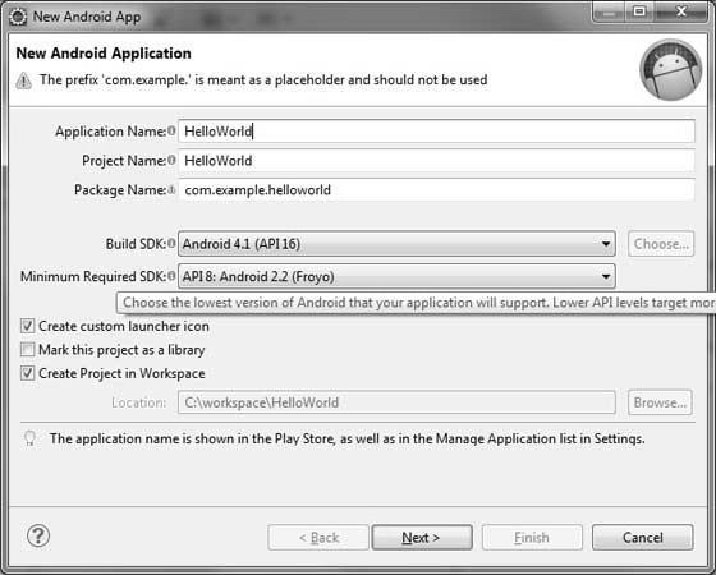
The first step is to create a simple Android Application using Eclipse IDE. Follow the option
File -> New -> Project and finally select Android New Application wizard from the wizard
list. Now name your application as HelloWorld using the wizard window as follows:
Next, follow the instructions provided and keep all other entries as default till the final step. Once your project is created successfully, you will have the following project screen:
Anatomy of Android Application
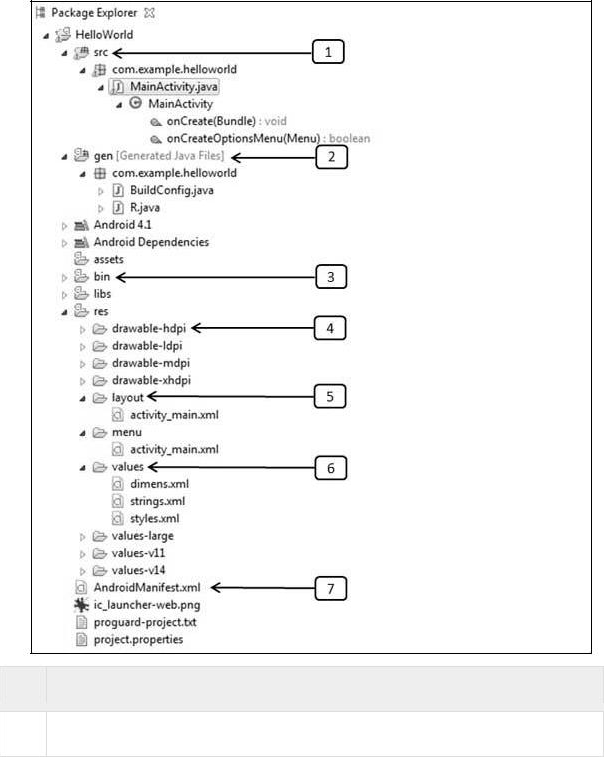
Before you run your app, you should be aware of a few directories and files in the Android project:
1. src
This contains the .java source files for your project. By default, it includes
anMainActivity.java source file having an activity class that runs when your app
is launched using the app icon.
2 gen
This contains the. R file, a compiler-generated file that references all the
resources found in your project. You should not modify this file.
3 bin
This folder contains the Android package files .apk built by the ADT during the
build process and everything else needed to run an Android application.
4 res/drawable-hdpi
This is a directory for drawable objects that are designed for high-density screens.
5 res/layout
This is a directory for files that define your app’s user interface.
6 res/values
This is a directory for other various XML files that contain a collection of resources,
such as strings and colors definitions.
7 AndroidManifest.xml
This is the manifest file that describes the fundamental characteristics of the
app and defines each of its components.
The following section will give a brief overview few of the important application files.
The Main Activity File
The main activity code is a Java file MainActivity.java. This is the actual application file which ultimately gets converted to a Dalvik executable and runs your application. Following is the default code generated by the application wizard for Hello World! application:
package com.example.helloworld;
import android.os.Bundle; import android.app.Activity; import android.view.Menu; import android.view.MenuItem;
import android.support.v4.app.NavUtils;
public class MainActivity extends Activity {
@Override
public void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) { super.onCreate(savedInstanceState); setContentView(R.layout.activity_main);
}
@Override
public boolean onCreateOptionsMenu(Menu menu) { getMenuInflater().inflate(R.menu.activity_main, menu); return true;
}
}
Here, R.layout.activity_main refers to the activity_main.xml file located in the res/layout folder. The onCreate() method is one of many methods that are fired when an activity is loaded.
