How AI is Revolutionizing Transportation , Transportation is at the core of how economies move, cities grow, and people live their daily lives. But as urban populations rise, traffic becomes more congested, and customer expectations around delivery speed and safety increase, traditional systems are struggling to keep up.
That’s where Artificial Intelligence (AI) steps in.
AI is no longer a futuristic concept in the transportation world. It’s actively changing how we drive, fly, ship, and commute—making the systems around us smarter, faster, and more efficient.
In this article, we’ll explore how AI is transforming the transportation industry, break down the key benefits it offers, look at real-world use cases, and dive into examples of AI being used effectively today.
Table of Contents
The Growing Role of AI in Transportation
AI is essentially the simulation of human intelligence by machines—particularly through systems that can learn, adapt, and make decisions. In the transportation space, AI combines with big data, IoT sensors, GPS systems, and real-time analytics to deliver smarter, more efficient mobility solutions.
Imagine cars that drive themselves, logistics systems that auto-optimize delivery routes, or city traffic that adjusts signals in real time to reduce congestion—that’s all AI at work.
Key Benefits of AI in Transportation
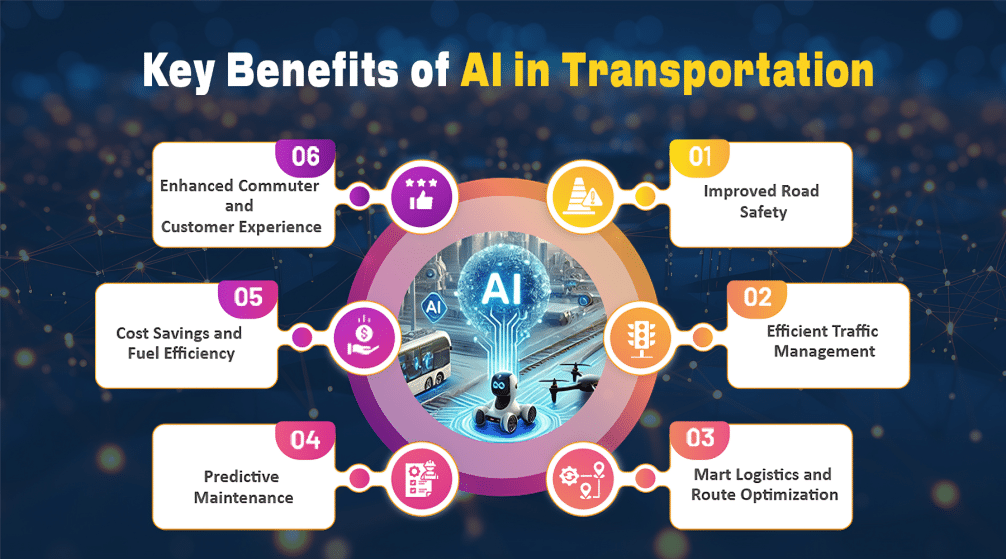
1. Improved Road Safety
AI helps reduce human error—the number one cause of road accidents. With AI-powered driver-assist technologies like automatic emergency braking, lane-keeping assistance, and driver monitoring systems, vehicles can alert or even take control to avoid collisions.
Example: Tesla’s Autopilot and Full Self-Driving capabilities rely on AI algorithms to help the car navigate roads, avoid obstacles, and manage speed safely.
2. Efficient Traffic Management
Urban areas around the world are turning to AI-powered traffic systems. By using data from road sensors, surveillance cameras, and GPS systems, AI can:
- Predict traffic patterns
- Adjust traffic lights dynamically
- Recommend alternate routes in real timeThis not only reduces travel time but also lowers emissions and fuel consumption.
Example: Cities like Los Angeles and Singapore have deployed adaptive traffic signal control systems that reduce congestion during peak hours.
3. Smart Logistics and Route Optimization
AI algorithms help logistics companies make smarter routing decisions by analyzing factors like:
- Current road conditions
- Delivery deadlines
- Vehicle availability
- Fuel efficiency
This leads to reduced delivery times, optimized fuel use, and better customer experiences.
Example: UPS uses an AI system called ORION (On-Road Integrated Optimization and Navigation) that saves the company millions of gallons of fuel each year.
4. Predictive Maintenance
One of the costliest issues in transportation is unexpected breakdowns. AI can analyze data from sensors embedded in vehicles or infrastructure to predict when maintenance is needed—before a failure occurs.
This ensures safety and reduces downtime for fleets, railways, or aircraft.
Example: Airlines use AI-driven systems to monitor aircraft engine performance and schedule maintenance, avoiding delays or in-flight issues.
5. Cost Savings and Fuel Efficiency
AI helps reduce overall operational costs in multiple ways:
- Shorter travel routes
- Fuel usage optimization
- Lower maintenance costs
- Reduced need for manual intervention
By cutting inefficiencies, transportation companies can scale without dramatically increasing expenses.
6. Enhanced Commuter and Customer Experience
AI delivers personalized and real-time experiences for end users. For public transit users, apps powered by AI can:
- Predict arrival/departure times
- Offer route suggestions
- Provide crowd level forecasts
For logistics customers, AI enables real-time tracking and proactive alerts.
Re al-World Use Cases of AI in Transportation
Here’s how AI is being used across different areas of transportation today:
Autonomous Vehicles
Self-driving cars and trucks use a mix of AI technologies such as computer vision, deep learning, and real-time decision-making.
- Use Case: Waymo (Alphabet) operates a fully autonomous ride-hailing service in Phoenix, Arizona.
- Impact: Reduces reliance on human drivers, lowers accident risks, and improves access to mobility.
AI in Freight & Logistics
AI helps companies forecast demand, manage fleets, and deliver products faster.
- Use Case: Amazon uses machine learning for inventory placement and last-mile delivery optimization.
- Impact: Faster deliveries, lower shipping costs, and fewer returns.
Public Transport Optimization
Governments and transit authorities use AI to manage routes and capacity.
- Use Case: Transport for London (TfL) uses AI to study travel patterns and predict maintenance needs.
- Impact: Reduced delays, smoother travel experiences.
Intelligent Traffic Monitoring
AI helps city planners manage congestion and even monitor violations.
- Use Case: Bengaluru and Delhi are piloting smart traffic signals to manage vehicle flow and penalize red-light violators automatically.
- Impact: Improved road discipline and reduced idle times.
Air Traffic Management
Airlines and airports rely on AI to manage flight schedules, security, and passenger flow.
- Use Case: Schiphol Airport (Amsterdam) uses AI to predict passenger wait times and optimize staffing.
- Impact: Smoother travel experience and better resource allocation.
Global Examples of AI in Transportation
Let’s take a quick look at companies and governments that are already reaping the benefits of AI:
- Tesla: Pioneering autonomous driving with AI-based systems.
- Uber: Uses AI for dynamic pricing, route optimization, and customer matching.
- Cruise (General Motors): Testing AI-based robotaxis in urban areas.
- China’s Smart Highways: Integrating AI with 5G and IoT to monitor traffic and communicate with autonomous vehicles.
Future of AI in Transportation
The future looks incredibly promising. Here’s what’s coming next:
- Connected Vehicles: Cars will communicate with each other and traffic infrastructure to avoid accidents and optimize routes.
- AI + 5G + IoT: Real-time coordination between vehicles and city systems for faster, more efficient travel.
- Mobility-as-a-Service (MaaS): Seamless AI-driven platforms will combine public, private, and shared transportation under a single app.
- Sustainable Urban Mobility: AI will help cities reduce carbon footprints through better transport planning.
Final Thoughts
The integration of AI into transportation is no longer a prediction—it’s a present-day reality. From your local ride-hailing app to international shipping giants, AI is at the core of smarter, safer, and more efficient movement.
Whether you’re a transportation business looking to innovate or a government agency aiming to optimize city planning, embracing AI isn’t just an option anymore—it’s a strategic necessity.
AI in transportation holds the power to reduce accidents, minimize delays, lower environmental impact, and most importantly, reshape how the world moves.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q1. Is AI reliable enough to manage transportation systems?
Yes, especially when combined with human oversight. AI excels in processing data and detecting patterns faster than humans can, though ongoing testing and safety protocols are essential.
Q2. Will AI eliminate human drivers?
Not entirely—at least not anytime soon. AI will augment human drivers, make roads safer, and may take over certain repetitive or high-risk tasks, especially in logistics.
Q3. Is AI expensive to implement?
While there is an upfront investment, the long-term savings on fuel, maintenance, and manpower outweigh initial costs. Scalable AI solutions are also available for small to mid-sized companies.
Q4. Can AI reduce traffic congestion in my city?
Yes. Many cities using AI-enabled traffic systems have seen significant reductions in congestion, especially when paired with data from public transportation and smart devices.
Q5. What kind of companies can benefit from AI in transportation?
From local taxi services to global freight companies, every transportation-related business can benefit—whether it’s route optimization, driver assistance, or customer service automation.