The Manifest File
Whatever component you develop as a part of your application, you must declare all its components in a manifest file called AndroidManifest.xml which resides at the root of the application project directory. This file works as an interface between Android OS and your application, so if you do not declare your component in this file, then it will not be considered by the OS. For example, a default manifest file will look like as following file:
< manifest xmlns:android=”http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android” package=”com.example.helloworld” android:versionCode=”1″ android:versionName=”1.0″ >
< uses-sdk android:minSdkVersion=”8″ android:targetSdkVersion=”15″ />
< application android:icon=”@drawable/ic_launcher” android:label=”@string/app_name” android:theme=”@style/AppTheme” >
< activity android:name=”.MainActivity” android:label=”@string/title_activity_main” >
< intent-filter>
< action android:name=”android.intent.action.MAIN” />
< category android:name=”android.intent.category.LAUNCHER”/>
< /intent-filter>
< /activity>
< /application>
< /manifest>
Here … tags enclosed the components related to the application. The attribute android: the icon will point to the application icon available under res/drawable-hdpi. The application uses the image named ic_launcher.png located in the drawable folders.
The tag is used to specify activity and the android: name attribute specifies the fully qualified class name of the Activity subclass and the android: label attributes specify a string to use as the label for the activity. You can specify multiple activities using tags.
The action for the intent filter is named android.intent.action.MAIN to indicate that this activity serves as the entry point for the application. The category for the intent filter is named android.intent.category.LAUNCHER to indicate that the application can be launched from the device’s launcher icon.
The @string refers to the strings.xml file explained below. Hence, @string/app_name refers to the app_name string defined in the strings.xml file, which is “HelloWorld”. Similar way, other strings get populated in the application.
Following is the list of tags that you will use in your manifest file to specify different Android application components:
• elements for activities
• elements for services
• elements for broadcast receivers
• elements for content providers
The Strings File
The strings.xml file is located in the res/values folder and it contains all the text that your application uses. For example, the names of buttons, labels, default text, and similar types of strings go into this file. This file is responsible for its textual content. For example, a default string file will look like the following file:
< resources>
< string name=”app_name”>HelloWorld Hello world! Settings
< string name=”title_activity_main”>MainActivity
< /resources>
The R File
The gen/com.example.helloworld/R.java file is the glue between the activity Java files likeMainActivity.java and the resources like strings.xml. It is an automatically generated file and you should not modify the content of the R.java file. Following is a sample of the R.java file:
/* AUTO-GENERATED FILE. DO NOT MODIFY.
*
* This class was automatically generated by the
* aapt tool from the resource data it found. It
* should not be modified by hand.
*/
package com.example.helloworld;
public final class R {
public static final class attr {
}
public static final class dimen {
public static final int padding_large=0x7f040002; public static final int padding_medium=0x7f040001; public static final int padding_small=0x7f040000;
}
public static final class drawable {
public static final int ic_action_search=0x7f020000; public static final int ic_launcher=0x7f020001;
}
public static final class id {
public static final int menu_settings=0x7f080000;
}
public static final class layout {
public static final int activity_main=0x7f030000;
}
public static final class menu {
public static final int activity_main=0x7f070000;
}
public static final class string {
public static final int app_name=0x7f050000; public static final int hello_world=0x7f050001; public static final int menu_settings=0x7f050002;
public static final int title_activity_main=0x7f050003;
}
public static final class style {
public static final int AppTheme=0x7f060000;
}
}
The Layout File
The activity_main.xml is a layout file available in res/layout directory that is referenced by your application when building its interface. You will modify this file very frequently to change the layout of your application. For your “Hello World!” application, this file will have following content related to default layout:
< RelativeLayout xmlns:android=”http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android” xmlns:tools=”http://schemas.android.com/tools” android:layout_width=”match_parent” android:layout_height=”match_parent” >
< TextView android:layout_width=”wrap_content” android:layout_height=”wrap_content” android:layout_centerHorizontal=”true” android:layout_centerVertical=”true” android:padding=”@dimen/padding_medium” android:text=”@string/hello_world” tools:context=”.MainActivity” />
< /RelativeLayout>
This is an example of a simple RelativeLayout which we will study in a separate chapter. TheTextView is an Android control used to build the GUI and it has various attributes like android:layout_width, android:layout_height, etc., which are being used to set its width and height, etc. The @string refers to the strings.xml file located in the res/values folder. Hence, @string/hello_world refers to the hello string defined in the strings.xml file, which is “Hello World!”.
Running the Application
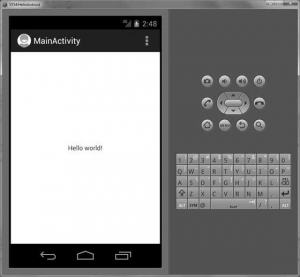
Let’s try to run our Hello World! the application we just created. We assume you had created your AVD while doing the environment setup. To run the app from Eclipse, open one of your project’s activity files and click the Run icon from the toolbar. Eclipse installs the app on your AVD and starts it and if everything is fine with your setup and application, it will display the following Emulator window:
Congratulations! You have developed your first Android Application and now just keep following the rest of the tutorials step by step to become a great Android Developer. All the very best!
Thanks for reading our post “Easy Tips to Speed up Your Website”, please connect with us for any further inquiry. We are Next Big Technology, a leading web & Mobile Application Development Company. We build high-quality applications to full fill all your business needs.